<Back to Index>
- Physicist Gordon Gould, 1920
- Painter Hippolyte Delaroche, 1797
- 5th Vice President of the United States Elbridge Thomas Gerry, 1744
PAGE SPONSOR

Hippolyte Delaroche (17 July 1797 – 4 November 1856), commonly known as Paul Delaroche, was a French painter born in Paris. Delaroche was born into a wealthy family and was trained by Antoine-Jean, Baron Gros, who then painted life size histories and had many students.
The first Delaroche picture exhibited was the large Josabeth saving Joas (1822). This exhibition led to his acquaintance with Théodore Géricault and Eugène Delacroix, with whom he became friends. The three of them formed the core of a large group of Parisian historical painters. He visited Italy in 1838 and 1843, when his father-in-law, Horace Vernet, was director of the French Academy in Rome.
Delaroche's studio in Paris was in the Rue Mazarine. His subjects were painted with a firm, solid, smooth surface, which gave an appearance of the highest finish. This texture was the manner of the day and was also found in the works of Vernet, Ary Scheffer, Louis-Leopold Robert and Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres. Among his students were British landscape artist Henry Mark Anthony (1817 – 1886) and British history painter Edward Armitage R.A. (1817 – 1896).
Delaroche's
paintings, with their straightforward technique and dramatic
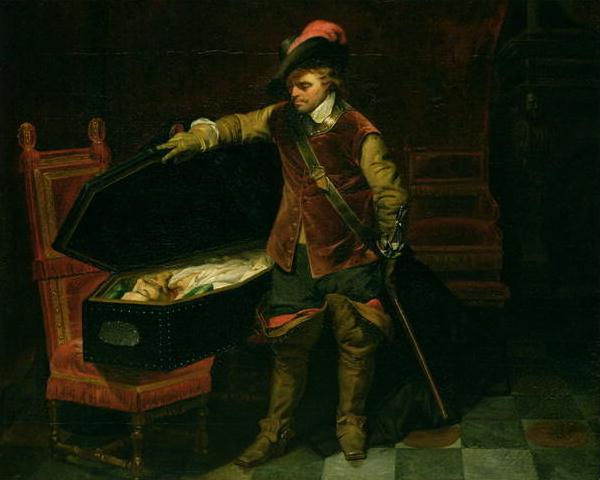
compositions, became very popular. He applied essentially the same
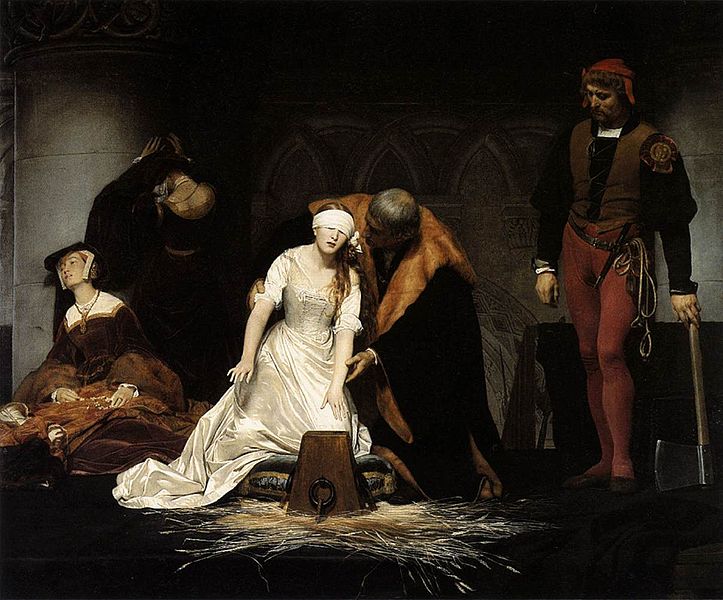
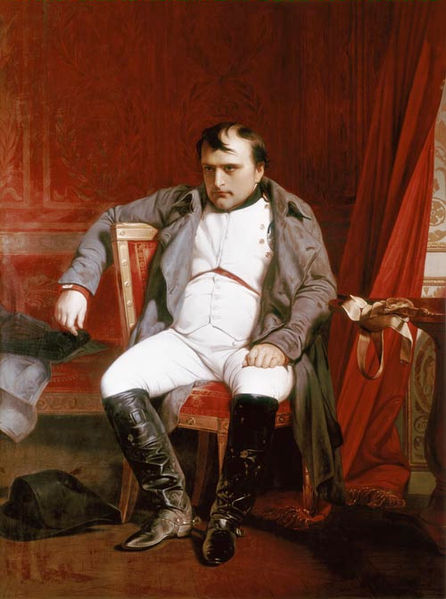
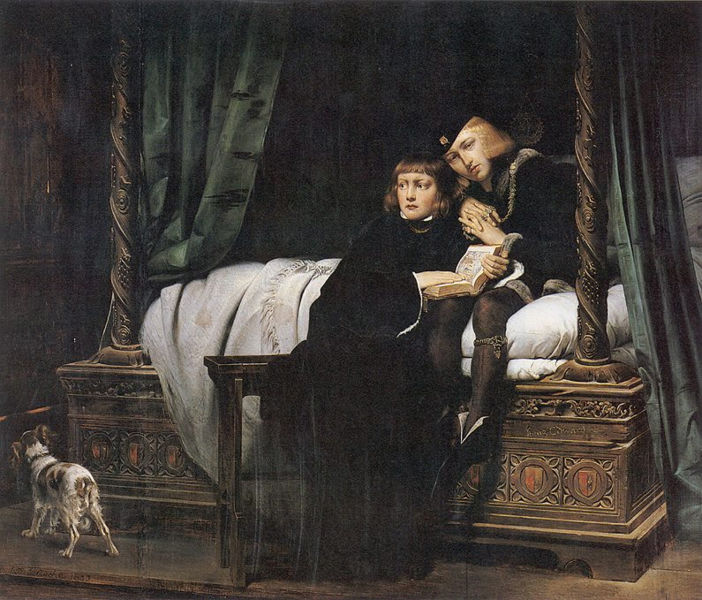
treatment to the characters of distant historical times, the founders of Christianity, and various figures of his own day such as "Napoleon at Fontainebleau," "Napoleon at St Helena," or "Marie Antoinette leaving the Convention after her sentence." His dramatic paintings include Strafford Led to Execution, depicting the English Archbishop Laud stretching his arms out of the small high window of his cell to bless Thomas Wentworth, 1st Earl of Strafford, as Strafford passes along the corridor to be executed, and the Assassination of the duc de Guise at Blois. Another famous work shows Cardinal Richelieu in a gorgeous barge, preceding the boat carrying Cinq-Mars and De Thou carried to their execution. Other important Delaroche works include The Princes in the Tower and the La Jeune Martyre (showing a young female martyr floating dead on the Tiber). Delaroche's work was sometimes ahistorical. Cromwell lifting the Coffin-lid and looking at the Body of Charles is based on an urban legend, and The Execution of Lady Jane Grey is
represented as taking place in a dungeon, which is badly inaccurate. He
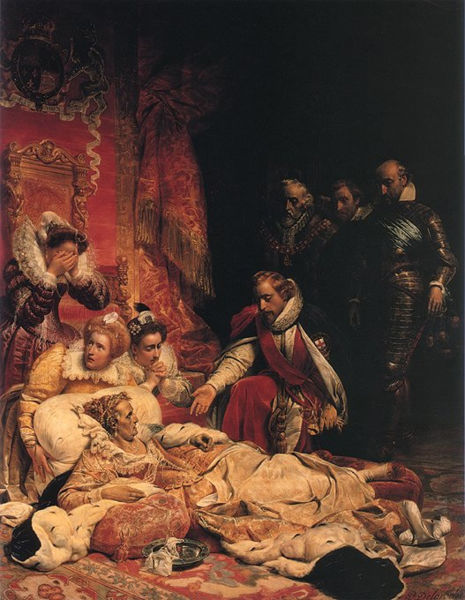
tended to care more about dramatic effect than historical truth: e.g., in The King in the Guardroom, villainous Puritan soldiers blow tobacco smoke in the face of King Charles, and Queen Elizabeth Dying on the Ground.
Delaroche's love for Horace Vernet's young daughter Louise was the absorbing passion of his life. In 1835, he exhibited Head of an Angel, which was based on a study of her. It is said that Delaroche never
recovered from the shock of her 1845 death. After her death he produced
a sequence of small elaborate pictures of incidents in Jesus' Passion.
He focused attention on the human drama of the Passion, as in a
painting where Mary and the apostles hear the crowd cheering Jesus on
the Via Dolorosa, and another where St. John escorts Mary home after her son's death. In
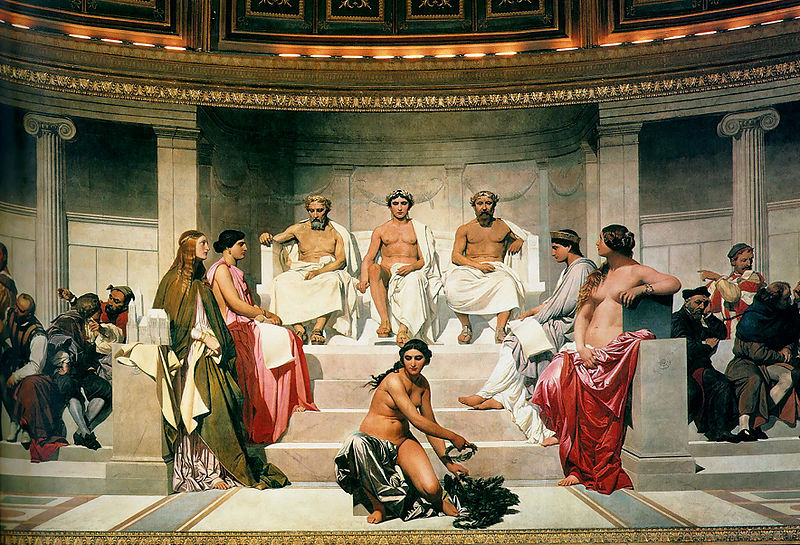
1837 Delaroche received the commission for the great picture, 27 metres
(88.5 ft) long, in the hemicycle of the award theatre of the École des Beaux Arts. The commission came from the Ecole's architect, Felix Duban.
The painting represents seventy five great artists of all ages, in
conversation, assembled in groups on either hand of a central elevation
of white marble steps, on the topmost of which are three thrones filled
by the creators of the Parthenon: architect Phidias, sculptor Ictinus, and painter Apelles, symbolizing the unity of these arts. To supply the female element in this vast composition he introduced the genii or muses, who symbolize or reign over the arts, leaning against the balustrade of
the steps, depicted as idealized female figures. The painting is done
directly on the wall, in oil paints. Delaroche finished the work in
1841, but it was considerably damaged by a fire in 1855. He immediately
set about trying to re-paint and restore the work, but died on 4
November 1856, before he had accomplished much of this. The restoration
was finished by Joseph-Nicolas Robert-Fleury.