<Back to Index>
- Jurist Alberico Gentili, 1552
- Painter Berthe Morisot, 1841
- General of the Roman Army Marcus Antonius, 83 B.C.
PAGE SPONSOR
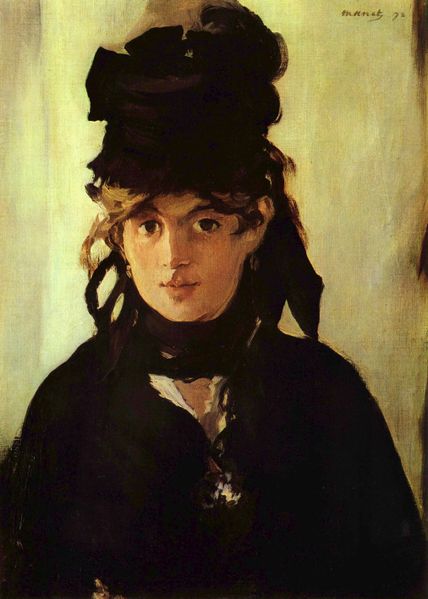


Berthe Morisot (January 14, 1841 – March 2, 1895) was a painter and a member of the circle of painters in Paris who became known as the Impressionists. Undervalued for over a century, possibly because she was a woman, she is now considered among the first league of Impressionist painters.
In 1864, she exhibited for the first time in the highly esteemed Salon de Paris. Sponsored by the government, and judged by academicians, the Salon was the official, annual exhibition of the Académie des beaux-arts in Paris. Her work was selected for exhibition in six subsequent Salons until, in 1874, she joined the "rejected" Impressionists in the first of their own exhibitions, which included Paul Cézanne, Edgar Degas, Claude Monet, Morisot, Camille Pissarro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley. It was held at the studio of the photographer Nadar. She became the sister-in-law of her friend and colleague, Édouard Manet, when she married his brother, Eugène. Morisot was born in Bourges, Cher, France into a successful bourgeois family. Both she and her sister, Edma Morisot,
chose to become painters. Once Berthe Morisot settled on pursuing art,
her family did not impede her career. She was born into a family that,
according to family tradition, had included one of the most prolific Rococo painters of the ancien régime, Fragonard, whose
handling of color and expressive, confident brushwork influenced later
painters. By age twenty, she had met and befriended the important, and
pivotal, landscape painter of the Barbizon School, Camille Corot, who excelled in figure painting as well. The
older artist instructed Berthe and her sister in painting and
introduced them to other artists and teachers. Under Corot's influence,
Morisot took up the plein air method
of working. As art students, Berthe and Edma worked closely together
until Edma married, had children, and no longer had time to paint so
intensely as Berthe. Letters between them show a loving and cordial
relationship, underscored by Berthe's regret at the distance between
them and about Edma's withdrawal from painting. Edma wholeheartedly
supported Berthe's continued work and the families of the two sisters
always remained close.
Morisot's first appearance in the Salon de Paris came at the age of twenty-three in 1864, with the acceptance of two landscape paintings. She continued to show regularly in the Salon, to generally favorable
reviews, until 1873, the year before the first Impressionist exhibition. Meanwhile, in 1868 Morisot became acquainted with Édouard Manet.
He took a special interest in Morisot, as is evident from his warm
portrayal of her in several paintings, including a striking portrait
study of Morisot in a black veil, while in mourning for her father's
death. Correspondence between
them bespeaks affection. He once gave her an easel as a Christmas present.
He also interfered in one of her Salon submissions when he was engaged
to transport it. Manet mistook one of Morisot's self-criticisms as an
invitation to add his corrections, which he did, much to Morisot's
dismay. Although
traditionally Manet has been related as the master and Morisot as the
follower, there is evidence that their relationship was a reciprocating
one. Morisot
had developed her own distinctive artistic style. Records of paintings
show Manet's approval and appreciation of certain stylistic and
compositional decisions that Morisot originated. He incorporated some
of these characteristics into his own work. It was Morisot who convinced Manet to attempt plein air painting, which she had been practicing since having been introduced to it by Corot. She
also drew Manet into the circle of painters who soon became known as
the Impressionists. In 1874, Morisot married Manet's brother, Eugene,
and they had one daughter, Julie. Julie Manet became the subject for many of her mother's paintings and a book of her memoirs Growing Up with the Impressionists: The Diary of Julie Manet, was published in 1987. As a doctrinaire Impressionist as well as a member of the haute bourgeoisie,
Morisot painted what she experienced on a daily basis. Her paintings
reflect the 19th century cultural restrictions of her class and gender.
She avoided urban and street scenes as well as the nude figure and,
like her fellow female Impressionist Mary Cassatt, focused on domestic
life and portraits in which she could use family and personal friends
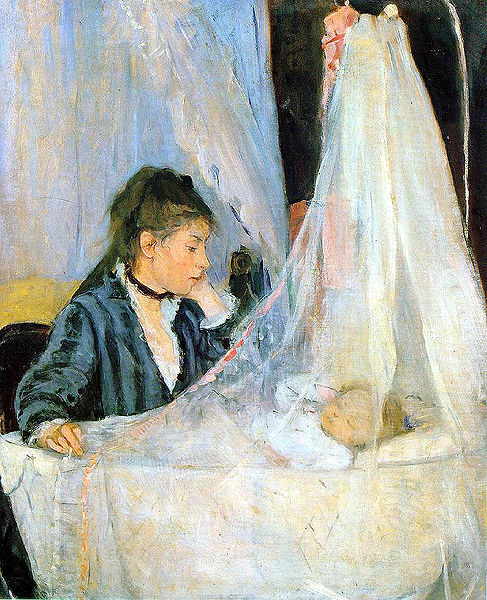
as models. Paintings like The Cradle (1872),
in which she depicted current trends for nursery furniture, reflect her
sensitivity to fashion and advertising, both of which would have been
apparent to her female audience. Her
works include not only landscapes, portraits, garden settings and
boating scenes, but also subjects portraying the comfort and intimacy
of family and domestic life, as did her colleagues, Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Mary Cassatt. Berthe Morisot died of pneumonia contracted while attending to her daughter Julie's similar illness on March 2, 1895 in Paris and was interred in the Cimetière de Passy.