<Back to Index>
- Chrystallographer Carl Hermann, 1898
- Graphic Artist Maurits Cornelis Escher, 1898
- King of England Edward I, 1239
PAGE SPONSOR


Edward I (17 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England from 1272 to 1307. The first son of Henry III, Edward was involved early in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included an outright rebellion by the English barons. In 1259 he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was hostage to the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and joined the fight against Simon de Montfort. Montfort was defeated at the Battle of Evesham in 1265, and within two years the rebellion was extinguished. With England pacified, Edward left on a crusade to the Holy Land. The crusade accomplished little, and Edward was on his way home in 1272 when he was informed that his father had died. Making a slow return, he reached England in 1274 and he was crowned king at Westminster on 19 August.
Edward's reign had two main phases. He spent the first years reforming royal administration. Through an extensive legal inquiry, Edward investigated the tenure of various feudal liberties, while the law was reformed through a series of statutes regulating criminal and property law. Increasingly, however, Edward's attention was drawn towards military affairs. After suppressing a minor rebellion in Wales in 1276–77, Edward responded to a second rebellion in 1282–83 with a full-scale war of conquest. After a successful campaign, Edward subjected Wales to English rule, built a series of castles and towns in the countryside and settled them with Englishmen. Next, his efforts were directed towards Scotland. Initially invited to arbitrate a succession dispute, Edward claimed feudal suzerainty over the kingdom. In the war that followed, the Scots persevered, even though the English seemed victorious at several points. At the same time there were problems at home. In the mid 1290s, extensive military campaigns required high levels of taxation, and Edward met with both lay and ecclesiastical opposition. These crises were initially averted, but issues remained unsettled. When the king died in 1307, he left behind a number of financial and political problems to his son Edward II, as well as an ongoing war with Scotland.
Edward I was a tall man for his era, hence the nickname "Longshanks". He was also temperamental, and this, along with his height, made him an intimidating man, and he often instilled fear in his contemporaries. Nevertheless, he held the respect of his subjects for the way in which he embodied the medieval ideal of kingship, as a soldier, an administrator and a man of faith. Modern historians have been more divided on their assessment of the king; while some have praised him for his contribution to the law and administration, others have criticised him for his uncompromising attitude to his nobility. Currently, Edward I is credited with many accomplishments during his reign, including restoring royal authority after the reign of Henry III, establishing parliament as a permanent institution and thereby also a functional system for raising taxes, and reforming the law through statutes. At the same time, he is also often criticised for other actions, such as his brutal conduct towards the Scots, and the expulsion of the Jews from England in 1290.
Edward was born at the Palace of Westminster on the night of 17-18 June 1239, to King Henry III and Eleanor of Provence.
Although the young prince was seriously ill on several occasions, in
1246, 1247, and 1251, he grew up to be strong and healthy. Edward was
in the care of Hugh Giffard — father of the future Chancellor Godfrey Giffard — until Bartholomew Pecche took over at Giffard's death in 1246. Among his childhood friends was his cousin Henry of Almain, son of King Henry's brother Richard of Cornwall. Henry
of Almain would remain a close companion of the prince, both through
the civil war that followed, and later on the crusade. In 1254, English fears of a Castilian invasion of the English province of Gascony induced Edward's father to arrange a politically expedient marriage between his fourteen year old son and Eleanor, the half-sister of King Alfonso X of Castile. Eleanor and Edward were married on 1 November 1254 in the Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas in Castile. As part of the marriage agreement, the young prince received grants of land worth 15,000 marks a year. Though
the endowments King Henry made were sizable, they offered Edward little
independence. He had already received Gascony as early as 1249, but Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester,
had been appointed as royal lieutenant the year before and,
consequently, drew its income, so in practice Edward derived neither
authority nor revenue from this province. The grant he received in 1254 included most of Ireland, and much land in Wales and England, including the earldom of Chester,
but the king retained much control over the land in question,
particularly in Ireland, so Edward's power was limited there as well,
and the king derived most of the income from those lands. From 1254 to 1257, Edward was under the influence of his mother's relatives, known as the Savoyards, the most notable of whom was Peter of Savoy, the queen's uncle. After 1257, Edward increasingly fell in with the Poitevin or Lusignan faction — the half-brothers of his father Henry III — led by such men as William de Valence. This
association was significant, because the two groups of privileged
foreigners were resented by the established English aristocracy, and
they would be at the centre of the ensuing years' baronial reform
movement. There
were tales of unruly and violent conduct by Edward and his Lusignan
kinsmen, which raised questions about the royal heir's personal
qualities. The next years would be formative on Edward's character. Edward
had shown independence in political matters as early as 1255, when he
sided with the Soler family in Gascony, in the ongoing conflict between
the Soler and Colomb families. This ran contrary to his father's policy
of mediation between the local factions. In May 1258, a group of magnates drew up a document for reform of the king’s government — the so-called Provisions of Oxford —
largely directed against the Lusignans. Edward stood by his political
allies and strongly opposed the Provisions. The reform movement
succeeded in limiting the Lusignan influence, however, and gradually
Edward’s attitude started to change. In March 1259, he entered into a
formal alliance with one of the main reformers, Richard de Clare, Earl of Gloucester. Then, on 15 October 1259, he announced that he supported the barons' goals, and their leader, Simon de Montfort. The
motive behind Edward's change of heart could have been purely
pragmatic; Montfort was in a good position to support his cause in
Gascony. When the king left for France in November, Edward's behaviour turned into
pure insubordination. He made several appointments to advance the cause
of the reformers, causing his father to believe that his son was
considering a coup d'état. When the king returned from France, he initially refused to see his son, but through the mediation of the Earl of Cornwall and the archbishop of Canterbury, the two were eventually reconciled. Edward was sent abroad, and in November 1260 he once more united with the Lusignans, who had been exiled to France. Back
in England, early in 1262, Edward fell out with some of his former
Lusignan allies over financial matters. The next year, King Henry sent
him on a campaign in Wales against Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, with only limited results. Around
the same time, Simon de Montfort, who had been out of the country since
1261, returned to England and reignited the baronial reform movement. It
was at this pivotal moment, as the king seemed ready to resign to the
barons' demands, that Edward began to take control of the situation.
Whereas he had so far been unpredictable and equivocating, from this
point on he remained firmly devoted to protecting his father's royal
rights. He reunited with some of the men he had alienated the year before — among them his childhood friend, Henry of Almain, and John de Warenne, Earl of Surrey — and retook Windsor Castle from the rebels. Through the arbitration of King Louis IX of France, an agreement was made between the two parties. This so-called Mise of Amiens was largely favourable to the royalist side, and laid the seeds for further conflict.
The years 1264–1267 saw the conflict known as the Barons' War, in which baronial forces led by Simon de Montfort fought against those who remained loyal to the king. The first scene of battle was the city of Gloucester, which Edward managed to retake from the enemy. When Robert de Ferrers, earl of Derby,
came to the assistance of the rebels, Edward negotiated a truce with
the earl, the terms of which he later broke. Edward then proceeded to
capture Northampton from Montfort's son Simon, before embarking on a retaliatory campaign against Derby's lands. The baronial and royalist forces finally met at the Battle of Lewes, on 14 May 1264. Edward, commanding the right wing, performed well,
and soon defeated the London contingent of Montfort's forces. Unwisely,
however, he followed the scattered enemy in pursuit, and on his return
found the rest of the royal army defeated. By the agreement known as the Mise of Lewes, Edward and his cousin Henry of Almain were given up as prisoners to Montfort. Edward remained in captivity until March, and even after his release he was kept under strict surveillance. Then, on 28 May, he managed to escape his custodians and joined up with the Earl of Gloucester, who had recently defected to the king's side. Montfort's support was now dwindling, and Edward retook Worcester and Gloucester with relatively little effort. In
the meanwhile, Montfort had made an alliance with Llywelyn and started
moving east to join forces with his son Simon. Edward managed to make a
surprise attack at Kenilworth Castle, where the younger Montfort was quartered, before moving on to cut off the earl of Leicester. The two forces then met at the second great encounter of the Barons' War — the Battle of Evesham,
on 4 August 1265. Montfort stood little chance against the
superior royal forces, and after his defeat he was killed and mutilated
on the field. Through
such episodes as the deception of Derby at Gloucester, Edward acquired
a reputation as untrustworthy. During the summer campaign, though, he
began to learn from his mistakes, and acted in a way that gained the
respect and admiration of his contemporaries. The
war did not end with Montfort's death, and Edward participated in the
continued campaigning. At Christmas, he came to terms with the younger
Simon de Montfort and his associates at the Isle of Axholme in Lincolnshire, and in March he led a successful assault on the Cinque Ports. A
contingent of rebels held out in the virtually impregnable Kenilworth
Castle and did not surrender until the drafting of the conciliatory Dictum of Kenilworth. In
April it seemed as if Gloucester would take up the cause of the reform
movement, and civil war would resume, but after a renegotiation of the
terms of the Dictum of Kenilworth, the parties came to an agreement. Edward,
however, was little involved in the settlement negotiations following
the wars; at this point his main focus was on planning his upcoming crusade. Edward took the crusader's cross in an elaborate ceremony on 24 June 1268, with his brother Edmund and
cousin Henry of Almain. Among others who committed themselves to the
Ninth Crusade were Edward's former adversaries — like the earl of
Gloucester, though the earl did not ultimately participate. With the country pacified, the greatest impediment to the project was providing sufficient finances. King Louis IX of France, who was the leader of the crusade, provided a loan of about £17,500. This, however, was not enough; the rest had to be raised through a tax on the laity, which had not been levied since 1237. In May 1270, Parliament granted a tax of a twentieth, in exchange for which the king agreed to reconfirm Magna Carta, and to impose restrictions on Jewish money lending. On 20 August Edward sailed from Dover for France. Historians
have been unable to determine the size of the force with any certainty,
but Edward probably brought with him around 225 knights and all
together less than 1000 men. Originally, the Crusaders intended to relieve the beleaguered Christian stronghold of Acre, but Louis had been diverted to Tunis. The French king and his brother Charles of Anjou, who had made himself king of Sicily, decided to attack the emirate in order to establish a stronghold in North Africa. The
plans failed when the French forces were struck by an epidemic which,
on 25 August, took the life of King Louis himself. By
the time Edward arrived at Tunis, Charles had already signed a treaty
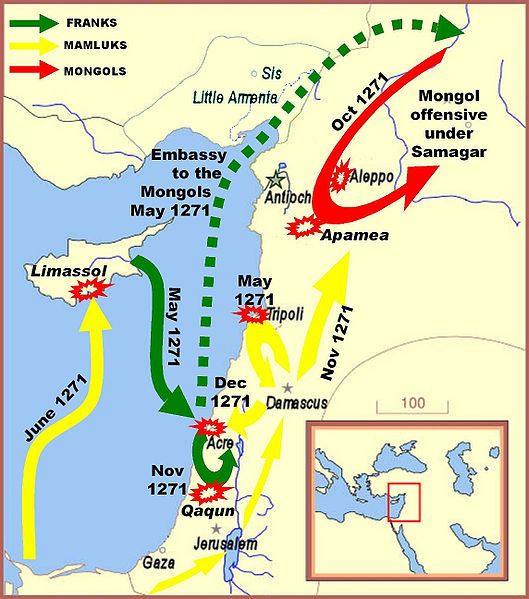
with the emir, and there was little else to do but return to Sicily. The crusade was postponed until next spring, but a devastating storm off the coast of Sicily dissuaded Charles of Anjou and Louis's successor Philip III from any further campaigning. Edward decided to continue alone, and on 9 May 1271 he finally landed at Acre. By then, the situation in the Holy Land was a precarious one. Jerusalem had fallen in 1244, and Acre was now the centre of the Christian state. The Muslim states were on the offensive under the Mamluk leadership of Baibars,
and were now threatening Acre itself. Though Edward's men were an
important addition to the garrison, they stood little chance against
Baibars' superior forces, and an initial raid at nearby St Georges-de-Lebeyne in June was largely futile. An embassy to the Mongols helped bring about an attack on Aleppo in the north, which helped to distract Baibar's forces. In November, Edward led a raid on Qaqun,
which could have served as a bridgehead to Jerusalem, but both the
Mongol invasion and the attack on Qaqun failed. Things now seemed
increasingly desperate, and in May 1272 Hugh III of Cyprus, who was the nominal king of Jerusalem, signed a ten–year truce with Baibars. Edward was initially defiant, but an attack by a Muslim assassin in
June forced him to abandon any further campaigning. Although he managed
to kill the assassin, he was struck in the arm by a dagger feared to be
poisoned, and became severely weakened over the following months. It
was not until 24 September that Edward left Acre. Arriving in
Sicily, he was met with the news that his father had died on
16 November. Edward
was deeply saddened by this news, but rather than hurrying home at
once, he made a leisurely journey northwards. This was partly due to
his health still being poor, but also due to a lack of urgency. The
political situation in England was stable after the mid century
upheavals, and Edward was proclaimed king at his father's death, rather
than at his own coronation, as had up until then been customary. In Edward's absence, the country was governed by a royal council, led by Robert Burnell. The
new king embarked on an overland journey through Italy and France,
where among other things he visited the pope in Rome and suppressed a
rebellion in Gascony. Only on 2 August 1274 did he return to England, and was crowned on 19 August. The Hundred Rolls formed the basis for the later legal inquiries called the Quo warranto proceedings. The purpose of these inquiries was to establish by what warrant (Latin: Quo warranto) various liberties were held. If
the defendant could not produce a royal licence to prove the grant of
the liberty, then it was the crown's opinion – based on the
writings of the influential thirteenth century legal scholar Bracton – that the liberty should revert to the king. By enacting Statute of Gloucester in
1278 the king challenged baronial rights through a revival of the
system of general eyres (royal justices to go on tour throughout the
land) and through a significant increase in the number of pleas of quo
warranto to be heard by such eyres. This caused great consternation
among the aristocracy, who insisted that long use in itself constituted license. A
compromise was eventually reached in 1290, whereby a liberty was
considered legitimate as long as it could be shown to have been
exercised since the coronation of King Richard I, in 1189. Royal gains from the Quo warranto proceedings were insignificant; few liberties were returned to the king. Edward
had nevertheless won a significant victory, in clearly establishing the
principle that all liberties essentially emanated from the crown. The 1290 statute of Quo warranto was only one part of a wider legislative effort, which was one of the most important contributions of Edward I's reign. This era of legislative action had started already at the time of the baronial reform movement; the Statute of Marlborough (1267) contained elements both of the Provisions of Oxford and the Dictum of Kenilworth. The compilation of the Hundred Rolls was followed shortly after by the issue of Westminster I (1275), which asserted the royal prerogative and outlined restrictions on liberties. In the Mortmain (1279), the issue was grants of land to the church. The first clause of Westminster II (1285), known as De donis conditionalibus, dealt with family settlement of land, and entails. Merchants (1285) established firm rules for the recovery of debts, while Winchester (1285) dealt with peacekeeping on a local level. Quia emptores (1290) – issued along with Quo warranto – set out to remedy land ownership disputes resulting from alienation of land by subinfeudation. The age of the great statutes largely ended with the death of Robert Burnell in 1292. Llywelyn ap Gruffudd enjoyed an advantageous situation in the aftermath of the Barons' War. Through the 1267 Treaty of Montgomery, he officially obtained land he had conquered in the Four Cantrefs of Perfeddwlad and was recognised in his title of Prince of Wales. Armed conflicts nevertheless continued, in particular with certain dissatisfied Marcher Lords, such as the earl of Gloucester, Roger Mortimer and Humphrey de Bohun, Earl of Hereford. Problems were exacerbated when Llywelyn's younger brother Dafydd and Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn of Powys, after failing in an assassination attempt against Llywelyn, defected to the English in 1274. Citing ongoing hostilities and the English king's harbouring of his enemies, Llywelyn refused to do homage to Edward. For Edward, a further provocation came in the form of Llywelyn's planned marriage to Eleanor, daughter of Simon de Montfort. In November 1276, war was declared. Initial operations were launched under the captaincy of Mortimer, Lancaster (Edward's brother Edmund) and William de Beauchamp, Earl of Warwick. Support for Llywelyn was weak among his own countrymen. In July 1277 Edward invaded with a force of 15,500 — of whom 9,000 were Welshmen. The campaign never came to a major battle, and Llywelyn soon realised he had no choice but to surrender. By the Treaty of Aberconwy in November 1277, he was left only with the land of Gwynedd, though he was allowed to retain the title of Prince of Wales. When
war broke out again in 1282, it was an entirely different undertaking.
For the Welsh, this war was over national identity, enjoying wide
support, provoked particularly by attempts to impose English law on Welsh subjects. For Edward, it became a war of conquest rather than simply a punitive expedition, like the former campaign. The war started with a rebellion by Dafydd, who was discontented with the reward he had received from Edward in 1277. Llywelyn
and other Welsh chieftains soon joined in, and initially the Welsh
experienced military success. In June, Gloucester was defeated at the Battle of Llandeilo Fawr. On 6 November, while John Peckham, archbishop of Canterbury, was conducting peace negotiations, Edward's commander of Anglesey, Luke de Tany, decided to carry out a surprise attack. A pontoon bridge had
been built to the mainland, but shortly after Tany and his men crossed
over, they were ambushed by the Welsh and suffered heavy losses at the Battle of Moel-y-don. The Welsh advances ended on 11 December, however, when Llywelyn was lured into a trap and killed at the Battle of Orewin Bridge. The submission of Wales was complete with the capture in June 1283 of Dafydd, who was taken to Shrewsbury and executed as a traitor the following autumn.
Further rebellions occurred in 1287–8 and, more seriously, in 1294 — with five under Madog ap Llywelyn,
a distant relative of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd. This last conflict demanded
the king's own attention, but in both cases the rebellions were put
down. By the 1284 Statute of Rhuddlan, the Principality of Wales was incorporated into England, and Wales was given an administrative system like the English, with counties policed by sheriffs. English
law was introduced in criminal cases, though the Welsh were allowed to
maintain their own customary laws in some cases of property disputes. After
1277, and increasingly after 1283, Edward embarked on a full-scale
project of English settlement of Wales, creating new towns like Flint, Aberystwyth, and Rhuddlan. An extensive project of castle building was also initiated. The assignment was given to Master James of Saint George, a prestigious architect whom Edward had met in Savoy on his return from the crusade. Among the major buildings were the castles of Beaumaris, Caernarfon, Conwy and Harlech. His programme of castle building in Wales heralded the introduction of the widespread use of arrowslits in castle walls across Europe, drawing on Eastern influences. Also a product of the Crusades was the introduction of the concentric castle, and four of the eight castles Edward founded in Wales followed this design. In 1284, King Edward's son Edward — the later Edward II —
was born at Caernarfon Castle, and it was also here, in 1301, that the
young Edward was the first English prince to be invested with the title
of Prince of Wales.
Edward
never again went on crusade after his return to England in 1274, but he
maintained an intention to do so, and took the cross again in 1287. This
intention guided much of his foreign policy, until at least 1291. To
stage a European wide crusade, it was essential to prevent conflict
between the greater princes on the continent. A major obstacle to this
was represented by the conflict between the French House of Anjou ruling southern Italy, and the kingdom of Aragon in Spain. In 1282, the citizens of Palermo rose up against Charles of Anjou and turned for help to Peter of Aragon, in what has become known as the Sicilian Vespers. In the war that followed, Charles of Anjou's son, Charles of Salerno, was taken prisoner by the Aragonese. The
French began planning an attack on Aragon, raising the prospect of a
large scale European war. To Edward, it was imperative that such a war
be avoided, and in Paris in 1286 he brokered a truce between France and
Aragon that helped secure Charles' release. As
far as the crusades were concerned, however, Edward's efforts proved
ineffective. A devastating blow to his plans came in 1291, when the
Mamluks captured Acre, the last Christian stronghold in the Holy Land. After
the fall of Acre, Edward's international role changed from that of a
diplomat to an antagonist. He had long been deeply involved in the
affairs of his own Duchy of Gascony. In 1278 he assigned an investigating commission to his trusted associates Otto de Grandson and the chancellor Robert Burnell, which caused the replacement of the seneschal Luke de Tany. In 1286, Edward visited the region himself and stayed for almost three years. The
perennial problem, however, was the status of Gascony within the
kingdom of France, and Edward's role as the French king's vassal. On
his diplomatic mission in 1286, Edward had paid homage to the new king, Philip IV,
but in 1294 Philip declared Gascony forfeit when Edward refused to
appear before him in Paris to discuss the recent conflict between
English, Gascon, and French sailors (that had resulted in several
French ships being captured, along with the sacking of the French port
of La Rochelle). In
the war that followed, Edward planned for a two-pronged attack. While
the English forces focused on Gascony, alliances were made with the
princes of the Low Countries, Germany, and Burgundy, who would attack France from the north. The
alliances proved volatile, however, and Edward was facing trouble at
home at the time, both in Wales and Scotland. It was not until August
1297 that he was finally able to sail for Flanders, at which times his
allies there had already suffered defeat. The support from Germany never materialised, and Edward was forced to seek peace. His marriage to the French princess Margaret in 1299 put an end to the war, but the whole affair had proven both costly and fruitless for the English.
The relationship between the nations of England and Scotland by the 1280s was one of relatively harmonious coexistence. The issue of homage did not reach the same level of controversy as it did in Wales; in 1278 King Alexander III of Scotland paid homage to Edward I, but apparently only for the lands he held of Edward in England. Problems
arose only with the Scottish succession crisis of the early 1290s. In
the years from 1281 to 1284, Alexander's two sons and one daughter died
in quick succession. Then, in 1286, King Alexander died himself,
leaving as heir to the throne of Scotland the three year old Margaret, the Maid of Norway, who was born in 1283 to Alexander's daughter Margaret and King Eric II of Norway. By the Treaty of Birgham, it was agreed that Margaret should marry King Edward's then one year old son Edward of Carnarvon, though Scotland would remain free of English overlordship. Margaret, by now seven years of age, sailed from Norway for Scotland in the autumn of 1290, but fell ill on the way and died in Orkney. This left the country without an obvious heir, and led to the succession dispute known to history as the Great Cause. Even though as many as fourteen claimants put forward their claims to the title, the real contest was between John Balliol and Robert Bruce. The Scottish magnates made a request to Edward to arbitrate in the dispute. At
Birgham, with the prospect of a personal union between the two realms,
the question of suzerainty had not been of great importance to Edward.
Now he insisted that, if he were to settle the contest, he had to be
fully recognised as Scotland's feudal overlord. The
Scots were reluctant to make such a concession, and replied that since
the country had no king, no one had the authority to make this decision. This
problem was circumvented when the competitors agreed that the realm
would be handed over to Edward until a rightful heir had been found. After a lengthy hearing, a decision was made in favour of John Balliol on 17 November 1292. Even
after Balliol's accession, Edward still continued to assert his
authority over Scotland. Against the objections of the Scots, he agreed
to hear appeals on cases ruled on by the court of guardians that had
governed Scotland during the interregnum. A further provocation came in a case brought by Macduff, son of Malcolm, Earl of Fife, in which Edward demanded that Balliol appear in person before the English Parliament to answer the charges. This
the Scottish king did, but the final straw was Edward's demand that the
Scottish magnates provide military service in the war against France. This was unacceptable; the Scots instead formed an alliance with France and launched an unsuccessful attack on Carlisle. Edward responded by invading Scotland in 1296 and taking the town of Berwick in a particularly bloody attack. At the Battle of Dunbar, Scottish resistance was effectively crushed. Edward confiscated the Stone of Destiny – the Scottish coronation stone – and brought it to Westminster, deposed Balliol and placed him in the Tower of London, and installed Englishmen to govern the country. The campaign had been a great success, but the English triumph would only be temporary.
Edward I's frequent military campaigns put a great financial strain on the nation. There were several ways through which the king could raise money for war, including customs duties, money lending and lay subsidies.
In 1275, Edward I negotiated an agreement with the domestic
merchant community that secured a permanent duty on wool. In 1303, a
similar agreement was reached with foreign merchants, in return for
certain rights and privileges. The revenues from the customs duty were handled by the Riccardi, a group of bankers from Lucca in Italy. This
was in return for their service as money lenders to the crown, which
helped finance the Welsh Wars. When the war with France broke out, the
French king confiscated the Riccardi's assets, and the bank went
bankrupt. After this, the Frescobaldi of Florence took over the role as money lenders to the English crown. Another source of crown income was represented by England's Jews. The Jews were the king's personal property, and he was free to tax them at will. By
1280, the Jews had been exploited to a level at which they were no
longer of much financial use to the crown, but they could still be used
in political bargaining. Their usury business –
a practice forbidden to Christians – had made many people indebted
to them and caused general popular resentment. In 1275, Edward had issued the Statute of the Jewry, which outlawed usury and encouraged the Jews to take up other professions; in 1279, in the context of a crack-down on coin-clippers, he arrested all the heads of Jewish households in England and had around 300 of them executed. In
1280, he ordered all Jews to attend special sermons, preached by
Dominican friars, with the hope of persuading them to convert, but
these exhortations were not followed. The final attack on the Jews in England came in the form of the Edict of Expulsion in 1290, whereby Edward formally expelled all Jews from England. This
not only generated revenues through royal appropriation of Jewish loans
and property, but it also gave Edward the political capital to
negotiate a substantial lay subsidy in the 1290 Parliament. The expulsion, which was not reversed until 1656, followed a precedent set by other European territorial princes: Philip II of France had expelled all Jews from his own lands in 1182; John I, Duke of Brittany, drove them out of his duchy in 1239; and in the late 1240s Louis IX of France had expelled the Jews from the royal demesne before his first passage to the East. Among the main achievements of the reign of Edward I were the reforms of the institution of the English Parliament and its transformation into a source for generating revenues. Edward held Parliament at a more or less regular basis throughout his reign. In 1295, however, a significant change occurred. For this Parliament, in
addition to the secular and ecclesiastical lords, two knights from each
county and two representatives from each borough were summoned. The
representation of commons in Parliament was nothing new; what was new
was the authority under which these representatives were summoned.
Whereas previously the commons had been expected simply to assent to
decisions already made by the magnates, it was now proclaimed that they
should meet with the full authority (plena potestas) of their communities, to give assent to decisions made in Parliament. The
king now had full backing for collecting lay subsidies from the entire
population. Lay subsidies were taxes collected at a certain fraction of
the moveable property of all laymen. Whereas Henry III had only collected four of these in his reign, Edward I collected nine. This format eventually became the standard for later Parliaments, and historians have named the assembly the "Model Parliament".
The
incessant warfare of the 1290s put a great financial demand on Edward's
subjects. Whereas the king had only levied three lay subsidies up until
1294, four such taxes were granted in the years 1294–97, raising over
£200,000. In addition to this came the burden of prises (appropriation of food), seizure of wool and hides, and the unpopular additional duty on wool, dubbed the maltolt. The
fiscal demands on the king's subjects caused resentment, and this
resentment eventually led to serious political opposition. The initial
resistance was not caused by the lay taxes, however, but by clerical
subsidies. In 1294, Edward made a demand of a grant of one half of all
clerical revenues. There was some resistance, but the king responded by
threatening without lawry, and the grant was eventually made. At the time, the archbishopric of Canterbury was vacant, since Robert Winchelsey was in Italy to receive consecration. Winchelsey
returned in January 1295 and had to consent to another grant in
November of that year. In 1296, however, his position changed when he
received the papal bull Clericis laicos. This bull prohibited the clergy from paying taxes to lay authorities without explicit consent from the Pope. When the clergy, with reference to the bull, refused to pay, Edward responded with outlawry. Winchelsey
was presented with a dilemma between loyalty to the king and upholding
the papal bull, and he responded by leaving it to every individual
clergyman to pay as he saw fit. By the end of the year, a solution was offered by the new papal bull Etsi de statu, which allowed clerical taxation in cases of pressing urgency. Opposition
from the laity took longer to surface. This resistance focused on two
things: the king's right to demand military service, and his right to
levy taxes. At the Salisbury parliament of February 1297, Roger Bigod, Earl of Norfolk, in his capacity as Marshal of England,
objected to a royal summons of military service. Bigod argued that the
military obligation only extended to service alongside the king; if the
king intended to sail to Flanders, he could not send his subjects to
Gascony. In July, Bigod and Humphrey de Bohun, Earl of Hereford and Constable of England, drew up a series of complaints known as the Remonstrances, in which objections to the extortionate level of taxation were voiced. Undeterred,
Edward requested another lay subsidy. This one was particularly
provocative, because the king had sought consent only from a small
group of magnates, rather than from representatives from the
communities in parliament. While Edward was in Winchelsea, preparing for the campaign in Flanders, Bigod and Bohun turned up at the Exchequer to prevent the collection of the tax. As the king left the country with a greatly reduced force, the kingdom seemed to be on the verge of civil war. What resolved the situation was the English defeat by the Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge. The renewed threat to the homeland gave king and magnates common cause. Edward signed the Confirmatio cartarum – a confirmation of Magna Carta and its accompanying Charter of the Forest – and the nobility agreed to serve with the king on a campaign in Scotland. Edward's
problems with the opposition did not end with the Falkirk campaign.
Over the following years he would be held up to the promises he had
made, in particular that of upholding the Charter of the Forest. In the parliament of 1301, the king was forced to order an assessment of the royal forests, but in 1305 he obtained a papal bull that freed him from this concession. Ultimately,
it was a failure in personnel that spelt the end of the opposition
against Edward I. Bohun died late in 1298, after returning from
the Falkirk campaign. As
for Bigod, in 1302 he arrived at an agreement with the king that was
beneficial for both: Bigod, who had no children, made Edward his heir,
in return for a generous annual grant. Edward finally got his revenge on Winchelsey in 1305, when Clement V was
elected pope. Clement was a Gascon sympathetic to the king, and on
Edward's instigation had Winchelsey suspended from office. The
situation in Scotland had seemed resolved when Edward left the country
in 1296, but resistance soon emerged under the leadership of the
strategically gifted and charismatic William Wallace. On 11 September 1297, a large English force under the leadership of John de Warenne, Earl of Surrey, and Hugh de Cressingham was routed by a much smaller Scottish army led by Wallace and Andrew Moray at Stirling Bridge. The
defeat sent shockwaves into England, and preparations for a retaliatory
campaign started immediately. Soon after Edward returned from Flanders,
he headed north. On 22 July 1298, in the only major battle he had fought since Evesham in 1265, Edward defeated Wallace's forces at the Battle of Falkirk. Edward, however, was not able to take advantage of the momentum, and the next year the Scots managed to recapture Stirling Castle. Even
though Edward campaigned in Scotland both in 1300 and 1301, the Scots
refused to engage in open battle again, preferring instead to raid the
English countryside in smaller groups. The
English managed to subdue the country by other means, however. In 1303,
a peace agreement was reached between England and France, effectively
breaking up the Franco-Scottish alliance. Robert the Bruce, the grandson of the claimant to the crown in 1291, had sided with the English in the winter of 1301–02. By
1304, most of the other nobles of the country had also pledged their
allegiance to Edward, and this year the English also managed to re-take
Stirling Castle. A great propaganda victory was achieved in 1305 when Wallace was betrayed by Sir John de Menteith and turned over to the English, who had him taken to London where he was publicly executed. With Scotland largely under English control, Edward installed Englishmen and collaborating Scots to govern the country. The situation changed again on 10 February 1306, when Robert the Bruce murdered his rival John Comyn and a few weeks later, on 25 March, had himself crowned king of Scotland. Bruce now embarked on a campaign to restore Scottish independence, and this campaign took the English by surprise. Edward
was suffering ill health by this time, and instead of leading an
expedition himself, he gave different military commands to Aymer de Valence and Henry Percy, while the main royal army would be led by the Prince of Wales. The English initially met with success; on 19 June, Aymer de Valence routed Bruce at the Battle of Methven. Bruce was forced into hiding, while the English forces recaptured their lost territory and castles. Edward
responded with severe brutality against Bruce's allies; it was clear
that he now regarded the struggle not as a war between two nations, but
as the suppression of a rebellion of disloyal subjects. This brutality, though, rather than helping to subdue the Scots, had the opposite effect, and rallied growing support for Bruce. In February Bruce reappeared and started gathering men, and in May he defeated Aymer de Valence at the Battle of Loudoun Hill. Edward,
who had rallied somewhat, now moved north himself. On the way, however,
he developed dysentery, and his condition deteriorated. On 6 July
he encamped at Burgh by Sands,
just south of the Scottish border. When his servants came the next
morning to lift him up so that he could eat, he died in their arms. Various
stories emerged about Edward’s deathbed wishes; according to one
tradition, he requested that his heart be carried to the Holy Land,
along with an army to fight the infidels. A more dubious story tells of
how he wished for his bones be carried along on future expeditions
against the Scots. Another account of his deathbed scene is more
credible; according to one chronicle, Edward gathered around him the
earls of Lincoln and Warwick, Aymer de Valence, and Robert Clifford, and charged them with looking after his son Edward. In particular they should make sure that Piers Gaveston was not allowed to return to the country. This wish, however, the son ignored, and had his favourite recalled from exile almost immediately. Edward I's
body was brought south, and after a lengthy vigil he was buried in
Westminster Abbey on 27 October. The new king, Edward II,
remained in the north until August, but then abandoned the campaign and
headed south. He was crowned king on 25 February 1308.
Upon
returning home, Edward immediately embarked on the administrative
business of the nation, and his major concern was restoring order and
re-establishing royal authority after the disastrous reign of his
father. In
order to accomplish this, he immediately ordered an extensive change of
administrative personnel. The most important of these was the
appointment of Robert Burnell as chancellor, a man who would remain in the post until 1292 as one of the king's closest associates. Edward then proceeded to replace most local officials, such as the escheators and sheriffs. This last measure was done in preparation for an extensive inquest covering all of England, that would hear complaints about abuse of power by royal officers. The inquest produced the set of so-called Hundred Rolls, from the administrative subdivision of the hundred. The second purpose of the inquest was to establish what land and rights the crown had lost during the reign of Henry III.

