<Back to Index>
- Explorer Jacques Cartier, 1491
- Painter Henri Émile Benoit Matisse, 1869
- U.S. Secretary of State General George Catlett Marshall, 1880
PAGE SPONSOR

Jacques Cartier (December 31, 1491 – September 1, 1557) was a French explorer of Breton origin who claimed what is now Canada for France. He was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, which he named "The Country of Canadas", after the Iroquois names for the two big settlements he saw at Stadacona (Quebec City) and at Hochelaga (Montreal Island).
Jacques Cartier was born in 1491 in Saint-Malo, the port on the extreme north-east coast of Brittany. Cartier, who was a respectable mariner, improved his social status in 1520 by marrying Mary Catherine des Granches, member of a leading family. His good name in Saint-Malo is recognized by its frequent appearance on baptismal registers as godfather or witness.
In 1534, the year the Duchy of Brittany was formally united with France in the Edict of Union, Cartier was introduced to King Francis I by Jean le Veneur, bishop of Saint-Malo and abbot of Mont-Saint-Michel, at the Manoir de Brion. The king had previously invited (although not formally commissioned) the Florentine explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano to explore the eastern coast of North America on behalf of France in 1524. Cartier is believed to have accompanied da Verrazzano on this expedition, which explored the coast from South Carolina to Nova Scotia, and islands such as Newfoundland; on another voyage they went to Brazil. Le Veneur cited these voyages to Newfoundland and Brazil as proof of Cartier's ability to "lead ships to the discovery of new lands in the New World".
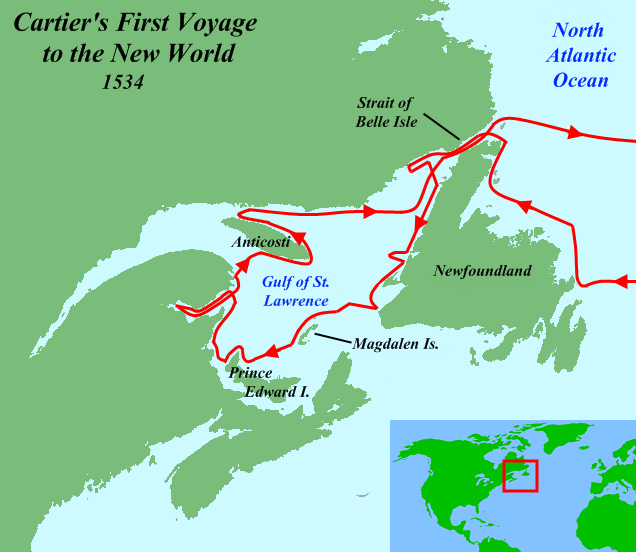
In 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of Asia. In the words of the commission, he was to "discover certain islands and lands where it is said that a great quantity of gold and other precious things are to be found". It took him twenty days to sail across the ocean. Starting on May 10 of that year, he explored parts of Newfoundland, the areas now the Canadian Atlantic provinces and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. During one stop at Îles aux Oiseaux (Islands of the Birds, now the Rochers-aux-Oiseaux federal bird sanctuary, northeast of Brion Island in the Magdalen Islands), his crew slaughtered around 1000 birds, most of them great auks (now extinct). Cartier's first two encounters with aboriginal peoples in Canada on the north side of Chaleur Bay, most likely the Mi'kmaq, were brief; some trading occurred. His third encounter took place on the shores of Gaspé Bay with a party of St. Lawrence Iroquoians, where on July 24, he planted a 10 meter cross bearing the words "Long Live the King of France" and took possession of the territory in the name of the king. The change in mood was a clear indication that the Iroquoians understood Cartier's actions. Here he kidnapped the two sons of their captain. Cartier wrote that they later told him this region where they were captured (Gaspé) was called by them Honguedo. The natives' captain at last agreed that they could be taken, under the condition that they return with European goods to trade. Cartier returned to France in September 1534, sure that he had reached an Asian coast.
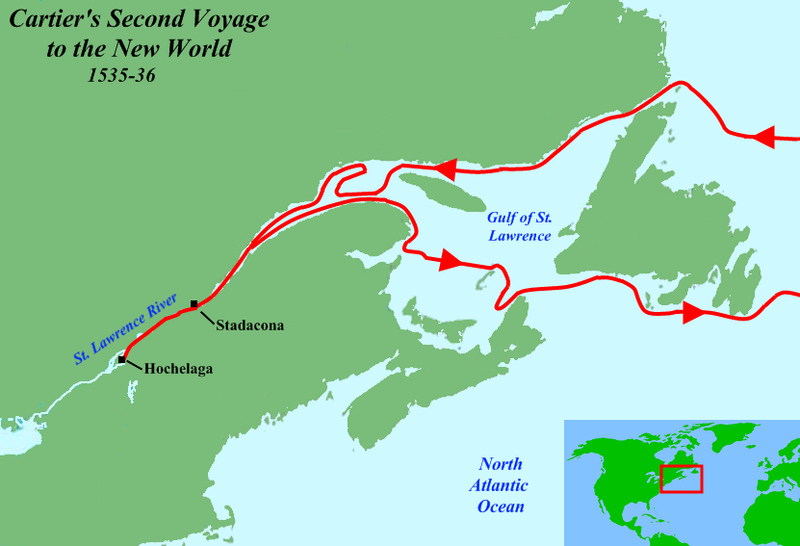
Jacques Cartier set sail for a second voyage on May 19 of the following year with three ships, 110 men, and the two natives. Reaching the St. Lawrence, he sailed up-river for the first time, and reached the Iroquoian capital of Stadacona, where Chief Donnacona ruled. Jacques Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his smallest ship to continue up-river and visit Hochelaga (now Montreal) where he arrived October 2, 1535. Hochelaga was far more impressive than the small and squalid village of Stadacona, and more than 1,000 Iroquoians came to the river edge to greet the Frenchmen. The site of their arrival has been confidently identified as the beginning of the Sainte-Marie Sault - where the bridge named after him now stands. The expedition could proceed no further, as the river was blocked by rapids. So certain was Cartier that the river was the Northwest Passage and that the rapids were all that was preventing him from sailing to China, that the rapids and the town that eventually grew up near them came to be named after the French word for China, La Chine: the Lachine Rapids and the town of Lachine, Quebec.
After
spending two days among the people of Hochelaga, Cartier returned to
Stadacona on October 11. It is not known exactly when he decided to
spend the winter of 1535 - 1536 in Stadacona, and it was by then too late
to return to France. Cartier and his men prepared for the winter by
strengthening their fort, stacking firewood, and salting down game and fish. During
this winter, Cartier compiled a sort of gazetteer that included several
pages on the manners of the natives — in particular, their habit of
wearing only leggings and loincloths even in the dead of winter.... From mid November 1535 to mid April 1536, the French fleet lay frozen solid at the mouth of the St. Charles River, under the Rock of Quebec. Ice was over a fathom (1.8 m) thick on the river, with snow four feet (1.2 m) deep ashore. To add to the discomfort, scurvy broke
out — first among the Iroquoians, and then among the French. In
his journal, Cartier states that by mid February, "out of 110 that we
were, not ten were well enough to help the others, a pitiful thing to
see". Cartier estimated the number of natives dead at 50. One
of the natives who survived was Dom Agaya, the chief's son who had been
taken to France the previous year. During a friendly visit by Domagaya
to the French fort, Cartier enquired and learned from him that a
concoction made from a tree known as annedda (probably arbor vitae) would cure scurvy. This remedy likely saved the expedition from destruction, allowing 85 Frenchmen to survive the winter. Ready
to return to France in early May 1536, Cartier decided to take Chief
Donnacona to France, so that he might personally tell the tale of a
country further north, called the "Kingdom of Saguenay",
said to be full of gold, rubies and other treasures. After an arduous
trip down the St. Lawrence and a three-week Atlantic crossing, Cartier
and his men arrived in Saint-Malo on July 15, 1536, concluding the
second, 14 month voyage, which was to be Cartier's most profitable. On
October 17, 1540, Francis I ordered the Breton navigator to return to
Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be
"captain general". However, January 15, 1541 saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a Huguenot courtier and friend of the king named as the first lieutenant general of French Canada.
Roberval was to lead the expedition, with Cartier as his chief
navigator. While Roberval waited for artillery and supplies, he gave
permission to Cartier to sail on ahead with his ships. On
May 23, 1541, Cartier departed Saint-Malo on his third voyage with five
ships. This time, any thought of finding a passage to the Orient was
forgotten. The goals were now to find the "Kingdom of Saguenay" and its
riches, and to establish a permanent settlement along the St. Lawrence
River. Anchoring at Stadacona, Cartier again met the Iroquoians,
but found their "show of joy" and their numbers worrisome, and decided
not to build his settlement there. Sailing a few miles up-river to a
spot he had previously observed, he decided to settle on the site of
present-day Cap-Rouge,
Quebec. The convicts and other colonists were landed, the cattle that
had survived three months aboard ship were turned loose, earth was
broken for a kitchen garden, and seeds of cabbage, turnip, and lettuce
were planted. A fortified settlement was thus created and was named Charlesbourg-Royal. Another fort was also built on the cliff overlooking the settlement, for added protection. The
men also began collecting what they believed to be diamonds and gold,
but which upon return to France were discovered to be merely quartz
crystals and iron pyrites, respectively — which gave rise to a French expression: "faux comme les diamants du Canada" ("As false as Canadian diamonds"). Two of the ships were dispatched home with some of these minerals on September 2. Having
set tasks for everyone, Cartier left with the longboats for a
reconnaissance in search of "Saguenay" on September 7. Having reached
Hochelaga, he was prevented by bad weather and the numerous rapids from
continuing up to the Ottawa River.
Returning
to Charlesbourg-Royal, Cartier found the situation ominous. The
Iroquoians no longer made friendly visits or peddled fish and game, but
prowled about in a sinister manner. No records exist about the winter
of 1541 - 1542 and the information must be gleaned from the few details
provided by returning sailors. It seems the natives attacked and killed
about 35 settlers before the Frenchmen could retreat behind their
fortifications. Even though scurvy was cured through the native remedy (Thuja occidentalis infusion),
the impression left is of a general misery, and of Cartier's growing
conviction that he had insufficient manpower either to protect his base
or to go in search of the Saguenay Kingdom. Cartier
left for France in early June 1542, encountering Roberval and his ships
along the Newfoundland coast, at about the time Roberval marooned Marguerite de La Rocque.
Despite Roberval's insistence that he accompany him back to Saguenay,
Cartier slipped off under the cover of darkness and continued on to
France, still convinced his vessels contained a wealth of gold and
diamonds. He arrived there in October, in what proved to be his last
voyage. Meanwhile, Roberval took command at Charlesbourg-Royal, but it
was abandoned in 1543 after disease, foul weather and hostile natives
drove the would-be settlers to despair.
Cartier spent the rest of his life in Saint-Malo and his nearby estate, where he often was useful as an interpreter in Portuguese, and he died aged 65 or 66 on September 1, 1557 from an epidemic. No permanent European settlements were made in Canada before 1608, when Samuel Champlain founded Quebec City. Cartier is interred in St. Vincent's Cathedral. Having
already located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage,
he now opened up the greatest waterway for the European penetration of
North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of
Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration
of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St.
Lawrence Iroquoians were dishonourable, he did try at times to
establish friendship with them and other native peoples living along
the St. Lawrence River — an indispensable preliminary to French
settlement in their lands. Cartier was the first to document the name Canada to designate the territory on the shores of the St Lawrence River. The name is derived from the Huron-Iroquois word "kanata", or village, which was incorrectly interpreted as the native term for the newly discovered land. Cartier used the name to describe Stadacona, the surrounding land and the river itself. And Cartier named "Canadiens" the inhabitants (Iroquoians) he had seen there. Thereafter the name Canada was used to designate the
small French colony on these shores, and the French colonists were
called Canadiens, until the mid-nineteenth century, when the name started to be applied to the loyalist colonies on the Great Lakes and later to all of British North America.
In this way Cartier is not strictly the European discoverer of Canada
as this country is understood today, a vast federation stretching a mari usque ad mare (from
sea to sea). Eastern parts had previously been visited by the Norse, as
well as Basque, Galician and Breton fishermen, and perhaps the Corte-Real brothers and John Cabot (in
addition of course to the Natives who first inhabited the territory).
Cartier's particular contribution to the discovery of Canada is as the
first European to penetrate the continent, and more precisely the
interior eastern region along the St. Lawrence River. His explorations
consolidated France's claim of the territory that would later be
colonized as New France, and his third voyage produced the first documented European attempt at settling North America since that of Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón in 1526-27. Cartier's
professional abilities can be easily ascertained. Considering that
Cartier made three voyages of exploration in dangerous and hitherto
unknown waters without losing a ship, and that he entered and departed
some 50 undiscovered harbors without serious mishap, he may be
considered one of the most conscientious explorers of the period. Cartier was also one of the first to formally acknowledge that the New World was a separate land mass from Europe/Asia.
On August 18, 2006, Quebec Premier Jean Charest announced that Canadian archaeologists had discovered the precise location of Cartier's lost first colony of Charlesbourg-Royal. The
colony was built where the Cap Rouge river runs into the St. Lawrence
River and is based on the discovery of burnt wooden timber remains that
have been dated to the mid-16th century, and a fragment of a decorative
Istoriato plate manufactured in Faenza,
Italy, between 1540 and 1550, that could only have belonged to a member
of the French aristocracy in the colony. Most probably this was the Sieur de Roberval, who replaced Cartier as the leader of the settlement. This colony was the first known European settlement in modern day Canada since the c.1000 AD L'Anse aux Meadows Viking village in northern Newfoundland. Its rediscovery has been hailed by archaeologists as the most important
find in Canada since the L'Anse aux Meadows rediscovery.