<Back to Index>
- Mathematician John von Neumann, 1903
- Painter Ludolf Backhuysen, 1630
- 28th President of the United States Thomas Woodrow Wilson, 1856
PAGE SPONSOR
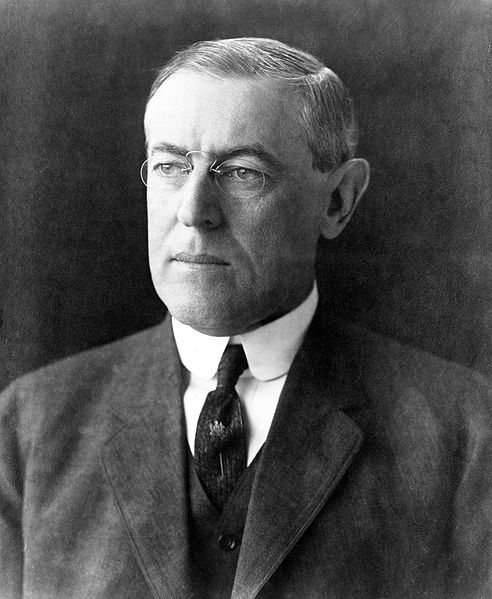


Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856 – February 3, 1924) was the 28th President of the United States. A leading intellectual of the Progressive Era, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913. With Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft dividing the Republican Party vote, Wilson was elected President as a Democrat in 1912.
In his first term, Wilson persuaded a Democratic Congress to pass the Federal Reserve Act, Federal Trade Commission, the Clayton Antitrust Act, the Federal Farm Loan Act and America's first-ever federal progressive income tax in the Revenue Act of 1913. Wilson brought many white Southerners into his administration, and tolerated their expansion of segregation in many federal agencies. Narrowly re-elected in 1916, Wilson's second term centered on World War I. He based his re-election campaign around the slogan "he kept us out of the war", but U.S. neutrality was challenged in early 1917 when the German government proposed to Mexico a military alliance in a war against the U.S., and began unrestricted submarine warfare, sinking without warning every American merchant ship its submarines could find. Wilson in April 1917 asked Congress to declare war. He focused on diplomacy and financial considerations, leaving the waging of the war primarily in the hands of the Army. On the home front in 1917, he began the United States' first draft since the US civil war, raised billions in war funding through Liberty Bonds, set up the War Industries Board, promoted labor union growth, supervised agriculture and food production through the Lever Act, took over control of the railroads, enacted the first federal drug prohibition, and suppressed anti-war movements. National women's suffrage was also achieved under Wilson's presidency. In the late stages of the war, Wilson took personal control of negotiations with Germany, including the armistice. He issued his Fourteen Points, his view of a post-war world that could avoid another terrible conflict. He went to Paris in 1919 to create the League of Nations and shape the Treaty of Versailles, with special attention on creating new nations out of defunct empires. Largely for his efforts to form the League, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. In 1919, during the bitter fight with the Republican-controlled Senate over the U.S. joining the League of Nations, Wilson collapsed with a debilitating stroke. He refused to compromise, effectively destroying any chance for ratification. The League of Nations was established anyway, but the United States never joined. A Presbyterian of deep religious faith, he appealed to a gospel of service and infused a profound sense of moralism into Wilsonianism. Wilson's idealistic internationalism, now referred to as "Wilsonianism", which calls for the United States to enter the world arena to fight for democracy, has been a contentious position in American foreign policy, serving as a model for "idealists" to emulate and "realists" to reject ever since.
Wilson was born in Staunton, Virginia, on
December 28, 1856 as the third of four children of Reverend Dr. Joseph
Ruggles Wilson (1822 – 1903) and Jessie Janet Woodrow (1826 – 1888). His ancestry was Scottish and Scots-Irish. His paternal grandparents immigrated to the United States from Strabane, County Tyrone, Ireland (now Northern Ireland), in 1807. His mother was born in Carlisle, England, the daughter of Rev. Dr. Thomas Woodrow, born in Paisley, Scotland, and Marion Williamson from Glasgow. His grandparents' whitewashed house
has become a tourist attraction in Northern Ireland. Descendants of the
Wilsons still live in the farmhouse next door to it. Wilson's father was originally from Steubenville, Ohio, where his grandfather published a newspaper, The Western Herald and Gazette, that was pro-tariff and abolitionist. Wilson's parents moved South in 1851 and identified with the Confederacy. His father defended slavery, owned slaves and set up a Sunday school
for them. They cared for wounded soldiers at their church. The father
also briefly served as a chaplain to the Confederate Army. Woodrow Wilson's earliest memory, from the age of three, was of hearing that Abraham Lincoln had been elected and that a war was coming. Wilson would forever recall standing for a moment at Robert E. Lee's side and looking up into his face. Wilson's father was one of the founders of the Southern Presbyterian Church in the United States (PCUS)
after it split from the northern Presbyterians in 1861. Joseph R.
Wilson served as the first permanent clerk of the southern church's
General Assembly, was Stated Clerk from 1865 – 1898 and was Moderator of
the PCUS General Assembly in 1879. Wilson spent the majority of his
childhood, up to age 14, in Augusta, Georgia, where his father was minister of the First Presbyterian Church.
Wilson was over ten years of age before he learned to read. His difficulty reading may have indicated dyslexia, but as a teenager he taught himself shorthand to compensate. He
was able to achieve academically through determination and
self-discipline. He studied at home under his father's guidance and
took classes in a small school in Augusta. During Reconstruction, Wilson lived in Columbia, South Carolina, the state capital, from 1870 – 1874, where his father was professor at the Columbia Theological Seminary. In 1873, he spent a year at Davidson College in North Carolina, then transferred to Princeton as a freshman, graduating in 1879, becoming a member of Phi Kappa Psi fraternity.
Beginning in his second year, he read widely in political philosophy
and history. Wilson credited the British parliamentary sketch-writer Henry Lucy as his inspiration to enter public life. He was active in the undergraduate American Whig-Cliosophic Society discussion club, and organized a separate Liberal Debating Society. In 1879, Wilson attended law school at the University of Virginia for one year. Although he never graduated, during his time at the University he was heavily involved in the Virginia Glee Club and the Jefferson Literary and Debating Society, serving as the Society's president. His frail health dictated withdrawal, and he went home to Wilmington, North Carolina, where he continued his studies. In January 1882, Wilson started a law practice in Atlanta. One of his University of Virginia classmates,
Edward Ireland Renick, invited him to join his new law practice as
partner and Wilson joined him in May 1882. He passed the Georgia Bar.
On October 19, 1882, he appeared in court before Judge George Hillyer to
take his examination for the bar, which he passed easily. Competition
was fierce in the city with 143 other lawyers, and he found few cases
to keep him occupied. Nevertheless,
he found staying current with the law obstructed his plans to study
government to achieve his long-term plans for a political career. In
April 1883, Wilson applied to the Johns Hopkins University to study for a doctorate in history and political science and began his studies there in the fall. Wilson's mother was possibly a hypochondriac and Wilson himself seemed to think that he was often in poorer health than he really was. He did suffer from hypertension at a relatively early age and may have suffered his first stroke at age 39. In 1885, he married Ellen Louise Axson, the daughter of a minister from Rome, Georgia. They had three daughters: Margaret Woodrow Wilson (1886 – 1944); Jessie Wilson (1887 – 1933); and Eleanor R. Wilson (1889 – 1967). Axson died in 1914, and the following year Wilson married Edith Galt, a direct descendant of the famous Native American Pocahontas. Wilson is one of only three presidents to be widowed while in office. Wilson was an early automobile enthusiast, and he took daily rides while he was President. His favorite car was a 1919 Pierce-Arrow, in which he preferred to ride with the top down. His enjoyment of motoring made him an advocate of funding for public highways. Wilson was an avid baseball fan. In 1915, he became the first sitting president to attend a World Series game. Wilson had been a center fielder during
his Davidson College days. When he transferred to Princeton he was
unable to make the varsity team and so became the team's assistant
manager. He was the first President to throw out a first ball at a
World Series game. He cycled regularly, including several cycling vacations in the English Lake District. Unable to cycle around Washington, D.C. as President, Wilson took to playing
golf, although he played with more enthusiasm than skill. Wilson holds the record of all the presidents for the most rounds of golf, over 1,000, or almost one every other day. During the winter, the Secret Service would paint golf balls with black paint so Wilson could hit them around in the snow on the White House lawn. He began his graduate studies at Johns Hopkins University in
1883 and three years later he completed his doctoral dissertation,
"Congressional Government: A Study in American Politics", and received
a Ph.D. in history and political science. For his doctorate, Wilson had
to learn German. He received academic appointments at Bryn Mawr College (1885–88) and Wesleyan University (1888–90). At Wesleyan, he also coached the football team and founded the debate team – it is still called the T. Woodrow Wilson debate team. He then joined the Princeton faculty as professor of jurisprudence and political economy in 1890. While there, he was one of the faculty members of the short-lived coordinate college, Evelyn College for Women. Additionally, Wilson became the first lecturer of Constitutional Law at New York Law School where he taught with Charles Evans Hughes. Wilson
delivered an oration at Princeton's sesquicentennial celebration (1896)
entitled "Princeton in the Nation's Service". This phrase became the
motto of the University, later expanded to "Princeton in the Nation's
Service and in the Service of All Nations". In
this speech, he outlined his vision of the university in a democratic
nation, calling on institutions of higher learning "to illuminate duty by every lesson that can be drawn out of the past". Wilson
was annoyed that Princeton was not living up to its potential,
complaining "There's a little college down in Kentucky which in 60
years has graduated more men who have acquired prominence and fame than
has Princeton in her 150 years." Under the influence of Walter Bagehot's The English Constitution, Wilson saw the United States Constitution as pre-modern, cumbersome, and open to corruption. An admirer of Parliament, Wilson favored a parliamentary system for the United States. After experiencing the vigorous presidencies of William McKinley and Theodore Roosevelt, Wilson no longer entertained thoughts of parliamentary government for the United States. In his last scholarly work in 1908, Constitutional Government of the United States,
Wilson said that the presidency "will be as big as and as influential
as the man who occupies it". By the time of his presidency, Wilson
merely hoped that Presidents could be party leaders in the same way
British prime ministers were. Wilson also hoped that the parties could
be reorganized along ideological, not geographic, lines. He wrote,
"Eight words contain the sum of the present degradation of our
political parties: No leaders, no principles; no principles, no
parties." Wilson
also studied public administration, which he called "government in
action; it is the executive, the operative, the most visible side of
government, and is of course as old as government itself". He believed that by studying public administration governmental efficiency could be increased. Wilson
was concerned with the implementation of government. He faulted
political leaders who focused on philosophical issues and the nature of
government and dismissed the critical issues of government
administration as mere "practical detail". He thought such attitudes
represented the requirements of smaller countries and populations. By his day, he thought, "it is getting to be harder to run a constitution than to frame one." He
thought it time "to straighten the paths of government, to make its
business less unbusinesslike, to strengthen and purify its
organization, and it to crown its dutifulness". He
complained that studies of administration drew principally on the
history of Continental Europe and an American equivalent was required. He
summarized the growth of such foreign states as Prussia, France, and
England, highlighting the events that led to advances in administration. By
contrast, he thought American required greater compromise because of
the diversity of public opinion and the difficulty of forming a
majority opinion. Thus practical reform to the government is
necessarily slow. Yet Wilson insisted that "administration lies outside the proper sphere of politics" and that "general laws which direct these things to be done are as obviously outside of and above administration." He likens administration to a machine that functions independent of the changing mood of its leaders. Such
a line of demarcation is intended to focus responsibility for actions
taken on the people or persons in charge. As Wilson put it, "public
attention must be easily directed, in each case of good or bad
administration, to just the man deserving of praise or blame. There is
no danger in power, if only it be not irresponsible. If it be divided,
dealt out in share to many, it is obscured..." Essentially,
the items under the discretion of administration must be limited in
scope, as to not block, nullify, obfuscate, or modify the
implementation of governmental decree made by the executive branch. The trustees promoted Professor Wilson to president of Princeton in 1902, replacing Francis Landey Patton,
whom the Trustees perceived to be an inefficient administrator.
Although the school's endowment was barely $4 million, Wilson sought $2
million for a preceptorial system of teaching, $1 million for a school
of science, and nearly $3 million for new buildings and salary
increases. As a long-term objective, Wilson sought $3 million for a
graduate school and $2.5 million for schools of jurisprudence and electrical engineering, as well as a museum of natural history. He
achieved little of those ambitious plans because he was not a strong
fund raiser, but he did increase the faculty from 112 to 174, most of
whom he selected himself on the basis of their records as outstanding
teachers. The curriculum guidelines he developed proved important
progressive innovations in the field of higher education. To
emphasize the development of expertise, Wilson instituted academic
departments and a system of core requirements where students met in
groups of six with preceptors, followed by two years of concentration
in a selected major. He tried to raise admission standards and to
replace the "gentleman's C" with serious study. Wilson aspired, as he
told alumni, "to transform thoughtless boys performing tasks into
thinking men". In 1906–10, he attempted to curtail the influence of social elites by abolishing the upper-class eating clubs and
moving the students into colleges, also known as quadrangles. Wilson's
Quad Plan was met with fierce opposition from Princeton's alumni, most
importantly Moses Taylor Pyne,
the most powerful of Princeton's Trustees. Wilson refused any proposed
compromises that stopped short of abolishing the clubs because he felt
that to compromise "would be to temporize with evil". In
October 1907, due to the intensity of alumni opposition and Wilson's
refusal to compromise, the Board of Trustees withdrew its support for
the Quad Plan and instructed Wilson to withdraw it. Even
more damaging to Wilson's administration of the University was his
confrontation with Andrew Fleming West, Dean of the graduate school,
and West's ally, former President Grover Cleveland,
a trustee. Wilson wanted to integrate the proposed graduate building
into the same area with the undergraduate colleges. West wanted them to
remain separate. The trustees rejected Wilson's plan for colleges in
1908, and then endorsed West's alternative in 1909. The national press
covered the confrontation as a battle of the elites represented by West versus democracy represented by Wilson. Wilson served as president of the American Political Science Association in
1910. Around this time, Wilson decided to leave his post at Princeton.
After considering an immediate resignation, he decided instead to take
up invitations to enter New Jersey state politics. In 1910 Wilson ran for Governor of New Jersey against the Republican candidate Vivian M. Lewis,
the State Commissioner of Banking and Insurance. Wilson's campaign
focused on his independence from machine politics, and he promised that
if elected he would not be beholden to party bosses. Wilson soundly
defeated Lewis in the general election by a margin of more than 49,000
votes, although Republican William Howard Taft had carried New Jersey in the 1908 presidential election by more than 80,000 votes. In the 1910 election the Democrats also took control of the General Assembly. The State Senate,
however, remained in Republican control by a slim margin. After taking
office, Wilson set in place his reformist agenda, ignoring the demands
of party machinery. While governor, in a period spanning six months,
Wilson established state primaries. This all but took the party bosses
out of the presidential election process in the state. He also revamped
the public utility commission, and introduced worker's compensation. Wilson's
popularity as governor and his status in the national media gave
impetus to his presidential campaign in 1912. He selected William Frank
McCombs, a New York lawyer and a friend from college days, to manage
his campaign. Much of Wilson's support came from the South, especially
from young progressives in that region, especially intellectuals,
editors and lawyers. Wilson managed to maneuver through the
complexities of local politics. For example, in Tennessee the
Democratic Party was divided on the issue of prohibition. Wilson was
progressive and sober, but not a dry, and appealed to both sides. They
united behind him to win the presidential election in the state, but
divided over state politics and lost the gubernatorial election. The
convention deadlocked for more than 40 ballots as no candidate could
reach the two-thirds vote required to win the nomination. A leading
contender was House Speaker Champ Clark, a prominent progressive strongest in the border states. Other contenders were Governor Judson Harmon of Ohio, and Representative Oscar Underwood of Alabama. They lacked Wilson's charisma and dynamism. Publisher William Randolph Hearst, a leader of the left-wing of the party, supported Clark. William Jennings Bryan,
the nominee in 1896, 1900 and 1908, played a critical role in
opposition to any candidate who had the support of "the financiers of
Wall Street". He finally announced for Wilson, who won on the 46th
ballot. In
the campaign Wilson promoted the "New Freedom", emphasizing limited
federal government and opposition to monopoly powers — positions that he
reversed on coming to office. Wilson enjoyed the support of many black
leaders including W.E.B. DuBois and William Monroe Trotter. Wilson's speeches and letters expressed the sentiments of a defender of the underprivileged. In a bitter contest for the Republican nomination, President William Howard Taft defeated former president Theodore Roosevelt,
but when Roosevelt walked out of the Republican convention and ran as a
third party candidate, Wilson's success in the electoral college was
assured. He won 41.8% of the popular vote.
Wilson is the only President to hold a Ph.D. degree
and the only President to serve in a political office in New Jersey
before election to the Presidency. He was the first person identified
with the South to be elected President since Zachary Taylor and the first Southerner in the White House since Andrew Johnson left in 1868. Wilson
had a strong base of support in the South. He was the first president
to deliver his State of the Union address before Congress personally
since John Adams in 1799. Wilson was also the first Democrat elected to the presidency since Grover Cleveland in 1892 and only the second Democrat in the White House since the Civil War. In
resolving economic policy issues, he had to manage the conflict between
two wings of his party, the agrarian wing led by Bryan and the
pro-business wing. With large Democratic majorities in Congress and a
healthy economy, he promptly seized the opportunity to implement his
agenda. Wilson experienced early success by implementing his "New Freedom" pledges of antitrust modification, tariff revision, and reform in banking and currency matters. He held the first modern presidential press conference, on March 15, 1913, in which reporters were allowed to ask him questions. Wilson's first wife Ellen died on August 6, 1914 of Bright's disease. In 1915, he met Edith Galt. They married later that year on December 18. Wilson secured passage of the Federal Reserve Act in late 1913. Wilson had tried to find a middle ground between conservative Republicans led by Senator Nelson W. Aldrich and those, especially the powerful left wing of the Democratic party led by William Jennings Bryan, who opposed all banking schemes and strenuously denounced private banks and Wall Street.
The latter group wanted a government-owned central bank that could
print paper money as Congress required. The compromise, based on the
Aldrich Plan but sponsored by Democratic Congressmen Carter Glass and Robert Owen,
allowed the private banks a certain influence over the new Federal
Reserve, but appeased the populists by placing controlling interest in
a central, public board. This Board of Governors included members
appointed by the President and approved by Congress who would outnumber
the board members selected by bankers. Moreover, Wilson convinced
Bryan's supporters that because Federal Reserve notes were obligations
of the government, the plan met their demands. Wilson's plan also
organized the Federal Reserve system into 12 districts, a structure
meant to weaken the influence of the powerful New York banks, a key
demand of Bryan's allies in the South and West. This decentralization
was a key factor in winning the support of Congressman Glass. The
final plan passed in December 1913. Some bankers felt it gave too much
control to Washington, and some reformers felt it allowed bankers to
maintain too much power. Several Congressmen claimed that New York
bankers feigned their disapproval. Wilson named Paul Warburg and
other prominent bankers to direct the new system. While power was
supposed to be decentralized, the New York branch dominated the Fed as
the "first among equals". The new system began operations in 1915 and played a major role in financing the Allied and American war effort. In 1913, the Underwood tariff lowered the tariff. The revenue thereby lost was replaced by a new federal income tax (authorized by the 16th Amendment,
which had been sponsored by the Republicans). The "Seaman's Act" of
1915 improved working conditions for merchant sailors. A response to the RMS Titanic disaster, it also required all ships to be retrofitted with lifeboats. A
series of programs were targeted at farmers. The "Smith Lever" act of
1914 created the modern system of agricultural extension agents
sponsored by the state agricultural colleges. The agents taught new
techniques to farmers. The 1916 "Federal Farm Loan Board" issued
low-cost long-term mortgages to farmers. Child labor was curtailed by the Keating-Owen Act of 1916, but the U.S. Supreme Court declared it unconstitutional in 1918. No major child labor prohibition would take effect until the 1930s. The
railroad brotherhoods threatened in summer 1916 to shut down the
national transportation system. Wilson tried to bring labor and
management together, but when management refused he had Congress pass
the "Adamson Act"
in September 1916, which avoided the strike by imposing an 8-hour work
day in the industry (at the same pay as before). It helped Wilson gain
union support for his reelection; the act was approved by the Supreme
Court.
Wilson broke with the big lawsuit tradition of his predecessors Taft and Roosevelt asTrustbusters, finding a new approach to encouraging competition through the Federal Trade Commission, which stopped perceived unfair trade practices. In addition, he pushed through Congress the Clayton Antitrust Act making
certain business practices illegal (such as price discrimination,
agreements prohibiting retailers from handling other companies'
products, and directorates and agreements to control other companies).
The power of this legislation was greater than previous anti-trust
laws, because individual officers of corporations could be held
responsible if their companies violated the laws. More importantly, the
new laws set out clear guidelines that corporations could follow, a
dramatic improvement over the previous uncertainties. This law was
considered the "Magna Carta" of labor by Samuel Gompers because
it ended union liability antitrust laws. In 1916, under threat of a
national railroad strike, he approved legislation that increased wages
and cut working hours of railroad employees; there was no strike. Wilson spent 1914 through the beginning of 1917 trying to keep America out of the war in Europe. He offered to be a mediator, but neither the Allies nor the Central Powers took his requests seriously. Republicans, led by Theodore Roosevelt, strongly criticized Wilson's refusal to build up the U.S. Army in
anticipation of the threat of war. Wilson won the support of the U.S.
peace element by arguing that an army buildup would provoke war.
Secretary of State William Jennings Bryan, whose pacifist recommendations were ignored by Wilson, resigned in 1915. On
18 December 1916 Wilson unsuccessfully offered to mediate peace. As a
preliminary he asked both sides to state their minimum terms necessary
for future security. The Central Powers replied
that victory was certain, and the Allies required the dismemberment of
their enemies' empires. No desire for peace or common ground existed,
and the offer lapsed. While
German submarines were killing sailors and civilian passengers Wilson
demanded that Germany stop, but he kept the U.S. out of the war.
Britain had declared a blockade of Germany to prevent neutral ships
from carrying contraband goods to Germany. Wilson protested some
British violation of neutral rights, where no one was killed. His
protests were mild, and the British knew America would not take action.
In 1912, "an unprecedented number" of
African Americans left the Republican Party to cast their vote for
Democrat Wilson. They were encouraged by his promises of support for
their issues. The issue of segregation came up early in his presidency
when, at an April 1913 cabinet meeting, Albert Burleson, Wilson's Postmaster General,
complained about working conditions at the Railway Mail Service.
Offices and restrooms became segregated, sometimes by partitions
erected between seating for white and African-American employees in
Post Office Department offices, lunch rooms, and bathrooms, as well as
in the Treasury and the Bureau of Engraving and Printing.
It also became accepted policy for "Negro" employees of the Postal
Service to be reduced in rank or dismissed. And unlike his predecessors Grover Cleveland and Theodore Roosevelt, Wilson accommodated Southern opposition to the re-appointment of an African American to the position of Register of the Treasury and
other positions within the federal government. This set the tone for
Wilson's attitude to race throughout his presidency, in which the
rights of African Americans were sacrificed, for what he felt would be
the more important longer term progress of the common good. Renominated
in 1916, Wilson used as a major campaign slogan "He kept us out of the
war", referring to his administration's avoiding open conflict with
Germany or Mexico while maintaining a firm national policy. Wilson,
however, never promised to keep out of war regardless of provocation.
In his acceptance speech on September 2, 1916, Wilson pointedly warned
Germany that submarine warfare that took American lives would not be
tolerated, saying "The nation that violates these essential rights must
expect to be checked and called to account by direct challenge and
resistance. It at once makes the quarrel in part our own." Wilson narrowly won the election, defeating Republican candidate Charles Evans Hughes.
As governor of New York from 1907 – 1910, Hughes had a progressive
record, strikingly similar to Wilson's as governor of New Jersey.
Theodore Roosevelt would comment that the only thing different between
Hughes and Wilson was a shave. However, Hughes had to try to hold
together a coalition of conservative Taft supporters and progressive
Roosevelt partisans and so his campaign never seemed to take a definite
form. Wilson ran on his record and ignored Hughes, reserving his
attacks for Roosevelt. When asked why he did not attack Hughes
directly, Wilson told a friend to "Never murder a man who is committing
suicide." The
result was exceptionally close and the outcome was in doubt for several
days. The vote came down to several close states. Wilson won California
by 3,773 votes out of almost a million votes cast and New Hampshire by
54 votes. Hughes won Minnesota by 393 votes out of over 358,000. In the final count, Wilson had 277 electoral votes vs. Hughes 254. Wilson was able to win reelection in 1916 by picking up many votes that had gone to Teddy Roosevelt or Eugene V. Debs in 1912. Before
entering the war in 1917, the U.S. had made a declaration of neutrality
in 1914. During this time of neutrality, President Wilson warned
citizens not to take sides in the war in fear of endangering wider U.S.
policy. In his address to congress in 1914, Wilson states, "Such
divisions amongst us would be fatal to our peace of mind and might
seriously stand in the way of the proper performance of our duty as the
one great nation at peace, the one people holding itself ready to play
a part of impartial mediation and speak the counsels of peace and
accommodation, not as a partisan, but as a friend." The U.S. maintained neutrality despite increasing pressure placed on Wilson after the sinking of the British passenger liner RMS Lusitania with
American citizens on board. This neutrality would deteriorate when
Germany began to initiate its unrestricted submarine warfare
threatening U.S. commercial shipping. When Germany started unrestricted submarine warfare in early 1917, despite the promises made in the Arabic pledge and the Sussex pledge, and attempted to enlist Mexico as an ally (Zimmermann Telegram),
Wilson took America into World War I as a war to make "the world safe
for democracy". He did not sign a formal alliance with the United
Kingdom or France but operated as an "associated" power. He raised a
massive army through conscription and gave command to General John J. Pershing, allowing Pershing a free hand as to tactics, strategy and even diplomacy. Woodrow
Wilson had decided by then that the war had become a real threat to
humanity. Unless the U.S. threw its weight into the war, as he stated
in his declaration of war speech on April 2, 1917, western
civilization itself could be destroyed. His statement announcing a "war
to end all wars" meant that he wanted to build a basis for peace that
would prevent future catastrophic wars and needless death and
destruction. This provided the basis of Wilson's Fourteen Points,
which were intended to resolve territorial disputes, ensure free trade
and commerce, and establish a peacemaking organization. Included in
these fourteen points was the proposal of the League of Nations. Woodrow Wilson delivered his War Message to
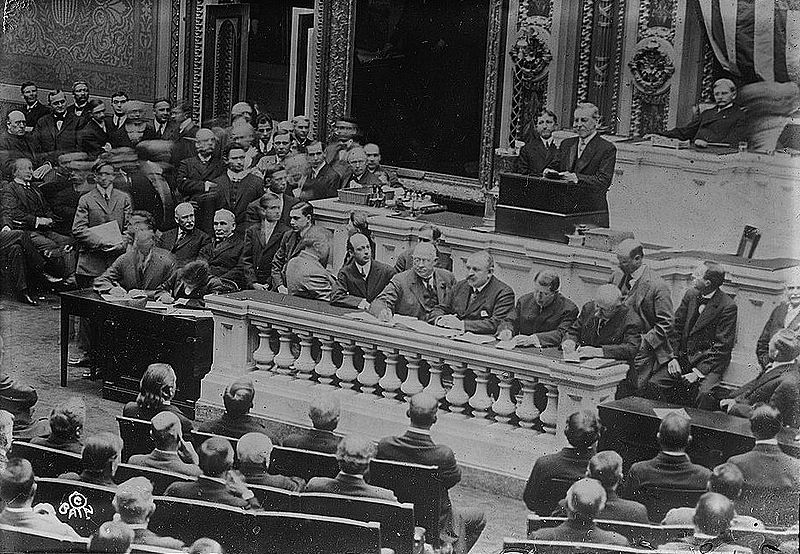
Congress on the evening of April 2, 1917. Introduced to great applause,
he remained intense and almost motionless for the entire speech, only
raising one arm as his only bodily movement. Wilson
announced that his previous position of "armed neutrality" was no
longer tenable now that the Imperial German Government had announced
that it would use its submarines to sink any vessel approaching the
ports of Great Britain, Ireland or any of the Western Coasts of Europe.
He advised Congress to declare that the recent course of action taken
by the Imperial German Government constituted an act of war. He
proposed that the United States enter the war to "vindicate principles
of peace and justice in the life of the world as against selfish and
autocratic power". He also charged that Germany had "filled our
unsuspecting communities and even our offices of government with spies
and set criminal intrigues everywhere afoot against our national unity
of counsel, our peace within and without our industries and our
commerce". Furthermore, the United States had intercepted a telegram sent to the German ambassador in Mexico City that
evidenced Germany's attempt to instigate a Mexican attack upon the U.S.
The German government, Wilson said, "means to stir up enemies against
us at our very doors". Wilson closed with the statement that the world
must be again safe for democracy. With 50 Representatives and 6 Senators in opposition, the declaration of war by the United States against Germany was passed by the Congress on April 4, 1917, and was approved by the President on April 6, 1917. In
a speech to Congress on January 8, 1918, Wilson articulated America's
war aims. It was the clearest expression of intention made by any of
the belligerent nations. The speech, authored principally by Walter Lippmann,
translated Wilson's progressive domestic policies into comparably
idealistic equivalents for the international arena: self-determination,
open agreements, international cooperation. Promptly dubbed the Fourteen Points,
Wilson attempted to make them the basis for the treaty that would mark
the end of the war. They ranged from the most generic principles like
the prohibition of secret treaties to such detailed outcomes as the
creation of an independent Poland with access to the sea. To counter opposition to the war at home, Wilson pushed the Espionage Act of 1917 and the Sedition Act of 1918 through Congress to suppress anti-British, pro-German, or anti-war opinions. He welcomed socialists who supported the war and pushed for deportation of foreign-born radicals. Citing
the Espionage Act, the U.S. Post Office refused to carry any written
materials that could be deemed critical of the U.S. war effort. Some
sixty newspapers were deprived of their second-class mailing rights. His wartime policies were strongly pro-labor. He worked closely with Samuel Gompers and the AFL, while suppressing antiwar groups trying to impede the war effort. The American Federation of Labor,
the railroad brotherhoods and other 'moderate' unions saw enormous
growth in membership and wages during Wilson's administration. There
was no rationing, so consumer prices soared. As income taxes increased, white-collar workers suffered. Appeals to buy war bonds were highly successful, however. Bonds had the result of shifting the cost of the war to the affluent 1920s. Wilson set up the first western propaganda office, the United States Committee on Public Information, headed by George Creel (thus its popular name, Creel Commission), which filled the country with patriotic anti-German appeals and conducted various forms of censorship. In 1917, Congress authorized ex-President Theodore Roosevelt to raise four divisions of volunteers to fight in France - Roosevelt's World War I volunteers;
Wilson refused to accept this offer from his political enemy. Other
areas of the war effort were incorporated into the government along
with propaganda. The War Industries Board headed by Bernard Baruch set war goals and policies for American factories. Future President Herbert Hoover was appointed to head the Food Administration which
encouraged Americans to participate in "Meatless Mondays" and
"Wheatless Wednesdays" to conserve food for the troops overseas. The Federal Fuel Administration run by Henry Garfield introduced daylight savings time and
rationed fuel supplies such as coal and oil to keep the US military
supplied. These and many other boards and administrations were headed
by businessmen recruited by Wilson for a dollar a day salary to make
the government more efficient in the war effort. Between 1914 and 1918, the United States intervened in Latin America, particularly in Mexico, Haiti, Cuba, and Panama. The U.S. maintained troops in Nicaragua throughout the Wilson administration and used them to select the president of Nicaragua and then to force Nicaragua to pass the Bryan-Chamorro Treaty.
American troops in Haiti, under the command of the federal government,
forced the Haitian legislature to choose the candidate Wilson selected
as Haitian president. American troops occupied Haiti between 1915 and
1934. Wilson ordered the military occupation of the Dominican Republic shortly after the resignation of its President Juan Isidro Jimenes Pereyra in 1916. The U.S. military worked in concert with wealthy Dominican landowners to suppress the gavilleros, a campesino guerrilla force
fighting the occupation. The occupation lasted until 1924, and was
notorious for its brutality against those in the resistance. After Russia left the war following the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917, the Allies sent troops there to prevent a German or Bolshevik takeover of allied-provided weapons, munitions and other supplies, previously
shipped as aid to the pre-revolutionary government. Wilson sent armed forces to assist the withdrawal of Czech and Slovak prisoners along the Trans-Siberian Railway, hold key port cities at Arkangel and Vladivostok.
Though not sent to engage the Bolsheviks, the U.S. forces engaged in
several armed conflicts against forces of the new Russian government.
Despite the apparent innocuousness of Wilson's motives, revolutionaries
in Russia resented the American intrusion. As Robert Maddox puts it,
"The immediate effect of the intervention was to prolong a bloody civil
war, thereby costing thousands of additional lives and wreaking
enormous destruction on an already battered society." Wilson withdrew most of the soldiers on April 1, 1920, though some remained until as late as 1922. In 1919 Wilson guided American foreign policy to "acquiesce" in the Balfour Declaration without
supporting Zionism in an official way. Wilson expressed sympathy for
the plight of Jews, especially in Poland and in France. In May 1920, after the Senate passed a resolution unanimously expressing sympathy for Armenia's suffering,
Wilson sent a proposal to Congress to establish an American mandate
over Armenia. It failed in the Senate with only 23 votes for and 52
against. He later requested an appropriation to underwrite a loan to
Armenia, but got no response from Congress. After
World War I, Wilson participated in negotiations with the stated aim of
assuring statehood for formerly oppressed nations and an equitable
peace. On January 8, 1918, Wilson made his famous Fourteen Points address,
introducing the idea of a League of Nations, an organization with a
stated goal of helping to preserve territorial integrity and political
independence among large and small nations alike. Wilson
intended the Fourteen Points as a means toward ending the war and
achieving an equitable peace for all the nations. He spent six months
in Paris for the 1919 Paris Peace Conference (making
him the first U.S. president to travel to Europe while in office). He
worked tirelessly to promote his plan. The charter of the proposed
League of Nations was incorporated into the conference's Treaty of Versailles. For his peace-making efforts, Wilson was awarded the 1919 Nobel Peace Prize,
however, he failed to even win US Senate support for ratification. The
United States never joined the League. Republicans under Henry Cabot Lodge controlled
the Senate after the 1918 elections, but Wilson refused to give them a
voice at Paris and refused to agree to Lodge's proposed changes. The
key point of disagreement was whether the League would diminish the
power of Congress to declare war. During this period, Wilson became
less trustful of the press and stopped holding press conferences for
them, preferring to use his propaganda unit, the Committee for Public
Information, instead. A
poll of historians in 2006 cited Wilson's failure to compromise with
the Republicans on U.S. entry into the League as one of the 10 largest
errors on the part of an American president. The
extensive restrictions in the Treaty of Versailles left the German
populace with a resentment against the treaty and ultimately
contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and World War II. When Wilson traveled to Europe to settle the peace terms, he visited Pope Benedict XV in Rome, making Wilson the first American President to visit the Pope while in office. Wilson's
administration did not plan for the process of demobilization at the
war's end. Though some advisers tried to engage the President's
attention to what they called "reconstruction", his tepid support for a
federal commission evaporated with the election of 1918. Republican
gains in the Senate meant that his opposition would have to consent to
the appointment of commission members. Instead, Wilson favored the
prompt dismantling of wartime boards and regulatory agencies. Demobilization
proved chaotic and violent. Four million soldiers were sent home with
little planning, little money, and few benefits. A wartime bubble in
prices of farmland burst, leaving many farmers bankrupt or deeply in
debt after they purchased new land. Major strikes in steel, coal, and
meatpacking followed in 1919. Serious race riots hit Chicago, Omaha and two dozen other cities. As
the election of 1920 approached, Wilson imagined that a deadlocked
Democratic convention might turn to him as the only candidate who would
make U.S. participation in the League of Nations the dominant issue. He
imagined and sometimes pretended he was healthy enough for the effort,
but several times admitted that he knew he could not survive a
campaign. No one around the President dared tell him that he was
incapable and that the campaign for the League was already lost. At the
Convention in late June, 1920, some Wilson partisans made efforts on
his behalf and sent Wilson hopeful reports, but they were quashed by
Wilson's wiser friends. The
immediate cause of Wilson's incapacitation was the physical strain of
the public speaking tour he undertook to obtain support for ratification of the Covenant of the League of Nations. In Pueblo, Colorado, on September 25, 1919 he collapsed. Then, on October 2, 1919, he suffered a serious stroke that
almost totally incapacitated him, leaving him paralyzed on his left
side and blind in his left eye. He was confined to bed for weeks,
sequestered from nearly everyone but his wife and his physician, Dr. Cary Grayson. For
at least a few months, he used a wheelchair. Later, he could walk only
with the assistance of a cane. The full extent of his disability was
kept from the public until after his death on February 3, 1924. With few exceptions, Wilson was kept out of the presence of Vice President Thomas R. Marshall, his cabinet and Congressional visitors to the White House for the remainder of his term. His wife, Edith,
served as his steward, selecting issues for his attention and
delegating other issues to his cabinet heads. Eventually, Wilson did
resume his attendance at cabinet meetings, but his input there was
perfunctory at best. This was one of the most serious cases of presidential disability in American history and was later cited as an argument for the 25th Amendment.
Wilson's chief of staff ("Secretary") was Joseph Patrick Tumulty 1913 – 1921, but he was largely upstaged after 1916 when Wilson's second wife, Edith Bolling Wilson, assumed full control of Wilson's schedule. The most important foreign policy advisor and confidant was "Colonel" Edward M. House until Wilson broke with him in early 1919. Wilson did not interfere with the well-established system of Jim Crow and
backed the demands of Southern Democrats that their states be left
alone to deal with issues of race and black voting without interference
from the North, ensuring there would be no challenge to the raft of
laws passed to disenfranchise African Americans across the region. While president of Princeton University,
Wilson discouraged blacks from even applying for admission, preferring
to keep the peace among white students than have black students
admitted. Many
black leaders supported Wilson in the 1912 election. However their
rejoicing over Wilson's victory was short-lived as segregationist white
Southerners took control of Congress and many executive departments. As President of the United States, Wilson ignored complaints that his cabinet officials had established official segregation in
most federal government offices, in some departments for the first time
since 1863. New buildings and facilities were built to house black
workers separately. "His administration imposed full racial segregation in Washington and
hounded from office considerable numbers of black federal employees." Wilson
and his cabinet members fired many black Republican office holders in
political appointee positions, but also appointed a few black Democrats
to such posts. W.E.B. Du Bois, a leader of the NAACP,
campaigned for Wilson and in 1918 was offered an Army commission in
charge of dealing with race relations; DuBois accepted, but he failed
his Army physical and did not serve. Wilson
drafted hundreds of thousands of blacks into the army, giving them
equal pay with whites, but kept them in all-black units with white
officers. When
a delegation of blacks protested the discriminatory actions, Wilson
told them "segregation is not a humiliation but a benefit, and ought to
be so regarded by you gentlemen." In 1914, he told The New York Times, "If the colored people made a mistake in voting for me, they ought to correct it." Wilson
was highly criticized by African Americans for his actions. He was also
criticized by such hard-line segregationists as Georgia's Thomas E. Watson,
who believed Wilson did not go far enough in restricting black
employment in the federal government. The segregation introduced into
the federal workplace by the Wilson administration was kept in place by
the succeeding presidents and not officially ended until the Truman Administration. Woodrow Wilson's "History of the American People" explained the Ku Klux Klan of the late 1860s as the natural outgrowth of Reconstruction, a lawless reaction to a lawless period. Wilson noted that the Klan
"began to attempt by intimidation what they were not allowed to attempt
by the ballot or by any ordered course of public action". Wilson
had harsh words to say about immigrants in his history books, but after
he entered politics in 1910, Wilson worked to integrate immigrants into
the Democratic party, the army, and American life. During the war, he
demanded in return that they repudiate any loyalty to enemy nations. Irish Americans were
powerful in the Democratic party and opposed going to war as allies of
their traditional enemy Great Britain, especially after the violent
suppression of the Easter Rebellion of
1916. Wilson won them over in 1917 by promising to ask Great Britain to
give Ireland its independence. At Versailles, however, he reneged and
the Irish-American community vehemently denounced him. Wilson, in turn,
blamed the Irish Americans and German Americans for lack of popular support for the League of Nations. Wilson nominated the first Jew to the Supreme Court, Louis Brandeis, starting a long line of Jewish justices who would serve on the nation's highest court in the future. In 1921, Wilson and his wife retired from the White House to a home in the Embassy Row section of Washington, D.C. Wilson continued going for daily drives and attended Keith's vaudeville theater on Saturday nights. Wilson was one of only two Presidents (Theodore Roosevelt was the first) to have served as president of the American Historical Association. Wilson died in his S Street home on February 3, 1924. He was buried in Washington National Cathedral. He is the only president buried in Washington, D.C. Mrs.
Wilson stayed in the home another 37 years, dying on December 28, 1961.
It was the day she was to be the guest of honor at the opening of the Woodrow Wilson Bridge near Washington, D.C. She died with her favorite dog, Rooter, at her bedside. Mrs. Wilson left the home to the National Trust for Historic Preservation to be made into a museum honoring her husband. The Woodrow Wilson House opened as a museum. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1964 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1966. Wilson wrote his one page will on May 31, 1917 and appointed his wife Edith as his executrix. He left his daughter Margaret an
annuity of $2500 annually for as long as she remained unmarried and
left what had been his first wife's personal property to his daughters.
The rest he left to Edith as a life estate with the provision that at
her death his daughters would divide the estate among themselves. In
the event that Edith had a child, her children would inherit on an
equal footing with his daughters. As the second Mrs Wilson had no
children from either of her marriages he was providing for the child of
a possible subsequent third marriage on her part. The USS Woodrow Wilson (SSBN-624),
a Lafayette-class ballistic missile submarine, was the only ship of the
United States Navy to be named for Wilson. She later was converted into
an attack submarine and redesignated SSN-624. The Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs was
founded at Princeton in 1930, created in the spirit of Wilson's
interest in preparing students for leadership in public and
international affairs. In 1929, Wilson's image appeared on the $100,000 bill. The bill, now out of print but still legal tender, was only used to transfer money between Federal Reserve banks. In 1944, Darryl F. Zanuck of 20th Century Fox produced a film titled Wilson. It looked back with nostalgia to the commander-in-chief of World War I.
Wilson started Congressional Government, his best known political work, as an argument for a parliamentary system, but he was impressed by Grover Cleveland, and Congressional Government emerged as a critical description of America's system, with frequent negative comparisons to Westminster. He said, "I am pointing out facts — diagnosing, not prescribing remedies." Wilson believed that America's intricate system of checks and balances was
the cause of the problems in American governance. He said that the
divided power made it impossible for voters to see who was accountable. Wilson singled out the United States House of Representatives for particular criticism. Wilson
said that the Congressional committee system was fundamentally
undemocratic in that committee chairs, who ruled by seniority,
determined national policy although they were responsible to no one
except their constituents; and that it facilitated corruption. By the time Wilson finished Congressional Government, Grover Cleveland was President, and Wilson's faith in the United States government was restored. When William Jennings Bryan captured
the Democratic nomination from Cleveland's supporters in 1896, however,
Wilson refused to support the ticket. Instead, he cast his ballot for John M. Palmer, the presidential candidate of the National Democratic Party, or Gold Democrats, a short-lived party that supported a gold standard, low tariffs, and limited government.