<Back to Index>
- Explorer Marie Joseph François Garnier, 1839
- Painter Thomas Cowperthwait Eakins, 1844
- Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Arthur James Balfour, 1848
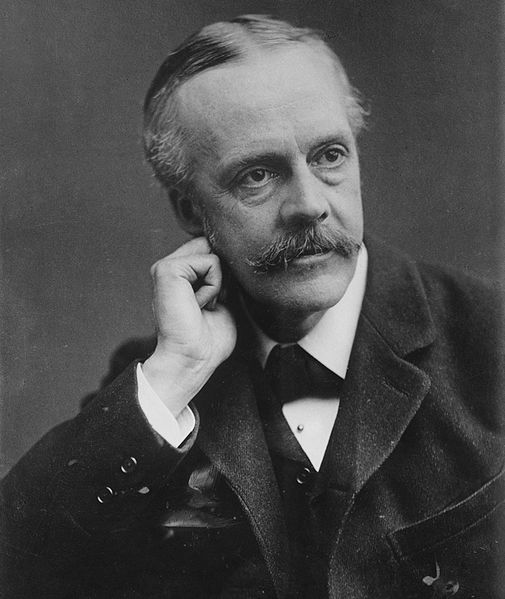
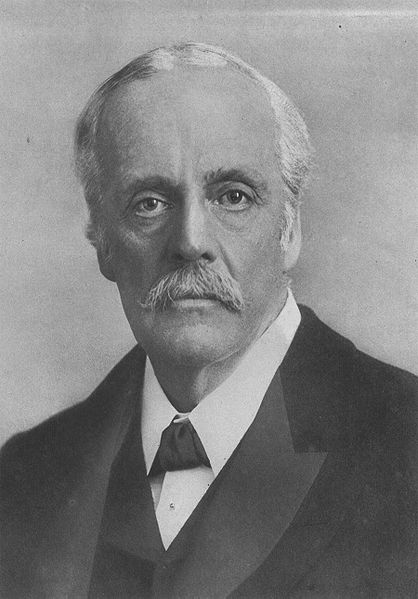


Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour, KG, OM, PC, DL (25 July 1848 – 19 March 1930) was a British Conservative politician and statesman. He authored the tough Perpetual Crimes Act (1887) (or Coercion Act) aimed at the prevention of boycotting, intimidation, unlawful assembly in Ireland during the Irish Land War, and was the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905, a time when his party and government became divided over the issue of tariff reform. Later, as Foreign Secretary, he authored the Balfour Declaration of 1917, which supported the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
Arthur Balfour was born at Whittingehame, East Lothian, Scotland, and was the eldest son of James Maitland Balfour (1820-1856) and Lady Blanche Gascoyne-Cecil (d. 1872, aged forty-seven). His father was a Scottish MP; his mother, a member of the Cecil family descended from Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury, was the daughter of the 2nd Marquess of Salisbury and a sister to the 3rd Marquess, the future Prime Minister. His godfather was the Duke of Wellington, after whom he was named. He was the eldest son, the third of eight children, and had four brothers and three sisters. Arthur Balfour was educated at the Grange preparatory school in Hoddesdon, Hertfordshire (1859-1861), Eton (1861-1866) where he studied with the influential Master William Johnson Cory, and Trinity College, Cambridge (1866-1869), where he read Moral sciences, graduating with a Second-Class Honours Degree. His younger brother was the renowned Cambridge embryologist Francis Maitland Balfour (1851-1882).
Although he coined the saying, "Nothing matters very much and few things matter at all," Balfour was distraught at the early death from typhus in 1875 of his cousin May Lyttelton, whom he had hoped to marry. Balfour remained a bachelor for the rest of his life, his serious intention to marry never renewed. Margot Tennant (later Margot Asquith) had wished to marry him - on being queried about this he replied "No, that is not so. I rather think of having a career of my own." His household was maintained by his (also) unmarried sister Alice. In middle age Balfour had a long friendship with Mary Wemyss, later Countess of Elcho. It is unclear whether the relationship was sexual.
In 1874 he was elected Conservative Member of Parliament (MP) for Hertford and represented that constituency until 1885. In the spring of 1878 Balfour became Private Secretary to his uncle, Lord Salisbury. In that capacity he accompanied Salisbury (then Foreign Secretary) to the Congress of Berlin and
gained his first experience in international politics in connection
with the settlement of the Russo-Turkish conflict. At the same time he
became known in the world of letters; the academic subtlety and
literary achievement of his Defence of Philosophic Doubt (1879) suggested that he might make a reputation for himself as a philosopher. Balfour
divided his time between the political arena and the academy. Released
from his duties as private secretary by the general election of 1880,
he began to take a more active part in parliamentary affairs. He was
for a time politically associated with Lord Randolph Churchill, Sir Henry Drummond Wolff and John Gorst. This quartet became known as the "Fourth Party" and gained notoriety for the leader Lord Randolph Churchill's free criticism of Sir Stafford Northcote, Lord Cross and other prominent members of the "old gang". Lord Salisbury made Balfour President of the Local Government Board in 1885 and later Secretary for Scotland in
1886, with a seat in the cabinet. These offices, while having few
opportunities for distinction, served as a sort of apprenticeship for
Balfour. In early 1887 Sir Michael Hicks-Beach, the Chief Secretary for Ireland,
resigned because of illness and Salisbury appointed his nephew in his
place. The selection took the political world by surprise and possibly
led to the British phrase "Bob's your uncle!".
Balfour surprised his critics by his ruthless enforcement of the Crimes
Act, earning the nickname "Bloody Balfour". Balfour's skill for steady
administration did much to dispel his reputation as a political
lightweight. In Parliament he resisted any overtures to the Irish Parliamentary Party on Home Rule, and, allied with Joseph Chamberlain's Liberal Unionists, strongly encouraged Unionist activism in Ireland. Balfour also broadened the basis of material prosperity to the less well off by creating the Congested Districts Board for Ireland in
1890. It was during this period of 1886-1892 that he sharpened his gift
of oratory and gained a reputation as one of the most effective public
speakers of the age. Impressive in matter rather than in delivery, his
speeches were logical and convincing, and delighted an ever wider audience. On the death of W.H. Smith in 1891, Balfour became First Lord of the Treasury- the last one in British history not to have been concurrently Prime Minister as well — and Leader of the House of Commons.
After the fall of the government in 1892 he spent three years is
opposition. On the return of the Conservatives to power in 1895, he
resumed the leadership of the House. His management of the abortive
education proposals of 1896 were thought to show a disinclination for
the continuous drudgery of parliamentary management. Yet he had the
satisfaction of seeing a bill pass providing Ireland with an improved
system of local government, and took an active role in the debates on
the various foreign and domestic questions that came before parliament
between 1895 to 1900. During the illness of Lord Salisbury in 1898, and
again in Lord Salisbury's absence abroad, Balfour was put in charge of
the Foreign Office,
and it was his job to conduct the critical negotiations with Russia on
the question of railways in North China. As a member of the cabinet responsible for the Transvaal negotiations in 1899, he bore his full share of controversy, and when the war began
disastrously, he was the first to realise the need to put the full
military strength of the country into the field. His leadership of the
House of Commons was marked by considerable firmness in the suppression
of obstruction, yet there was a slight revival of the criticisms of
1896. On
Lord Salisbury's resignation on 11 July 1902, Balfour succeeded him as
Prime Minister, with the approval of all sections of the Unionist
party. The new Prime Minister came into power practically at the same
moment as the coronation of Edward VII and the end of the South African War.
For a while no cloud appeared on the horizon. The Liberal party was
still disorganised over their attitude towards the Boers. The two chief
items of the ministerial parliamentary program were the extension of
the new Education Act to London and the Irish Land Purchase Act, by
which the British exchequer would advance the capital for enabling
tenants in Ireland to buy land. A notable achievement of Balfour's
government was the establishment of the Committee on Imperial Defence. In foreign affairs, Balfour and his foreign secretary, Lord Lansdowne presided over a dramatic improvement in relations with France, culminating in the Entente Cordiale of 1904. The period also saw the acute crisis of the Russo-Japanese War, when Britain, an ally of the Japanese, came close to war with Russia as a result of the Dogger Bank incident. On the whole, Balfour left the conduct of foreign policy to Lansdowne, being largely busy himself with domestic problems. The
budget was certain to show a surplus and taxation could be remitted.
Yet as events proved, it was the budget that would sow dissension,
override all other legislative concerns, and in the end signal the
beginning of a new political movement. Charles Thomson Ritchie's remission of the shilling import-duty on corn led to Joseph Chamberlain's crusade in favour of tariff reform — these were taxes on imported goods with trade preference given
to the Empire, with the threefold goal of protecting British industry
from competition, strengthening the British Empire in the face of
growing German and American economic power, and providing a source of
revenue, other than raising taxes, for the costs of social welfare
legislation. As the session proceeded, the rift grew in the Unionist
ranks. Tariff Reform proved popular with Unionist supporters, but the
threat of higher prices for food imports made the policy an electoral
albatross. Hoping to split the difference between the free traders and
tariff reformers in his cabinet and party, Balfour came out in favour
of retaliatory tariffs — tariffs designed to punish other powers that
had
tariffs against British goods, supposedly in the hope of encouraging
global free trade. This
was not, however, sufficient for either the free traders or the more
extreme tariff reformers in the government. With Balfour's agreement,
Chamberlain resigned from the Cabinet in late 1903 to stump the country
in favour of Tariff Reform. At the same time, Balfour tried to balance
the two factions by accepting the resignation of three free-trading
ministers, including Chancellor Ritchie, but the almost simultaneous
resignation of the free-trader Duke of Devonshire (who as Lord
Hartington had been the Liberal Unionist leader of the 1880s) left
Balfour's Cabinet looking weak. By 1905 relatively few Unionist MPs
were still free traders (the young Winston Churchill crossed over to
the Liberals in 1904 when threatened with deselection at Oldham), but
Balfour's long balancing act had drained his authority within the
government. Balfour
eventually resigned as Prime Minister in December 1905, hoping in vain
that the Liberal leader Campbell-Bannerman would be unable to form a
strong government. These hopes were dashed when Campbell-Bannerman
faced down an attempt (the "Relugas Compact") to "kick him upstairs" to
the House of Lords. The Conservatives were defeated by the Liberals at
the general election the following January (in terms of MPs, a Liberal
landslide), with Balfour himself losing his seat at Manchester East.
Only 157 Conservatives were returned to the House of Commons, at least
two-thirds of them followers of Chamberlain, who briefly chaired the
Conservative MPs until Balfour won a safe seat in the City of London. After the disaster of 1906 Balfour
remained party leader, his position strengthened by Joseph
Chamberlain's removal from active politics after his stroke in July
1906, but he was unable to make much headway against the huge Liberal
majority in the House of Commons. An early attempt to score a debating
triumph over the government, made in Balfour's usual abstruse,
theoretical style, saw Campbell-Bannerman respond with: "Enough of this
foolery," to the delight of his supporters in the House. Balfour made
the controversial decision, with Lord Lansdowne, to use the heavily Unionist House of Lords as an active check on the political program and legislation of the Liberal party in the House of Commons. Numerous pieces of legislation were vetoed or altered by amendments between 1906 and 1909, leading David Lloyd George to
remark that the Lords had become "not the watchdog of the Constitution,
but Mr. Balfour's poodle." The issue was eventually forced by the Liberals with Lloyd George's so-called People's Budget, provoking the constitutional crisis that eventually led to the Parliament Act 1911,
which replaced the Lords' veto authority with a greatly reduced power
to only delay bills for up to two years. After the Unionists had failed
to win an electoral mandate at either of the General Elections of 1910
(despite softening the Tariff Reform policy with Balfour's promise of a
referendum on food taxes), the Unionist peers split to allow the
Parliament Act to pass the House of Lords, in order to prevent a
mass-creation of new Liberal peers by the new King, George V. The
exhausted Balfour resigned as party leader after the crisis, and was
succeeded in late 1911 by Andrew Bonar Law. Balfour remained an important figure within the party, however, and when the Unionists joined Asquith's coalition government in May 1915, Balfour succeeded Winston Churchill as First Lord of the Admiralty.
When Asquith's government collapsed in December 1916, Balfour, who
seemed for a time a potential successor to the premiership, became Foreign Secretary in
Lloyd George's new administration, but was not actually included in the
small War Cabinet, and was frequently left out of the inner workings of
the government. Balfour's service as Foreign Secretary was most notable
for the issuance of the Balfour Declaration of 1917, a letter to Lord Rothschild promising the Jews a "national home" in Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire. Balfour resigned as Foreign Secretary following the Versailles Conference in 1919, but continued in the government (and the Cabinet after normal peacetime political arrangements resumed) as Lord President of the Council. In 1921-22 he represented the British Empire at the Washington Naval Conference. In
1922 he, along with most of the Conservative leadership, resigned with
Lloyd George's government following the Conservative back-bench revolt
against the continuance of the coalition. Bonar Law soon became Prime
Minister. In 1922 Balfour was created Earl of Balfour.
Like many of the Coalition leaders he did not hold office in the
Conservative governments of 1922-4, although as an elder statesman he
was consulted by the King in the choice of Baldwin as Bonar Law's
successor as Conservative leader in May 1923. When asked by a lady
whether "dear George" (the much more experienced Lord Curzon)
would be chosen he replied, referring to Curzon's wealthy wife Grace,
"No, dear George will not but he will still have the means of Grace." Balfour was again not initially included in Stanley Baldwin's second government in 1924, but in 1925 he once again returned to the Cabinet, serving in place of the late Lord Curzon as Lord President of the Council until the government ended in 1929. In 1925 he visited the Holy Land. Apart from a number of colds and occasional influenza,
Balfour had enjoyed good health until the year 1928, and remained until
then a regular tennis player. At the end of that year most of his teeth
had to be removed and he began to suffer from the unremitting
circulatory trouble which ended his life. Late in January 1929 Balfour
was conveyed from Whittingehame to Fisher's Hill, his brother Gerald's home near Woking, Surrey. In the past he had suffered from occasional bouts of phlebitis and by late 1929 he was immobilised by it. Finally, soon after receiving a visit from his friend Chaim Weizmann,
Balfour died at Fisher's Hill on 19 March 1930. At his request a public
funeral was declined and he was buried on 22 March beside members of
his family at Whittingehame in a Church of Scotland service, though he also belonged to the Church of England. Despite the snowy weather, attenders came from far and wide. By special remainder, the title passed to his brother Gerald.