<Back to Index>
- Mathematician Michel Rolle, 1652
- Novelist Charlotte Brontë, 1816
- Prime Minister of Denmark Hans Hedtoft Hansen, 1903
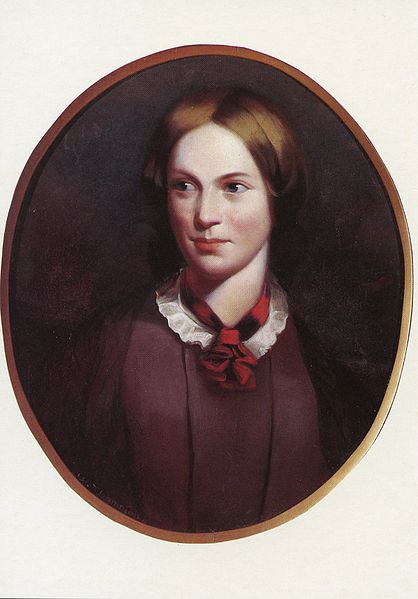


Charlotte Brontë (21 April 1816 – 31 March 1855) was an English novelist, the eldest of the three Brontë sisters whose novels are English literature standards. Under the pen name Currer Bell, she wrote Jane Eyre.
Charlotte was born in Thornton, Yorkshire in 1816, the third of six children, to Patrick Brontë (formerly "Patrick Brunty"), an Irish Anglican clergyman, and his wife, Maria née Branwell. In April 1821, the family moved a few miles to Haworth, where Patrick had been appointed Perpetual Curate. Mrs Brontë died of cancer on 15 September 1821, leaving five daughters and a son to be taken care of by her sister Elizabeth Branwell. In August 1824, Charlotte was sent with three of her sisters, Emily, Maria and Elizabeth, to the Clergy Daughters' School at Cowan Bridge in Lancashire (which she would describe as Lowood School in Jane Eyre). Its poor conditions, Charlotte maintained, permanently affected her health and physical development and hastened the deaths of her two elder sisters, Maria (born 1814) and Elizabeth (born 1815), who died of tuberculosis in June 1825 soon after their father removed them from the school on 1 June. At home in Haworth Parsonage, Charlotte and the other surviving children — Branwell, Emily and Anne — began chronicling the lives and struggles of the inhabitants of their imaginary kingdoms. Charlotte and Branwell wrote Byronic stories about their country — Angria — and Emily and Anne wrote articles and poems about theirs — Gondal. The sagas were elaborate and convoluted (and still exist in part manuscripts) and provided them with an obsessive interest in childhood and early adolescence, which prepared them for their literary vocations in adulthood.
Charlotte continued her education at Roe Head, Mirfield, from 1831 to 1832, where she met her lifelong friends and correspondents, Ellen Nussey and Mary Taylor. During this period, she wrote her novella The Green Dwarf (1833) under the name of Wellesley. Charlotte returned as a teacher from 1835 to 1838. In 1839, she took up the first of many positions as governess to various families in Yorkshire, a career she pursued until 1841.
In 1842 she and Emily travelled to Brussels to enroll in a boarding school run by Constantin Heger (1809 – 1896) and his wife Claire Zoé Parent Heger (1814 – 1891). In return for board and tuition, Charlotte taught English and Emily taught music. Their time at the boarding school was cut short when Elizabeth Branwell, their aunt who joined the family after the death of their mother to look after the children, died of internal obstruction in October 1842. Charlotte returned alone to Brussels in January 1843 to take up a teaching post at the boarding school. Her second stay at the boarding school was not a happy one; she became lonely, homesick and deeply attached to Constantin Heger. She finally returned to Haworth in January 1844 and later used her time at the boarding school as the inspiration for some of The Professor and Villette.
In
May 1846, Charlotte, Emily and Anne published a joint collection of
poetry under the assumed names of Currer, Ellis and Acton Bell.
Although only two copies were sold, the sisters continued writing for
publication and began their first novels. Charlotte used "Currer Bell"
when she published her first two novels. Her novels were deemed coarse by the critics. There was speculation about the identity of Currer Bell, and whether Bell was a man or a woman. Charlotte's brother, Branwell, the only son of the family, died of chronic bronchitis and marasmus exacerbated by heavy drinking in September 1848, although Charlotte believed his death was due to tuberculosis. Branwell was also a suspected "opium eater", (i.e. a laudanum addict).
Emily and Anne both died of pulmonary tuberculosis in December 1848 and
May 1849, respectively. Charlotte and her father were now left alone
together. In view of the enormous success of Jane Eyre, she was persuaded by her publisher to visit London occasionally, where she revealed her true identity and began to move in a more exalted social circle, becoming friends with Harriet Martineau, Elizabeth Gaskell, William Makepeace Thackeray and G. H. Lewes. Her book had sparked a movement in regards to feminism in literature. The main character, Jane Eyre, in her novel Jane Eyre,
was a parallel to herself, a woman who was strong. However, she never
left Haworth for more than a few weeks at a time as she did not want to
leave her aging father's side. In June 1854, Charlotte married Arthur Bell Nicholls, her father's curate,
and became pregnant soon thereafter. Her health declined rapidly during
this time, and according to Gaskell, her earliest biographer, she was
attacked by "sensations of perpetual nausea and ever-recurring
faintness." Charlotte
died, along with her unborn child, on 31 March 1855, at the young age
of 38. Her death certificate gives the cause of death as phthisis (tuberculosis),
but many biographers suggest she may have died from dehydration and
malnourishment, caused by excessive vomiting from severe morning sickness or hyperemesis gravidarum. There is also evidence to suggest that Charlotte died from typhus she
may have caught from Tabitha Ackroyd, the Brontë household's
oldest servant, who died shortly before her. Charlotte was interred in
the family vault in The Church of St. Michael and All Angels, Haworth,
West Yorkshire, England.