<Back to Index>
- Inventors Joseph Michel and Jacques Étienne Montgolfier, 1740 and 1745
- Engraver Paul Gustave Doré, 1832
- French Military Heroine Jeanne d'Arc, 1412
PAGE SPONSOR



Saint Joan of Arc or The Maid of Orléans (French: Jeanne d'Arc; ca. 1412 – 30 May 1431) is considered a national heroine of France and a Catholic saint. A peasant girl born in eastern France who claimed Divine guidance, she led the French army to several important victories during the Hundred Years' War which paved the way for the coronation of Charles VII. She was captured by the Burgundians, sold to the English, tried by an ecclesiastical court, and burned at the stake when she was nineteen years old. Twenty-five years after the execution, Pope Callixtus III examined the trial, pronounced her innocent and declared her a martyr. She was beatified in 1909 and canonized in 1920. She is, along with St. Denis, St. Martin of Tours, St. Louis IX, and St. Theresa of Lisieux, one of the patron saints of France.
Joan asserted that she had visions from God which instructed her to recover her homeland from English domination late in the Hundred Years' War. The uncrowned King Charles VII sent her to the siege of Orléans as
part of a relief mission. She gained prominence when she overcame the
dismissive attitude of veteran commanders and lifted the siege in only
nine days. Several more swift victories led to Charles VII's coronation
at Reims and settled the disputed succession to the throne. Down to the present day, Joan of Arc has remained a significant figure in Western culture. From Napoleon onward,
French politicians of all leanings have invoked her memory. Famous
writers and composers who have created works about her include: Shakespeare (Henry VI, Part 1), Voltaire (La Pucelle d'Orléans), Schiller (Die Jungfrau von Orléans), Verdi (Giovanna d'Arco), Tchaikovsky (Орлеанская дева), Mark Twain (Personal Recollections of Joan of Arc), Jean Anouilh (L'Alouette), Bertolt Brecht (Die heilige Johanna der Schlachthöfe), George Bernard Shaw (Saint Joan), and Maxwell Anderson (Joan of Lorraine). Depictions of her continue in film, theater, television, video games, music, and performance.
The historian Kelly DeVries describes
the period preceding her appearance in the following terms: "If
anything could have discouraged her, the state of France in 1429 should
have." The Hundred Years' War had begun in 1337 as a succession dispute over the French throne with intermittent periods of relative peace. Nearly all the fighting had taken place in France, and the English army's use of chevauchée tactics (similar to scorched earth strategies) had devastated the economy. The French population had not recovered from the Black Death of
the previous century and its merchants were isolated from foreign
markets. At the outset of her appearance, the English had nearly
achieved their goal of a dual monarchy under English control and the
French army had not achieved any major victories for a generation. In
DeVries's words, "the kingdom of France was not even a shadow of its
thirteenth century prototype." The French king at the time of Joan's birth, Charles VI, suffered bouts of insanity and was often unable to rule. The king's brother Duke Louis of Orléans and the king's cousin John the Fearless, Duke of Burgundy,
quarreled over the regency of France and the guardianship of the royal
children. This dispute escalated to accusations of an extramarital
affair with Queen Isabeau of Bavaria and the kidnappings of the royal children. The matter climaxed with the assassination of the Duke of Orléans in 1407, on the Duke of Burgundy's orders. The factions which were loyal to these two men became known as the Armagnacs and the Burgundians. The English king Henry V took advantage of this turmoil to invade France, winning a dramatic victory at Agincourt in 1415, and capturing many northern French towns. The future French king, Charles VII, assumed the title of Dauphin – the heir to the throne – at the age of fourteen, after all four of his older brothers died in succession. His
first significant official act was to conclude a peace treaty with
Burgundy in 1419. This ended in disaster when Armagnac partisans
assassinated John the Fearless during a meeting under Charles's guarantee of protection. The new duke of Burgundy, Philip the Good, blamed Charles for the murder and entered into an alliance with the English. Large sections of France were conquered. In 1420, Queen Isabeau of Bavaria concluded the Treaty of Troyes,
which granted the succession of the French throne to Henry V and his
heirs instead of her son Charles. This agreement revived rumors about
her alleged affair with the late duke of Orléans and raised
fresh suspicions that the Dauphin was illegitimate rather than the son
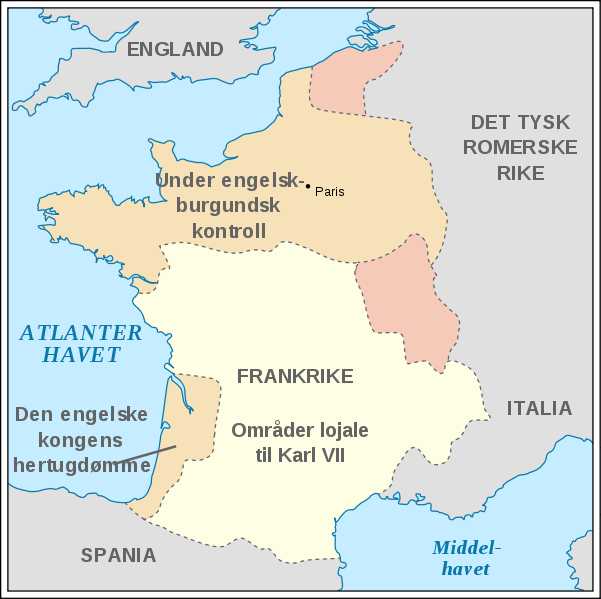
of the king. Henry V and Charles VI died within two months of each other in 1422, leaving an infant, Henry VI of England, the nominal monarch of both kingdoms. Henry V's brother, John of Lancaster, 1st Duke of Bedford, acted as regent. By
the beginning of 1429, nearly all of northern France and some parts of
the southwest were under foreign control. The English controlled Paris
while the Burgundians controlled Reims, the latter city being the
traditional site of French coronations. This was an important
consideration since neither claimant to the throne of France had yet
been officially crowned. The English had laid siege to Orléans,
one of the few remaining loyal French cities and a strategic position
along the Loire River
which made it the last obstacle to an assault on the remainder of the
French heartland. In the words of one modern historian, "On the fate of
Orléans hung that of the entire kingdom." No one was optimistic that the city could long withstand the siege. Joan was the daughter of Jacques d'Arc and Isabelle Romée in Domrémy, a village which was then in the duchy of Bar (later annexed to the province of Lorraine and renamed Domrémy-la-Pucelle). Her
parents owned about 50 acres (20 hectares) of land and her father
supplemented his farming work with a minor position as a village
official, collecting taxes and heading the local watch. They lived in an isolated patch of north-eastern territory that remained
loyal to the French crown despite being surrounded by Burgundian lands.
Several local raids occurred during her childhood and on one occasion
her village was burned. Joan
said she was about nineteen at her trial, so she must have been born
around the year 1412. She later testified that she experienced her
first vision around 1424 at the age of twelve years, when she was out
alone in a field and saw visions of figures she identified as Saint Michael, Saint Catherine, and Saint Margaret,
who told her to drive out the English and bring the Dauphin to Reims
for his coronation. She said she cried when they left, as they were so
beautiful. At the age of sixteen, she asked a kinsman, Durand Lassois, to bring her to nearby Vaucouleurs where she petitioned the garrison commander, Count Robert de Baudricourt, for permission to visit the royal French court at Chinon. Baudricourt's sarcastic response did not deter her. She returned the following January and gained support from two men of standing: Jean de Metz and Bertrand de Poulengy. Under their auspices, she gained a second meeting where she made a remarkable prediction about a military reversal near Orléans. Robert
de Baudricourt granted her an escort to visit Chinon after news from
the front confirmed her prediction. She made the journey through
hostile Burgundian territory in male disguise. Upon arriving at the Royal Court she impressed Charles VII during a private conference. During this time Charles's mother-in-law Yolande of Aragon was financing a relief expedition to Orléans.
Joan asked for permission to travel with the army and wear the
equipment of a knight. She depended on donated items for her armor,
horse, sword, banner, and other items utilized by her entourage.
Historian Stephen W. Richey explains her attraction to the Royal Court
by pointing out that they may have viewed her as the only source of
hope for a regime that was near collapse: After
years of one humiliating defeat after another, both the military and
civil leadership of France were demoralized and discredited. When the
Dauphin Charles granted Joan’s urgent request to be equipped for war
and placed at the head of his army, his decision must have been based
in large part on the knowledge that every orthodox, every rational,
option had been tried and had failed. Only a regime in the final
straits of desperation would pay any heed to an illiterate farm girl
who claimed that the voice of God was instructing her to take charge of
her country’s army and lead it to victory. Upon her arrival, Joan effectively turned the long standing Anglo-French conflict into a religious war. But
this course of action was not without its risks. Charles' advisers were
worried that unless Joan's orthodoxy could be established beyond doubt
— that she was not a heretic or a sorceress — Charles' enemies could
easily make the claim that his kingdom was a gift from the Devil. To
circumvent this possibility, the Dauphin ordered background inquiries
and a theological examination at Poitiers to
verify her morality. In April 1429, the commission of inquiry "declared
her to be of irreproachable life, a good Christian, possessed of the
virtues of humility, honesty and simplicity." The
theologians at Poitiers did not pass judgment on her divine
inspiration; rather, they informed the Dauphin that there was a
'favorable presumption' to be made on the divine nature of her mission.
This was enough for Charles, but they put the ball back in his court by
stating that he had an obligation to put Joan to the test. 'To doubt or
abandon her without suspicion of evil would be to repudiate the Holy
Spirit and to become unworthy of God's aid', they declared. The test for the truth of her claims would be the raising of the siege of Orléans. She arrived at the siege of Orléans on 29 April 1429, but Jean d'Orléans,
the acting head of the Orléans ducal family, initially excluded
her from war councils and failed to inform her when the army engaged
the enemy. This
did not prevent her from being present at most councils and battles.
The extent of her actual military leadership is a subject of historical
debate. Traditional historians such as Édouard Perroy conclude
that she was a standard bearer whose primary effect was on morale. This
type of analysis usually relies on the condemnation trial testimony,
where she stated that she preferred her standard to her sword. Recent
scholarship that focuses on the nullification trial testimony asserts
that the army's commanders esteemed her as a skilled tactician and a
successful strategist. Stephen W. Richey's opinion is one example: "She proceeded to lead the army in an astounding series of victories that reversed the tide of the war." In either case, historians agree that the army enjoyed remarkable success during her brief career.
She
rejected the cautious strategy that had characterized French leadership
during previous campaigns. During the five months of siege before her
arrival, the defenders of Orléans had attempted only one
aggressive move and that had ended in disaster. On 4 May the French
attacked and captured the outlying fortress of Saint Loup, which she
followed on 5 May with a march to a second fortress called Saint Jean
le Blanc, which was found deserted. The next day she opposed Jean
d'Orleans at a war council where she demanded another assault on the
enemy. D'Orleans ordered the city gates locked to prevent another
battle, but she summoned the townsmen and common soldiers and forced
the mayor to unlock a gate. With the aid of only one captain she rode
out and captured the fortress of Saint Augustin. That evening she
learned she had been excluded from a war council where the leaders had
decided to wait for reinforcements before acting again. Disregarding
this decision, she insisted on attacking the main English stronghold
called "les Tourelles" on 7 May. Contemporaries
acknowledged her as the heroine of the engagement after she was wounded
in the neck by an arrow but returned to lead the final charge.
The
sudden victory at Orléans led to many proposals for further
offensive action. The English expected an attempt to recapture Paris or
an attack on Normandy. In the aftermath of the unexpected victory, she
persuaded Charles VII to grant her co-command of the army with Duke John II of Alençon and
gained royal permission for her plan to recapture nearby bridges along
the Loire as a prelude to an advance on Reims and the coronation of
Charles VII. This was a bold proposal because Reims was roughly twice
as far away as Paris and deep within enemy territory. The army recovered Jargeau on 12 June, Meung-sur-Loire on 15 June, and Beaugency on
17 June. The Duke of Alençon agreed to all of Joan's decisions.
Other commanders including Jean d'Orléans had been impressed
with her performance at Orléans and became her supporters.
Alençon credited her with saving his life at Jargeau, where she
warned him of an imminent artillery attack. During
the same battle she withstood a blow from a stone cannonball to her
helmet as she climbed a scaling ladder. An expected English relief
force arrived in the area on 18 June under the command of Sir John Fastolf. The battle at Patay might be compared to Agincourt in reverse. The French vanguard attacked before the English archers could
finish defensive preparations. A rout ensued that decimated the main
body of the English army and killed or captured most of its commanders.
Fastolf escaped with a small band of soldiers and became the scapegoat
for the English humiliation. The French suffered minimal losses. The
French army set out for Reims from Gien-sur-Loire on 29 June and
accepted the conditional surrender of the Burgundian held city of Auxerre on 3 July. The other towns in their path returned to French allegiance without resistance. Troyes, the site of the treaty that had tried to disinherit Charles VII, capitulated after a bloodless four-day siege. The army was in short supply of food by the time it reached Troyes. Edward Lucie-Smith cites
this as an example of her luck: a wandering friar named Brother Richard
had been preaching about the end of the world at Troyes and had
convinced local residents to plant beans, a crop with an early harvest.
The hungry army arrived as the beans ripened. Reims
opened its gates to the army on July 16. The coronation took place the
following morning. Although Joan and the duke of Alençon urged a
prompt march on Paris, the royal court preferred a negotiated truce
with the duke of Burgundy. Duke Philip the Good broke the agreement,
using it as a stalling tactic to reinforce the defense of Paris. The
French army marched through towns near Paris during the interim and
accepted more peaceful surrenders. The Duke of Bedford headed an
English force and confronted the French army in a standoff on 15
August. The French assault at Paris ensued on 8 September. Despite a
wound to the leg from a crossbow bolt, Joan continued directing the
troops until the day's fighting ended. The following morning she
received a royal order to withdraw. Most historians blame French grand
chamberlain Georges de la Trémoille for the political blunders which followed the coronation. In October Joan took Saint-Pierre-le-Moûtier and was granted nobility. After a minor action at La-Charité-sur-Loire in November and December, Joan traveled to Compiègne the following April to help defend the city against an English and Burgundian siege. A risky skirmish on 23 May 1430 led to her capture. When she ordered a
retreat, she assumed the place of honor as the last to leave the field.
Burgundians surrounded the rear guard. She was unhorsed by an archer
and initially refused to surrender. It was
The trial for heresy was
politically motivated. The Duke of Bedford claimed the throne of France
for his nephew Henry VI. She had been responsible for the rival
coronation so to condemn her was an attempt to undermine her king's
legitimacy. Legal proceedings commenced on 9 January 1431 at Rouen, the seat of the English occupation government. The procedure was irregular on a number of points. To summarize some major problems : the jurisdiction of judge Bishop Cauchon was a legal fiction. He
owed his appointment to his partisan support of the English government
which financed the trial. Clerical notary Nicolas Bailly, commissioned
to collect testimony against Joan, could find no adverse evidence. Without
such evidence the court lacked grounds to initiate a trial. Opening a
trial anyway, the court also violated ecclesiastical law in denying her
right to a legal adviser. Upon the opening of the first public examination Joan complained that those present were all partisans
against her and asked for "ecclesiastics of the French side" to be
invited.
The
trial record demonstrates her remarkable intellect. The transcript's
most famous exchange is an exercise in subtlety. "Asked if she knew she
was in God's grace, she answered: 'If I am not, may God put me there;
and if I am, may God so keep me.'" The
question is a scholarly trap. Church doctrine holds that no one can be
certain of being in God's grace. If she had answered yes, then she
would have convicted herself of heresy. If she had answered no, then
she would have confessed her own guilt. Notary Boisguillaume later
testified that at the moment the court heard this reply, "Those who
were interrogating her were stupefied." In the twentieth century George Bernard Shaw found this dialogue so compelling that sections of his play Saint Joan are literal translations of the trial record. Several
court functionaries later testified that significant portions of the
transcript were altered in her disfavor. Many clerics served under
compulsion, including the inquisitor, Jean LeMaitre, and a few even
received death threats from the English. Under Inquisitorial guidelines, Joan should have been confined to an ecclesiastical prison under the supervision of female guards (i.e., nuns). Instead, the English kept her in a secular prison guarded by their own soldiers. Bishop Cauchon denied Joan's appeals to the Council of Basel and the pope, which should have stopped his proceeding. The twelve articles of accusation that summarize the court's finding contradict the already doctored court record. The illiterate defendant signed an abjuration document
she did not understand under threat of immediate execution. The court
substituted a different abjuration in the official record. Heresy was
a capital crime only for a repeat offense. Joan agreed to wear feminine
clothing when she abjured. A few days later she told a tribunal member
that "a great English lord had entered her prison and tried to take her
by force.". She
resumed male attire either as a defense against molestation or, in the
testimony of Jean Massieu, because her dress had been stolen and she
was left with nothing else to wear. In
terms of doctrine, she had been safe to disguise herself as a page
during her journey through enemy territory and she was safe to wear
armor during battle. The Chronique de la Pucelle states
that it deterred molestation while she was camped in the field. Clergy
who later testified at the posthumous rehabilitation trial affirmed
that she continued to wear male clothing in prison to deter molestation
and rape. Preservation of chastity was
another justifiable reason for cross-dressing: her apparel would have
slowed an assailant, and men would be less likely to think of her as a
sex object in any case. She
referred the court to the Poitiers inquiry when questioned on the
matter. The Poitiers record no longer survives but circumstances
indicate the Poitiers clerics had approved her practice. In other
words, she had a mission to do a man's work so it was fitting that she
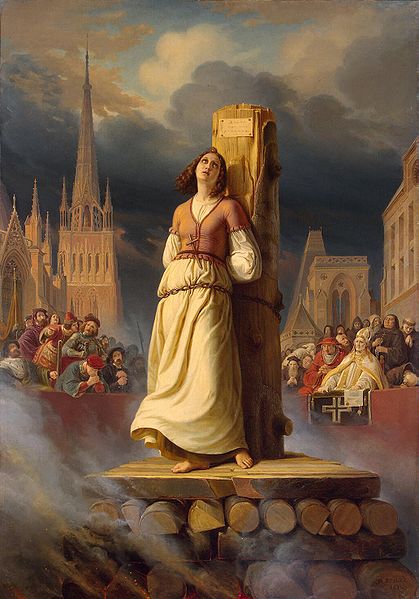
dress the part. She also kept her hair cut short through her military campaigns and while in prison. Her supporters, such as the theologian Jean Gerson, defended her hairstyle, as did Inquisitor Brehal later during the Rehabilitation trial. Nonetheless, at the trial in 1431 she was condemned and sentenced to die. Eyewitnesses described the scene of the execution by burning on
30 May 1431. Tied to a tall pillar in the Vieux-Marche in Rouen, she
asked two of the clergy, Fr Martin Ladvenu and Fr Isambart de la
Pierre, to hold a crucifix before
her. A peasant also constructed a small cross which she put in the
front of her dress. After she expired, the English raked back the coals
to expose her charred body so that no one could claim she had escaped
alive, then burned the body twice more to reduce it to ashes and
prevent any collection of relics. They cast her remains into the Seine. The executioner, Geoffroy Therage, later stated that he "...greatly feared to be damned." The
Hundred Years' War continued for twenty-two years after her death.
Charles VII succeeded in retaining legitimacy as the king of France in
spite of a rival coronation held for Henry VI in December 1431 on the
boy's tenth birthday. Before England could rebuild its military
leadership and force of longbowmen, lost in 1429, the country lost its
alliance with Burgundy at the Treaty of Arras in
1435. The Duke of Bedford died the same year and Henry VI became the
youngest king of England to rule without a regent; his weak leadership
was probably the most important factor in ending the conflict. Kelly
DeVries argues that Joan of Arc's aggressive use of artillery and
frontal assaults influenced French tactics for the rest of the war. In
1452, during the posthumous investigation into her execution, the
Church declared that a religious play in her honor at Orléans
would qualify as a pilgrimage meriting an indulgence. A posthumous retrial opened after the war ended. Pope Callixtus III authorized this proceeding, also known as the "nullification trial", at the request of Inquisitor General Jean Brehal and
Joan's mother Isabelle Romée. The aim of the trial was to
investigate whether the trial of condemnation and its verdict had been
handled justly and according to canon law. Investigations started with
an inquest by a priest, Guillaume Bouille. Brehal conducted an
investigation in 1452. A formal appeal followed in November 1455. The
appellate process involved clergy from throughout Europe and observed
standard court procedure. A panel of theologians analyzed testimony
from 115 witnesses. Brehal drew up his final summary in June 1456,
which describes Joan as a martyr and implicated the late Pierre Cauchon
with heresy for having convicted an innocent woman in pursuit of a secular vendetta. The technical reason for her execution had been a Biblical clothing law. The
nullification trial reversed the conviction in part because the
condemnation proceeding had failed to consider the doctrinal exceptions
to that stricture. The appellate court declared her innocent on 7 July
1456.
She became a symbol of the Catholic League during the 16th century. When Félix Dupanloup was
made bishop of Orléans in 1849, he pronounced a fervid panegyric
on Joan of Arc, which attracted attention in England as well as France
and he led the efforts which culminated in Joan of Arc's beatification
in 1909. Pope Benedict XV canonized Joan on 16 May 1920. As Saint Joan of Arc, she has become one of the most popular saints of the Roman Catholic Church.
Joan
of Arc became a semi-legendary figure for the next four centuries. The
main sources of information about her were chronicles. Five original
manuscripts of her condemnation trial surfaced in old archives during
the 19th century. Soon historians also located the complete records of
her rehabilitation trial, which contained sworn testimony from 115
witnesses, and the original French notes for the Latin condemnation
trial transcript. Various contemporary letters also emerged, three of
which carry the signature "Jehanne" in the unsteady hand of a person learning to write. This
unusual wealth of primary source material is one reason DeVries
declares, "No person of the Middle Ages, male or female, has been the
subject of more study". Joan
of Arc came from an obscure village and rose to prominence when she was
a teenager, and she did so as an uneducated peasant. The French and
English kings had justified the ongoing war through competing
interpretations of the thousand year old Salic law.
The conflict had been an inheritance feud between monarchs. She gave
meaning to appeals such as that of squire Jean de Metz when he asked,
"Must the king be driven from the kingdom; and are we to be English?" In
the words of Stephen Richey, "She turned what had been a dry dynastic
squabble that left the common people unmoved except for their own
suffering into a passionately popular war of national liberation." Richey also expresses the breadth of her subsequent appeal: Joan
of Arc was not a feminist. She operated within a religious tradition
that believed an exceptional person from any level of society might
receive a divine calling. She expelled women from the French army and
may have struck one stubborn camp follower with the flat of a sword. Nonetheless,
some of her most significant aid came from women. King Charles VII's
mother-in-law, Yolande of Aragon, confirmed Joan's virginity and
financed her departure to Orléans. Joan of Luxembourg, aunt to
the count of Luxembourg who held custody of her after Compiègne,
alleviated her conditions of captivity and may have delayed her sale to
the English. Finally, Anne of Burgundy, the duchess of Bedford and wife to the regent of England, declared Joan a virgin during pretrial inquiries. For
technical reasons this prevented the court from charging her with
witchcraft. Ultimately this provided part of the basis for her
vindication and sainthood. From Christine de Pizan to the present, women have looked to her as a positive example of a brave and active female. Joan of Arc has been a political symbol in France since the time of Napoleon. Liberals emphasised her humble origins. Early conservatives stressed her support of the monarchy. Later conservatives recalled her nationalism. During World War II, both the Vichy Regime and the French Resistance used
her image: Vichy propaganda remembered her campaign against the English
with posters that showed British warplanes bombing Rouen and the
ominous caption: "They Always Return to the Scene of Their Crimes." The resistance emphasised her fight against foreign occupation and her origins in the province of Lorraine, which had fallen under Nazi control. Three separate vessels of the French Navy have been named after her, including a helicopter carrier which was retired from active service on 7 June 2010. At present the controversial French far-right political party Front National holds
rallies at her statues, reproduces her likeness in party publications,
and uses a tricolor flame partly symbolic of her martyrdom as its
emblem. This party's opponents sometimes satirize its appropriation of
her image. The French civic holiday in her honour is the second Sunday of May. Traditionalist Catholics, in France and elsewhere, also use her as a symbol of inspiration, often comparing the 1988 excommunication of Archbishop Marcel Lefebvre (founder of the Society of St. Pius X and a dissident against the Vatican II reforms), to her excommunication. Philippe-Alexandre Le Brun de Charmettes is the first historian who wrote Joan of Arc's complete history in
1817, in an attempt to restore her family's reputation from Joan's
status as a relapsed heretic. His interest in Joan came at a time when
France was still struggling to define its new identity after the Revolution and the Napoleonic wars. The national ethos was
in search of non controversial heroes. A staunch supporter of King and
country, Joan of Arc was an acceptable symbol to the monarchists. As a
patriot and the daughter of commoners, she was seen as one prototype of
the low-born volunteers (the soldats de l'an II)
who had victoriously fought for revolutionary France in 1802 and as
such could be claimed by the Republicans. As a religious martyr, she
was also popular in the powerful Catholic community. De Charmette's Orleanide, today largely forgotten, was another attempt to magnify the national ethos as writers like Virgil (the Aeneid), or Camoens (the Lusiad) had done for Rome and Portugal.
customary for a captive's family to ransom a prisoner of war. Joan and her family were peasants who lacked the money. Many historians condemn King Charles VII for failing to intervene. She attempted several escapes, on one occasion jumping from her 70 foot (21 m) tower in Vermandois to the soft earth of a dry moat, after which she was moved to the Burgundian town of Arras. The English government eventually purchased her from Duke Philip of Burgundy. Bishop Pierre Cauchon of Beauvais, an English partisan, assumed a prominent role in these negotiations and her later trial.