<Back to Index>
- Mathematician Renato Caccioppoli, 1904
- Writer Johannes Vilhelm Jensen, 1873
- 2nd Prime Minister of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland Raphael "Roy" Welensky, 1907
PAGE SPONSOR

Sir Raphael "Roy" Welensky, KCMG (20 January 1907 – 5 December 1991) was a Northern Rhodesian politician and the second and last prime minister of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland.
Born in Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia (now Harare, Zimbabwe) to parents of Jewish and Afrikaner ancestry,
he moved to Northern Rhodesia, became involved with the trade unions,
and entered the colonial legislative council in 1938. There, he
campaigned for the amalgamation of Northern and Southern Rhodesia (the
latter under white self-government, the former under the colonial
office). Although unsuccessful, he succeeded in the formation of the
Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, a state within the British Empire that sought to retain predominant power for the white minority while moving in a progressive political direction, in contrast to apartheid South Africa. Becoming
Prime Minister of the Federation in 1957, Welensky opposed British
moves towards native African rule, and used force to suppress
politically motivated violence in the territories. After the advent of
African rule in two of the Federation's three territories (Northern
Rhodesia and Nyasaland, now Zambia and Malawi respectively),
it collapsed in 1963. Welensky retired to Salisbury, where he
re-entered politics and attempted to stop Rhodesia (formerly Southern
Rhodesia) from unilaterally declaring itself independent. With the end of white rule in 1979, and the independence of Rhodesia as Zimbabwe under Robert Mugabe in
1980, Welensky moved to England, where he died in 1991. A fervent
admirer of Britain and the Empire, Welensky described himself as "half
Jewish, half Afrikaner [and] 100% British". Welensky was born in Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia. His father was Jewish, hailing from a village near Vilna in then Russian ruled Lithuania,
who settled in Southern Rhodesia after first emigrating to the United
States and then South Africa, while his mother was a ninth generation Afrikaner who was of Dutch ethnicity. Welensky's mother died when he was 11, being treated by Godfrey Huggins, a doctor who was later to become the Prime Minister of Southern Rhodesia. Although
not of British ancestry, Welensky was intensely pro-British, a
distinctive sentiment among Rhodesians. John Connell, in his foreword
to Welensky's book 4000 Days,
states, "Welensky, who had not a drop of British blood in his veins,
shared this pride and loyalty [towards Britain] to the full." After leaving school at the age of 14, Welensky found employment with Rhodesia Railways as a fireman, while putting his physical strength to work as a boxer. He rose through the ranks of Rhodesia Railways to become a railroad engineer and became involved in the trade union movement, becoming leader of the powerful European Railway Workers Union. While
working on the railways, he became the professional heavyweight boxing
champion of Rhodesia at 19 and held the position until he was 21.
During this time, Welensky met his first wife, Elizabeth Henderson, who
was working at a cafe in Bulawayo, Southern Rhodesia at the time. They married after a two-year courtship.
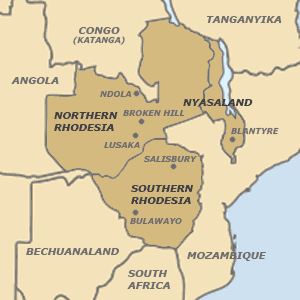
Welensky settled in Broken Hill,
Northern Rhodesia, and was elected to the Northern Rhodesian Legislative
Council in 1938. The Governor prevented Welensky from enlisting in the
armed forces in World War II and appointed him Director of Manpower. In 1941 he formed his own party, the Northern Rhodesian Labour Party, with the aim of amalgamating the colony with Southern Rhodesia under a new constitution. The
party won all five seats it contested in its first election. After the
leader of the unofficial members in the Legislative Council, Stewart Gore-Browne,
resigned in 1945 and stated that Africans had lost confidence in the
white settlers (due to the wish for amalgamation), Welensky was elected
leader.
From the beginning, Welensky was involved in the creation of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland.
He had earlier wanted an amalgamation of Northern and Southern Rhodesia
with a constitution similar to that of Southern Rhodesia (that had
granted responsible government to the settlers). After the British
Government rejected this idea, he set about the creation of a
federation, and against his judgement, the small colony of Nyasaland was
included. His main wish for amalgamation, and later federation, was
primarily so the complimentary economic strengths of the Rhodesias
could be put to best use. He felt that the colonies were missing out on
the post-war economic boom. To this end, Welensky organised a conference in February 1949 to investigate the idea of a federation. Held at the Victoria Falls Hotel
(a common venue for Rhodesian political conferences), representatives
from the Northern and Southern Rhodesian Governments were present, but
native Africans and the British Government were not. It was agreed that
continued pushes for amalgamation would fail, with both the British and
native Africans opposed. Welensky suggested that the Constitution of Australia be used as a basis for the proposed federal constitution, and pushed the idea of 'partnership' between blacks and whites. However, he insisted that "for as long as I can see, in that partnership [the whites] will be senior partners". Apart from organising the federation, Welensky won a significant political battle in Northern Rhodesia against the British South Africa Company (BSAC),
which controlled mineral rights and the associated royalties throughout
the territory. The company, and not the British crown, had signed the
treaties with African kings that surrendered mining rights, but the
BSAC had stopped administering Northern Rhodesia in 1924. Welensky
argued that the territory had a right to the royalties, and petitioned
the governor to take action. After many talks, the BSAC relented and
agreed to surrender mineral rights in 1986, and to pay 20% of its
profits from these rights to the government until then. In
March 1952, the colonial and the British governments met in London to
discuss federation. There, the idea for a federation was finalised and
settled, although the colonial governments had, again, insisted on
amalgamation. They were rebuffed by the left leaning public servant
(later Sir) Andrew Cohen,
who, after much deliberation, brought the parties to an agreement. It
was acknowledged by those at the meeting that all too often the racial
policies of the Rhodesias were confused with the emerging apartheid of South Africa,
and Welensky himself claimed to refute these ideas when being
interviewed by a South African newspaper. He was paternalistic towards
native Africans, but believed in the dictum of "equal rights for all
civilised men" and gradual advancement. Behind
the scenes, Welensky and the Rhodesians had been courting the
Conservatives, while the native Africans had been doing the same with
Labour. A British general election was held in 1951 and the Conservatives gained power. Labour,
mindful of the overwhelming opposition of Africans from both Northern
Rhodesia and Nyasaland and of the Colonial Office mandate to oversee
native interests, had been lukewarm at best to the idea of federation,
and had been wholly opposed to amalgamation. After the election, the
bipartisan approach to federation broke down and the British laws for
its creation passed only with the support of the Conservatives, with
both Liberal and Labour Parties now opposed.
Welensky stood for the federal legislature in 1953 for the United Federal Party (UFP), created by himself and Southern Rhodesian Prime Minister Sir Godfrey Huggins. The party was successful in its first election,
with twice the votes of the opposition Confederate Party. Welensky
himself gained more than 80% of the vote in the federal constituency of
Broken Hill and was immediately promoted to Minister for Transport. The
first few years of the federation were characterised by a relatively
peaceful political atmosphere and a booming economy. The government's
coffers were kept full through revenue from Northern Rhodesia's copper
mines, and overseas investment saw the rapid expansion of the cities of Salisbury, Bulawayo and Lusaka. High standard tar roads replaced dirt tracks and the railway system was expanded. Welensky credited the high rate of development to the astute management of the federal Minister of Finance, Donald Macintyre. The Southern Rhodesian Government, under the leadership of Garfield Todd,
began removing restrictions imposed on native Africans. The civil
service opened more positions to Africans, the title for male Africans
was changed from 'AM' (African male) to Mr., and diners and restaurants
were allowed to be multiracial; Welensky, as Transport Minister,
allowed for railway dining cars to be multiracial. However, when it
came to liberalising alcohol restrictions on Africans, Welensky argued
against doing so, stating that such an action would cause the UFP to
lose the next election. After repeated failed attempts to secure Dominion status
for the federation, Prime Minister Huggins opted not to stand again for
his party's leadership at their September 1956 conference. In October
he resigned and Welensky, the second most senior figure in the federal
arena, was chosen to replace him. Welensky took office on 1 November. On taking office, Welensky was forced to take sides in the Suez Crisis.
The government of the United Kingdom received heavy international
criticism for its actions, but Welensky's government, with those of
Australia and New Zealand, nonetheless stood behind Britain. It was
Welensky's first experience in international politics. In
the aftermouth of the Suez debacle British colonial policy changed
significantly, which would have adverse effects for the federation. It
marked the decline of a gradual approach to decolonisation, and a rapid
speeding up of the process. Politically, only three years after its
founding, the federation began to decline. International
attitudes to the federation were critical, particularly from the
Afro-Asian bloc in the United Nations. At a time when most colonial
powers were rushing their colonies towards independence, the federation
seemed to its opponents to be an unwelcome obstacle. In Britain, Labour
grew more critical, and African nationalists in
the federation itself became more vocal, unsatisfied with the
liberalisation that was taking place, and demanding faster moves
towards African advancement. The Governor of Northern Rhodesia, Sir
Arthur Benson, wrote a secret letter to his superiors in Britain,
highly critical of Welensky and the federation; this letter remained
undiscovered until 1958, when Huggins revealed it to Welensky. The Colonial Secretary Alan Lennox - Boyd visited
the federation in January 1957, while Welensky prepared to outline the
difficulties regarding African advancement. Seeking to bring Africans
into the established political processes, and hoping they would shun
the recently formed African National Congress (ANC)
parties, Welensky hit out at what he saw as the poor Colonial Office
practice of making the situation "[consist] of two opposed policies,
black rule and white rule. They naturally prefer to aim for black rule
and hope they will experience this, which they regard as the apotheosis
of Colonial Office policy". The Nyasaland African Congress (NAC)
was particularly vocal about increased African representation in the
Nyasaland Legislative Council, demanding in September 1957 an African
majority in the council. Nyasaland's inclusion in the federation was
never a goal of its proponents, it was there primarily because it was
not economically viable by itself. Welensky did not understand or
appreciate the party's goal of increased African representation or
secession when it relied on the federation for its well being. In
this, he failed to take account of the reputation of Rhodesia among
Nyasaland Africans as a racist state with a history of appropriating
African land — a highly sensitive issue. Dr Hastings Banda,
the leader of the Nyasaland nationalist cause, returned to the
territory in 1958 and began organising opposition to the federation.
Having lived outside the territory for more than 25 years and unable to
speak his native African language, he required the assistance of
interpreters to communicate with the population, whom he stirred into a
frenzy with his speeches. After the Governor and the federal government
refused to give Africans a majority in the Legislative Council, he
embarked on a speaking tour of the territory. In January 1959, he
stated in a speech that he "put Salisbury [the capital] on
fire ... I got Salisbury rocking, rocking, and got it awake out of
its political sleep ...", after which his followers stoned passing cars and police officers. The
federal government met with the territorial governments to plan for a
response should the violence get out of hand. Welensky did not rule out
deploying federal troops if the situation deteriorated. Speaking
to the defence chiefs in Salisbury, he said that "during the next three
months we can expect some fairly serious trouble in Nyasaland ...
It is my concern to ensure that this government is in a position to
exercise its responsibilities if trouble comes". A NAC meeting was held outside Blantyre on
25 January. It was alleged that the meeting discussed in detail a plan
for the overthrow of the territorial government and the massacre of the
territory's whites and any blacks who collaborated with them (although a subsequent Royal Commission found there was insufficient evidence to
make such a claim). Welensky obtained the meeting's proceedings in
early February and decided to act, calling a meeting of the federal and
territorial governments. Federal troops were deployed to Nyasaland on
21 February, the Governor proclaimed a state of emergency on 3 March
and the nationalist leaders were arrested and flown to jails in
Southern Rhodesia. In the subsequent fortnight, riots broke out and
troops used force to end the violence. Almost 50 people died in the
unrest. The
main militant African nationalist parties in each territory were banned
by the federal and territorial governments, but all reorganised under
new names only months later. The Southern Rhodesian ANC became the National Democratic Party (later ZAPU), the Northern Rhodesian ANC became the Zambian African National Congress, and the Nyasaland ANC became the Malawi Congress Party. The media's use of the term 'police state' to describe the response to the violence outraged the Liberals, the Church of Scotland, and leftist Conservatives, and particularly the Labour Party, in Britain. John Stonehouse, a Labour MP, had been deported prior to the declaration of the state of emergency, adding to the tension. A Royal Commission was
announced to investigate the violence. Welensky was indignant when
asked to contribute to the Royal Commission, and the Labour Party
boycotted it. In
addition to the Royal Commission that investigated the Nyasaland
violence (now known as the Devlin Report), the British Government
organised a second one, known as the Monckton Report, to advise on the
future of the federation. Released in October 1960, the report
advocated sweeping changes to be made to the federal structure,
including African majorities in the Nyasaland and Northern Rhodesian
legislatures. Welensky was outraged when the report was published,
calling it the "death knell of federation" and rejecting it out of hand. African
nationalist opinion was just as opposed, but on different grounds. All
of the nationalists wanted an end to federation, and the independence
of the territories as black majority ruled states. Welensky was opposed
to any talk of secession, and the Monckton Report suggested it in
writing when it stated that the territories should have the option
after five years under a new federal constitution. Early 1960 saw British Prime Minister Harold Macmillan journey
to the federation for the first and last time. There he held talks in
person with Welensky and the territorial governments, and took the
opportunity to gauge African opinion towards the federation. He also
wished to talk to the jailed African leaders, but was met with a rebuff
from Welensky. Dr Hastings Banda discussed the probability of his release from prison with the British Government through Labour MP Dingle Foot.
Welensky had Banda's cell wired for sound and was frustrated with what
he saw as the British government's "betrayal, duplicity, appeasement, cowardice and loss of nerve" when dealing with the African nationalists and the federation. Macmillan travelled on to South Africa, where he made his 'Wind of Change' speech to the South African Parliament, raising the attention of South African Prime Minister, Dr Hendrik Verwoerd.
Welensky was informed that Banda would be released so he could join in
discussions with the British Government over the future of the
federation. Losing
patience with the British, Welensky took a harder line against them:
"I've tried all along to behave in a reasonable and responsible manner.
Now I'm seriously wondering whether restraint has been the right
policy." After
Banda was released from prison against the wishes of Welensky, he
travelled to the United Kingdom, where he took part in the Nyasaland
constitutional talks. The outcome was a constitution which, through a
voting system that was as complex as that of the federation itself,
amounted to black majority rule for the territory. Bitter and angry at
what he saw as British ignorance to the situation, Welensky did not
comprehend how the British were willing to deal with Banda. In
Welensky's words, since his release from prison, "[Banda] was careful
to appeal for calm and to condemn violence", but
Welensky was averse to Banda's demands for black majority rule and
believed that granting it to the territory would mean the end of the
federation. In
Northern and Southern Rhodesia new constitutions were also enacted. The
Southern Rhodesian constitution was very cautious and prolonged white
rule. It had 50 A-roll seats with high voting qualifications
(essentially for whites), and 15 B-roll seats with lower qualifications
(for blacks). A system of 'cross voting' meant that results in A-roll
seats would be affected by the B-roll vote, and vice versa. All
constitutions were signed by the UFP and the African nationalist party
in each territory. However, there were immediate repercussions; Ian Smith,
chief whip for the UFP in the federal assembly, resigned in protest at
the new Southern Rhodesian constitution, calling it "racialist", whilst
the African nationalist party, the National Democratic Party, withdrew support for the constitution having earlier signed it. Eventually,
Welensky was comfortable with an African majority in Nyasaland and for
the province to secede, seeking to preserve only a union of the two
Rhodesias. But, as a Northern Rhodesian, he did not accept black
majority rule for the territory and a battle was had with the British
Government over its new constitution throughout 1961 – 62. Discussing
Northern Rhodesia under African rule with Smith: "I am not prepared to
hand power to the blacks. Personally I could not live in a country where they were in control." Welensky considered a federal unilateral declaration of independence when the new Northern Rhodesian constitution appeared likely to grant an African majority in its parliament. Determined
at one point to prevent changes, Welensky was convinced that if he
refused, the British would use military force to remove his government.
Believing that preparations were being made for an invasion from Kenya, he discussed the federation's ability to repel an attack with his defence chiefs and plans were set in motion. In the end, the idea of a British invasion was one of many options considered, and did not make it past cabinet discussion. After the Congo gained independence in 1960, it collapsed into a state of anarchy within
a fortnight. The large Belgian population of the Congo fled from the
violence into neighbouring states, including the federation. Welensky
dispatched the Royal Rhodesian Air Force (RRAF)
to assist in their evacuation, but was prevented by the British
government from entering the Congo itself. Refugees fled by foot to Ndola in
Northern Rhodesia, where RRAF planes picked them up and flew them to
camps in Salisbury. More than 6,000 people were evacuated by the RRAF. The president of Congo's Katanga Province, Moise Tshombe, requested British and Rhodesian forces to enter the country to restore
order. Welensky was sympathetic to the situation but unable to act; the
British government, which had ultimate jurisdiction over the
federation, disallowed him from mobilising the armed forces. Tshombe
declared Katanga unilaterally independent on 11 July, one day after
requesting British and Rhodesian assistance. Full
of hatred for the United Nations and mindful of the inability of the
new Congolese government to maintain order in the Congo, Welensky
repeatedly pleaded with Macmillan for the recognition of the Katanga
state and the deployment of Rhodesian forces. Macmillan rebuffed
Welensky each time, telling him that their hope was pinned on the UN
restoring order and hoping for a wholly neutral or anti-communist Congo. The United Nations Secretary General, Dag Hammarskjöld,
hoping to negotiate a solution to Katanga's secession, agreed to meet
Tshombe at Ndola. His plane crashed on landing, and Welensky was
subsequently blamed for the accident throughout the communist and
Afro-Asian world, becoming a hated figure and a lingering symbol of
colonialism. The attitude of Welensky towards Katanga and the Congo
would strain relations between the federation and the British until its
dissolution. With
new constitutions in place for the territories, elections were held
throughout 1961 – 62, with Welensky's UFP being beaten in each one. In
Nyasaland, the African nationalist Malawi Congress Party won
a huge majority and Banda set about lobbying the British Government for
the breakup of the federation and the independence of Nyasaland as
Malawi. In Northern Rhodesia, neither the UFP nor the two African
nationalist parties held a majority, but the African nationalists
united to push for independence. Welensky
hoped to get a display of confidence in federation, so he dissolved
parliament in mid 1962 and held elections. While his party won a huge
victory, it did so because it was completely unopposed. Neither the
recently formed Rhodesian Front (RF) nor the African nationalist parties bothered to contest it. In Southern Rhodesia, the UFP lost the hold that it and its successor parties had for decades in the October election. Ian Smith, a former federal member of the UFP, had united with Winston Field of the Dominion Party to
form the Rhodesian Front, a conservative party that was opposed to a
fast rate of African political advancement and the 1961 constitution,
and in support of Southern Rhodesian independence. The RF won 55% of
the vote and 35 A-roll seats, while the UFP won 44% of the vote, 15
A-roll seats and 14 B-roll seats. Welensky
now had parties in power in all three territorial legislatures that
were opposed to the federation and advocating independence for their respective territories. With Nyasaland and Northern Rhodesia now promised independence by Britain under 'one man, one vote'
constitutions, the federation was essentially dead. Southern Rhodesia,
still governed by its white minority, was subject to attacks in the
United Nations general assembly which regarded its constitution as
unsatisfactory. It demanded 'one man, one vote' elections, stating that
this was the only "realistic answer to the powerful and irresistible
urge of the indigenous people for freedom and equality". Accepting
the end of the federation, Welensky set about ensuring that the assets
of the federal government were transferred to Southern Rhodesia, making
this a condition of him attending dissolution talks at Victoria Falls. Welensky
refused to dine with the British delegates, on the grounds of "not
choking on his food", but ensured that the talks went smoothly. The federation was legally dissolved on 31 December 1963. With the collapse of the federation, Welensky moved to Salisbury, Rhodesia (renamed from Southern Rhodesia after Northern Rhodesia gained independence as Zambia).
After a short break, he was invited to lead the UFP in Rhodesia, which
had recently renamed itself the Rhodesia Party. With the Rhodesian
Front pushing for independence for the territory and a new
constitution, the Rhodesia Party advocated the same, but with a focus
on stemming white emigration and rebuilding the economy (all three
territories had slipped into recession with the end of the federation). With
the resignation of the RF member for the Salisbury constituency of
Arundel, Welensky was given a chance to re-enter the political arena. Clifford Dupont, Deputy Prime Minister, resigned his constituency in Charter to oppose Welensky. Welensky
knew that if the RF won the byelections it would seem to be a mandate
for unilateral independence (UDI); the campaign, for only two seats,
was intense. At public meetings, Welensky was heckled by opponents to
ironic cries of 'Communist', 'traitor', and 'coward'. Sharing
a television platform with Smith on 3 September, Welensky talked of the
economic and political dangers of a UDI, but nonetheless wished Smith
luck when he departed for independence talks in London. Welensky had much more antipathy for the British Government than his RF
opponents, and was disgusted at their treatment of the Rhodesians
during constitutional talks: On 1 October Welensky was soundly defeated by his RF opponent, with 633 votes to Dupont's 1079. In December he resigned the leadership of his party. When the RF declared unilateral independence on 11 November 1965, Welensky was upset at the constitutional break with Britain. He
believed that Rhodesia was entitled to her independence, and disagreed
with the British government's demand for 'no independence before
majority rule', but was opposed to illegal action. Welensky continued living in Rhodesia until Robert Mugabe gained power and the country became Zimbabwe.
While in London in 1971, and by then a widower, Welensky met his second
wife, Valerie Scott, an organiser for the London and Westminster
Conservative Association, who was thirty years younger. They left in 1981 for Blandford Forum, Dorset, England, where he died on 5 December 1991.