<Back to Index>
- Physicist Max Planck, 1858
- Painter Joseph Mallord William Turner, 1775
- Prime Minister of Canada Lester Bowles "Mike" Pearson, 1897
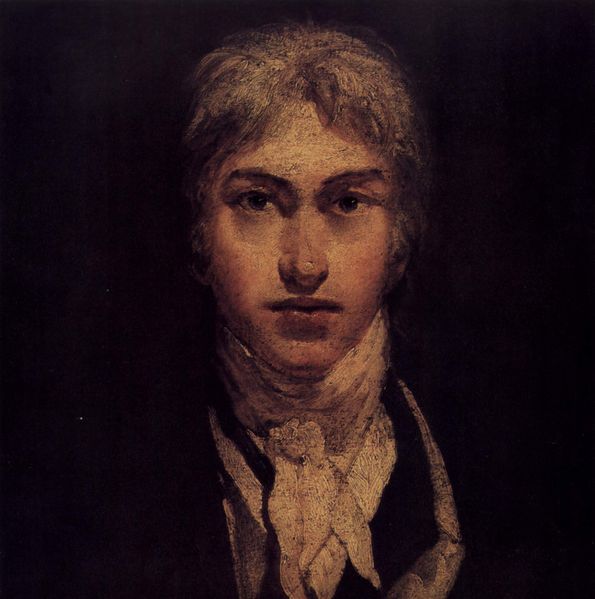

Joseph Mallord William Turner RA (23 April 1775 – 19 December 1851) was an English Romantic landscape painter, watercolourist and printmaker. Turner was considered a controversial figure in his day, but is now regarded as the artist who elevated landscape painting to an eminence rivalling history painting. Although renowned for his oil paintings, Turner is also one of the greatest masters of British watercolour landscape painting. He is commonly known as "the painter of light" and his work regarded as a Romantic preface to impressionism.
Turner was born in Maiden Lane, Covent Garden, London, England. His father, William Gay Turner (27 January 1738 – 7 August 1829), was a barber and wig maker. His mother, Mary Marshall, became increasingly mentally unstable, possibly due in part to the early death of Turner's younger sister, Helen Turner, in 1786. Mary Marshall died in 1804, after having been committed in 1799 to the Bethlem Royal Hospital, a mental asylum otherwise known as 'Bedlam'. Possibly due to the load placed on the family by these problems, the young Turner was sent to stay with his maternal uncle in Brentford in 1785, which was then a small town west of London on the banks of the River Thames. It was here that he first expressed an interest in painting. A year later he attended a school in Margate on the north-east Kent coast. By this time he had created many drawings, which his father exhibited in his shop window.
He entered the Royal Academy of Art schools in 1789, when he was only 14 years old, and was accepted into the academy a year later. Sir Joshua Reynolds, president of the Royal Academy, chaired the panel that admitted him. At first Turner showed a keen interest in architecture but was advised to continue painting by the architect Thomas Hardwick (junior). A watercolour by Turner was accepted for the Summer Exhibition of 1790 after only one year's study. He exhibited his first oil painting in 1796, Fishermen at Sea, and thereafter exhibited at the academy nearly every year for the rest of his life.
Turner travelled widely in Europe, starting with France and Switzerland in 1802 and studying in the Louvre in Paris in the same year. He also made many visits to Venice. On a visit to Lyme Regis, in Dorset, England, he painted a stormy scene (now in the Cincinnati Art Museum).
Important support for his work also came from Walter Ramsden Fawkes, of Farnley Hall, near Otley in
Yorkshire, who became a close friend of the artist. Turner first
visited Otley in 1797, aged 22, when commissioned to paint watercolours
of the area. He was so attracted to Otley and the surrounding area that
he returned to through his career. The stormy backdrop of Hannibal Crossing The Alpsis reputed to have been inspired by a storm over Otley's Chevin while Turner was staying at Farnley Hall. Turner was also a frequent guest of George O'Brien Wyndham, 3rd Earl of Egremont at Petworth House in West Sussex and
painted scenes that Egremont funded taken from the grounds of the house
and of the Sussex countryside, including a view of the Chichester Canal. Petworth House still displays a number of paintings. As
he grew older, Turner became more eccentric. He had few close friends
except for his father, who lived with him for thirty years, eventually
working as his studio assistant. His father's death in 1829 had a
profound effect on him, and thereafter he was subject to bouts of depression. He never married, although his two daughters by Sarah Danby were born in 1801 and 1811. He died in the house of his mistress Sophia Caroline Booth in Cheyne Walk, Chelsea on 19 December 1851. At his request he was buried in St Paul's Cathedral, where he lies next to Sir Joshua Reynolds. His last exhibition at the Royal Academy was in 1850. Turner's
talent was recognised early in his life. Financial independence allowed
Turner to innovate freely. Suitable vehicles for Turner's imagination
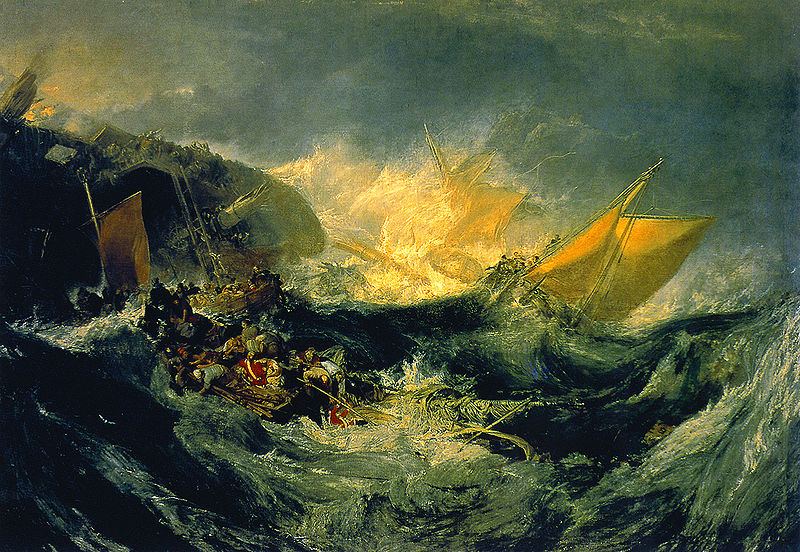
were to be found in the subjects of shipwrecks, fires (such as the burning of Parliament in 1834, an event which Turner rushed to witness first-hand, and which he transcribed in a series of watercolour sketches),
natural catastrophes, and natural phenomena such as sunlight, storm,
rain, and fog. He was fascinated by the violent power of the sea, as
seen in Dawn after the Wreck (1840) and The Slave Ship (1840). Turner's major venture into printmaking was the Liber Studiorum (Book of Studies), a set of seventy prints that the artist worked on from 1806 to 1819. The Liber Studiorum was an expression of his intentions for landscape art. Loosely based on Claude Lorrain's Liber Veritatis (Book
of Truth), the plates were meant to be widely disseminated, and
categorised the genre into six types: Marine, Mountainous, Pastoral,
Historical, Architectural, and Elevated or Epic Pastoral. Turner
placed human beings in many of his paintings to indicate his affection
for humanity on the one hand (note the frequent scenes of people
drinking and merry-making or working in the foreground), but its
vulnerability and vulgarity amid the 'sublime' nature of the world on
the other hand. His early works, such as Tintern Abbey (1795), stayed true to the traditions of English landscape. However, in Hannibal Crossing the Alps (1812),
an emphasis on the destructive power of nature had already come into
play. In
his later years he used oils ever more transparently, and turned to an
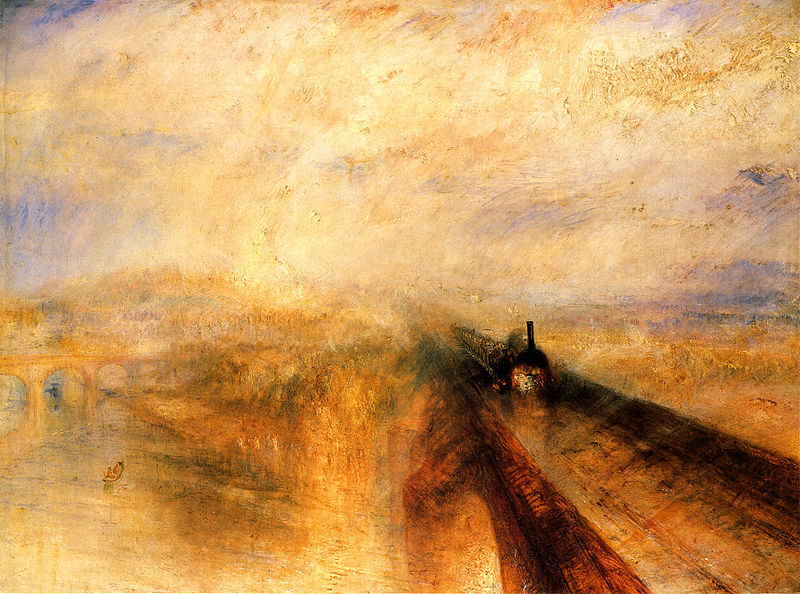
evocation of almost pure light by use of shimmering colour. A prime
example of his mature style can be seen in Rain, Steam and Speed - The Great Western Railway,
where the objects are barely recognizable. The intensity of hue and
interest in evanescent light not only placed Turner's work in the
vanguard of English painting, but later exerted an influence upon art
in France, as well; the Impressionists, particularly Claude Monet, carefully studied his techniques. High levels of ash in the atmosphere during 1816 the "Year Without a Summer," led to unusually spectacular sunsets during this period, and were an inspiration for some of Turner's work. The first American to buy a Turner painting was James Lenox of
New York City, a private collector. Lenox wished to own a Turner and in
1845 bought one unseen through an intermediary, his friend C. R.
Leslie. From among the paintings Turner had on hand and was willing to
sell for £500, Leslie selected and shipped the 1832 atmospheric
seascape Staffa, Fingal's Cave. Worried
about the painting's reception by Lenox, who knew Turner's work only
through his etchings, Leslie wrote Lenox that the quality of Staffa,
"a most poetic picture of a steam boat" would become apparent in time.
Upon receiving the painting Lenox was baffled, and "greatly
disappointed" by what he called the painting's "indistinctness". When
Leslie was forced to relay this opinion to Turner, Turner said "You
should tell Mr. Lenox that indistinctness is my forte." Staffa, Fingal's Cave is currently owned by the Yale Center for British Art, New Haven, Connecticut.