<Back to Index>
- Inventor Alexander Graham Bell, 1847
- Poet Edmund Waller, 1606
- Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Hungary Gyula Count Andrássy de Csíkszentkirály et Krasznahorka, 1823
PAGE SPONSOR
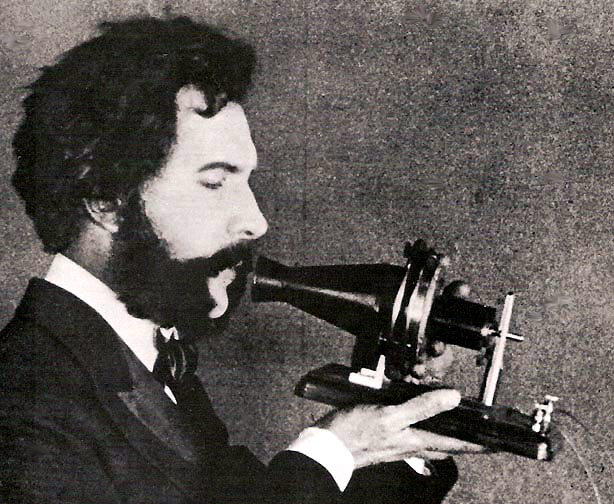
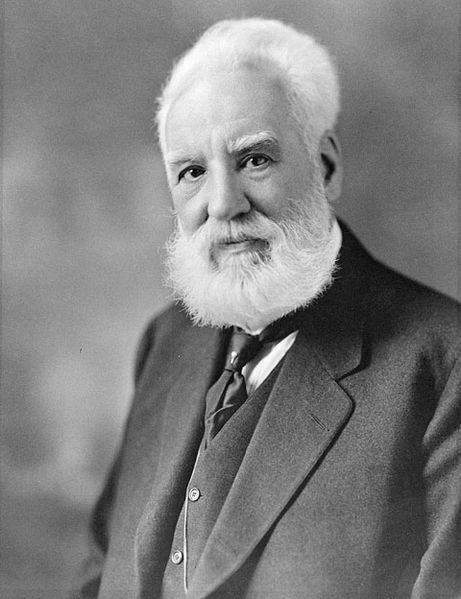

Alexander Graham Bell (March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was an eminent scientist, inventor, engineer and innovator who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone.
Bell's father, grandfather, and brother had all been associated with work on elocution and speech, and both his mother and wife were deaf, profoundly influencing Bell's life's work. His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices which eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the first U.S. patent for the telephone in 1876. In retrospect, Bell considered his most famous invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study. Many other inventions marked Bell's later life, including groundbreaking work in optical telecommunications, hydrofoils and aeronautics. In 1888, Alexander Graham Bell became one of the founding members of the National Geographic Society.
Alexander Bell was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, on March 3, 1847. The
family home was at 16 South Charlotte Street, and now has a
commemorative marker at the doorstep, marking it as Alexander Graham
Bell's birthplace. He had two brothers: Melville James Bell (1845 – 1870)
and Edward Charles Bell (1848 – 1867). Both of his brothers died of tuberculosis. His father was Professor Alexander Melville Bell, and his mother was Eliza Grace (née Symonds). Although he was born "Alexander", at age ten, he made a plea to his father to have a middle name like his two brothers. For
his 11th birthday, his father acquiesced and allowed him to adopt the
middle name "Graham", chosen out of admiration for Alexander Graham, a
Canadian being treated by his father and boarder who had become a
family friend. To close relatives and friends he remained "Aleck" which his father continued to call him into later life. As a child, young Alexander Graham Bell displayed a natural curiosity about his world, resulting in gathering botanical specimens as well as experimenting even at an early age. His best friend was Ben Herdman, a neighbour whose family operated a flour mill,
the scene of many forays. Young Aleck asked what needed to be done at
the mill. He was told wheat had to be dehusked through a laborious
process and at the age of 12, Bell built a homemade device that
combined rotating paddles with sets of nail brushes, creating a simple
dehusking machine that was put into operation and used steadily for a
number of years. In return, John Herdman gave both boys the run of a small workshop within which to "invent".
From
his early years, Bell showed a sensitive nature and a talent for art,
poetry and music that was encouraged by his mother. With no formal
training, he mastered the piano and became the family's pianist. Despite being normally quiet and introspective, he reveled in mimicry and "voice tricks" akin to ventriloquism that continually entertained family guests during their occasional visits. Bell
was also deeply affected by his mother's gradual deafness, (she began
to lose her hearing when he was 12) and learned a manual finger
language so he could sit at her side and tap out silently the
conversations swirling around the family parlour. He
also developed a technique of speaking in clear, modulated tones
directly into his mother's forehead wherein she would hear him with
reasonable clarity. Bell's preoccupation with his mother's deafness led him to study acoustics. His family was long associated with the teaching of elocution: his grandfather, Alexander Bell, in London, his uncle in Dublin,
and his father, in Edinburgh, were all elocutionists. His father
published a variety of works on the subject, several of which are still
well known, especially his The Standard Elocutionist (1860), which appeared in Edinburgh in 1868. The Standard Elocutionist appeared in 168 British editions and sold over a quarter of a million copies in
the United States alone. In this treatise, his father explains his
methods of how to instruct deaf-mutes (as
they were then known) to articulate words and read other people's lip
movements to decipher meaning. Aleck's father taught him and his
brothers not only to write Visible Speech but also to identify any symbol and its accompanying sound. Aleck
became so proficient that he became a part of his father's public
demonstrations and astounded audiences with his abilities in deciphering Latin, Gaelic and even Sanskrit symbols.
As
a young child, Bell, like his brothers, received his early schooling at
home from his father. At an early age, however, he was enrolled at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, Scotland, which he left at age 15, completing only the first four forms. His school record was undistinguished, marked by absenteeism and
lacklustre grades. His main interest remained in the sciences,
especially biology, while he treated other school subjects with
indifference, to the dismay of his demanding father. Upon
leaving school, Bell travelled to London to live with his grandfather,
Alexander Bell. During the year he spent with his grandfather, a love
of learning was born, with long hours spent in serious discussion and
study. The elder Bell took great efforts to have his young pupil learn
to speak clearly and with conviction, the attributes that his pupil
would need to become a teacher himself. At age 16, Bell secured a position as a "pupil-teacher" of elocution and music, in Weston House Academy, at Elgin, Moray,
Scotland. Although he was enrolled as a student in Latin and Greek, he
instructed classes himself in return for board and £10 per
session. The following year, he attended the University of Edinburgh; joining his older brother Melville who had enrolled there the previous year. Bell's father encouraged Aleck's interest in speech and, in 1863, took his sons to see a unique automaton, developed by Sir Charles Wheatstone based on the earlier work of Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen. The rudimentary "mechanical man" simulated a human voice.
Aleck was fascinated by the machine and after he obtained a copy of von
Kempelen's book, published in German, and had laboriously translated
it, he and his older brother Melville built their own automaton head.
Their father, highly interested in their project, offered to pay for
any supplies and spurred the boys on with the enticement of a "big
prize" if they were successful. While his brother constructed the throat and larynx,
Aleck tackled the more difficult task of recreating a realistic skull.
His efforts resulted in a remarkably lifelike head that could "speak",
albeit only a few words. The boys would carefully adjust the "lips" and when a bellows forced air through the windpipe, a very recognizable "Mama" ensued, to the delight of neighbors who came to see the Bell invention. Intrigued by the results of the automaton, Bell continued to experiment with a live subject, the family's Skye Terrier, "Trouve". After he taught it to growl continuously, Aleck would reach into its mouth and manipulate the dog's lips and vocal cords to
produce a crude-sounding "Ow ah oo ga ma ma." With little convincing,
visitors believed his dog could articulate "How are you grandma?" More
indicative of his playful nature, his experiments convinced onlookers
that they saw a "talking dog." However,
these initial forays into experimentation with sound led Bell to
undertake his first serious work on the transmission of sound, using tuning forks to explore resonance. At the age of 19, he wrote a report on his work and sent it to philologist Alexander Ellis, a colleague of his father (who would later be portrayed as Professor Henry Higgins in Pygmalion). Ellis
immediately wrote back indicating that the experiments were similar to
existing work in Germany. Dismayed to find that groundbreaking work had
already been undertaken by Hermann von Helmholtz who had conveyed vowel sounds by means of a similar tuning fork "contraption", he pored over the German scientist's book, Sensations of Tone.
Working from his own errant mistranslation of the original German
edition, Aleck fortuitously then made a deduction that would be the
underpinning of all his future work on transmitting sound, reporting: "Without knowing much about the subject, it seemed to me that if vowel sounds could be produced by electrical means so could consonants, so could articulate speech", and also later remarking: "I
thought that Helmhotz had done it ... and that my failure was due only
to my ignorance of electricity. It was a valuable blunder ... If I had
been able to read German in those days, I might never have commenced my
experiments!" In 1865, when the Bell family moved to London, Bell returned to Weston House as an assistant master and, in his spare hours, continued experiments on sound using a minimum of laboratory equipment. Bell concentrated on experimenting with electricity to convey sound and later installed a telegraph wire from his room in Somerset College to that of a friend. Throughout
late 1867, his health faltered mainly through exhaustion. His younger
brother, Edward "Ted," was similarly bed-ridden, suffering from tuberculosis. While Bell recovered (by then referring to himself in correspondence as
"A.G. Bell") and served the next year as an instructor at Somerset College, Bath, Somerset,
England, his brother's condition deteriorated. Edward would never
recover. Upon his brother's death, Bell returned home in 1867. His
older brother, Melville had married and moved out. With aspirations to
obtain a degree at the University College London,
Bell considered his next years as preparation for the degree
examinations, devoting his spare time at his family's residence to
studying. Helping his father in Visible Speech demonstrations and lectures brought Bell to Susanna E. Hull's private school for the deaf in South Kensington,
London. His first two pupils were "deaf mute" girls who made remarkable
progress under his tutelage. While his older brother seemed to achieve
success on many fronts including opening his own elocution school,
applying for a patent on an invention, and starting a family, Bell
continued as a teacher. However, in May 1870, Melville died from
complications due to tuberculosis, causing a family crisis. His father
had also suffered a debilitating illness earlier in life and had been
restored to health by a convalescence in Newfoundland.
Bell's parents embarked upon a long-planned move when they realized
that their remaining son was also sickly. Acting decisively, Alexander
Melville Bell asked Bell to arrange for the sale of all the family
property, conclude all of his brother's affairs (Bell took over his last student, curing a pronounced lisp), and join his father and mother in setting out for the "New World". Reluctantly,
Bell also had to conclude a relationship with Marie Eccleston, who, he
had surmised, was not prepared to leave England with him. In 1870, at age 23, Bell, his brother's widow, Caroline (Margaret Ottaway), and his parents travelled on the SS Nestorian to Canada. After landing at Quebec City, the Bells boarded a train to Montreal and later to Paris, Ontario, to
stay with the Reverend Thomas Henderson, a family friend. After a brief
stay with the Hendersons, the Bell family purchased a 10-and-a-half
acre farm at Tutelo Heights (now called Tutela Heights), near Brantford, Ontario. The property consisted of an orchard, large farm house, stable, pigsty, hen-house and a carriage house, which bordered the Grand River. At the homestead, Bell set up his own workshop in the converted carriage house near to what he called his "dreaming place", a large hollow nestled in trees at the back of the property above the river. Despite his frail condition upon arriving in Canada, Bell found the climate and environs to his liking, and rapidly improved. He continued his interest in the study of the human voice and when he discovered the Six Nations Reserve across the river at Onondaga, he learned the Mohawk language and
translated its unwritten vocabulary into Visible Speech symbols. For
his work, Bell was awarded the title of Honorary Chief and participated
in a ceremony where he donned a Mohawk headdress and danced traditional dances. After setting up his workshop, Bell continued experiments based on Helmholtz's work with electricity and sound. He designed a piano, which, by means of electricity, could transmit its music at a distance.
Once the family was settled in, both Bell and his father made plans to
establish a teaching practice and in 1871, he accompanied his father to
Montreal, where Melville was offered a position to teach his System of
Visible Speech. Subsequently, his father was invited by Sarah Fuller, principal of the Boston School for Deaf Mutes (which continues today as the public Horace Mann School for the Deaf), in Boston, Massachusetts,
United States, to introduce the Visible Speech System by providing
training for Fuller's instructors, but he declined the post, in favor
of his son. Traveling to Boston in April 1871, Bell proved successful
in training the school's instructors. He was subsequently asked to repeat the program at the American Asylum for Deaf-mutes in Hartford, Connecticut, and the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts. Returning home to Brantford after six months abroad, Bell continued his experiments with his "harmonic telegraph". The
basic concept behind his device was that messages could be sent through
a single wire if each message was transmitted at a different pitch, but
work on both the transmitter and receiver was needed. Unsure
of his future, he first contemplated returning to London to complete his studies, but decided to return to Boston as a teacher. His father helped him set up his private practice by contacting Gardiner Greene Hubbard,
the president of the Clarke School for the Deaf for a recommendation.
Teaching his father's system, in October 1872 Alexander Bell opened his
"School of Vocal Physiology and Mechanics of Speech" in Boston, which
attracted a large number of deaf pupils with his first class numbering
30 students. While he was working as a private tutor, one of his most famous pupils was Helen Keller,
who came to him as a young child unable to see, hear, or speak. She was
later to say that Bell dedicated his life to the penetration of that
"inhuman silence which separates and estranges." Several
influential people of the time, including Bell, viewed deafness as
something that ought to be eradicated, and also believed that with
resources and effort they could teach the deaf to speak and avoid the
use of sign language, thus enabling their integration within the wider society from which many were often being excluded. However
in several schools children were mistreated, for example by having
their hands tied behind their backs so they could not communicate by
signing — the only language they knew — and were therefore forced to
attempt oral communication.
In the following year, Bell became professor of Vocal Physiology and Elocution at the Boston University School
of Oratory. During this period, he alternated between Boston and
Brantford, spending summers in his Canadian home. At Boston University,
Bell was "swept up" by the excitement engendered by the many scientists
and inventors residing in the city. He continued his research in sound
and endeavored to find a way to transmit musical notes and
articulate speech, but although absorbed by his experiments, he found
it difficult to devote enough time to experimentation. While days and
evenings were occupied by his teaching and private classes, Bell began
to stay awake late into the night, running experiment after experiment
in rented facilities at his boarding house. Keeping up "night owl"
hours, he worried that his work would be discovered and took great
pains to lock up his notebooks and laboratory equipment. Bell had a
specially made table where he could place his notes and equipment
inside a locking cover. Worse still, his health deteriorated as he suffered severe headaches. Returning to Boston in fall 1873, Bell made a fateful decision to concentrate on his experiments in sound.
Deciding
to give up his lucrative private Boston practice, Bell only retained
two students, six-year old "Georgie" Sanders, deaf from birth and
15-year old Mabel Hubbard. Each pupil would serve to play an important
role in the next developments. George's father, Thomas Sanders, a
wealthy businessman, offered Bell a place to stay at nearby Salem with
Georgie's grandmother, complete with a room to "experiment". Although
the offer was made by George's mother and followed the year-long
arrangement in 1872 where her son and his nurse had moved to quarters
next to Bell's boarding house, it was clear that Mr. Sanders was
backing the proposal. The arrangement was for teacher and student to
continue their work together with free room and board thrown in. Mabel
was a bright, attractive girl who was ten years his junior but became
the object of Bell's affection. Losing her hearing after a bout of scarlet fever at age five, she had learned to read lips but her father, Gardiner Greene Hubbard, Bell's benefactor and personal friend, wanted her to work directly with her teacher. By
1874, Bell's initial work on the harmonic telegraph had entered a
formative stage with progress it made both at his new Boston
"laboratory" (a rented facility) as well as at his family home in
Canada a big success. While working that summer in Brantford, Bell experimented with a "phonautograph", a pen-like machine that could draw shapes of sound waves on smoked glass by
tracing their vibrations. Bell thought it might be possible to generate
undulating electrical currents that corresponded to sound waves. Bell
also thought that multiple metal reeds tuned to different frequencies
like a harp would be able to convert the undulatory currents back into
sound. But he had no working model to demonstrate the feasibility of
these ideas. In 1874, telegraph message traffic was rapidly expanding and in the words of Western Union President William Orton, had become "the nervous system of commerce". Orton had contracted with inventors Thomas Edison and Elisha Gray to find a way to send multiple telegraph messages on each telegraph line to avoid the great cost of constructing new lines. When
Bell mentioned to Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders that he was
working on a method of sending multiple tones on a telegraph wire using
a multi-reed device, the two wealthy patrons began to financially
support Bell's experiments. Patent matters would be handled by Hubbard's patent attorney, Anthony Pollok. In March 1875, Bell and Pollok visited the famous scientist Joseph Henry, who was then director of the Smithsonian Institution,
and asked Henry's advice on the electrical multi-reed apparatus that
Bell hoped would transmit the human voice by telegraph. Henry replied
that Bell had "the germ of a great invention". When Bell said that he
did not have the necessary knowledge, Henry replied, "Get it!" That
declaration greatly encouraged Bell to keep trying, even though he did
not have the equipment needed to continue his experiments, nor the
ability to create a working model of his ideas. However, a chance
meeting in 1874 between Bell and Thomas A. Watson, an experienced electrical designer and mechanic at the electrical machine shop of Charles Williams, changed all that. With
financial support from Sanders and Hubbard, Bell was able to hire
Thomas Watson as his assistant and the two of them experimented with acoustic telegraphy.
On 2 June 1875, Watson accidentally plucked one of the reeds and Bell,
at the receiving end of the wire, heard the overtones of the reed;
overtones that would be necessary for transmitting speech. That
demonstrated to Bell that only one reed or armature was necessary, not
multiple reeds. This led to the "gallows" sound powered telephone, which was able to transmit indistinct, voice-like sounds, but not clear speech.
In 1875, Bell developed an acoustic telegraph and drew up a patent application for
it. Since he had agreed to share U.S. profits with his investors
Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders, Bell requested that an associate
in Ontario, George Brown,
attempt to patent it in Britain, instructing his lawyers to apply for a
patent in the U.S. only after they received word from Britain (Britain
would issue patents only for discoveries not previously patented
elsewhere). Meanwhile,
Elisha Gray was also experimenting with acoustic telegraphy and thought
of a way to transmit speech using a water transmitter. On February 14,
1876, Gray filed a caveat with
the U.S. Patent Office for a telephone design that used a water
transmitter. That same morning, Bell's lawyer filed Bell's application
with the patent office.
There is considerable debate about who arrived first and Gray later
challenged the primacy of Bell's patent. Bell was in Boston on February
14, 1876. Bell's patent 174,465, was issued to Bell on March 7, 1876, by the U.S. Patent Office.
Bell's patent covered "the method of, and apparatus for, transmitting
vocal or other sounds telegraphically ... by causing electrical
undulations, similar in form to the vibrations of the air accompanying
the said vocal or other sound" Bell
returned to Boston the same day and the next day resumed work, drawing
in his notebook a diagram similar to that in Gray's patent caveat. On
March 10, 1876, three days after his patent was issued, Bell succeeded
in getting his telephone to work, using a liquid transmitter similar to
Gray's design. Vibration of the diaphragm caused a needle to vibrate in
the water, varying the electrical resistance in the circuit. When Bell spoke the famous sentence "Mr Watson — Come here — I want to see you" into the liquid transmitter, Watson, listening at the receiving end in an adjoining room, heard the words clearly.
Although Bell was accused, and is still accused, of stealing the
telephone from Gray, Bell used Gray's water transmitter design only
after Bell's patent was granted and only as a proof of concept scientific
experiment to prove to his own satisfaction that intelligible
"articulate speech" (Bell's words) could be electrically transmitted. After
March 1876, Bell focused on improving the electromagnetic telephone and
never used Gray's liquid transmitter in public demonstrations or
commercial use. The patent examiner, Zenas Fisk Wilber, later stated in a sworn affidavit that he was an alcoholic who was much in debt to Bell's lawyer, Marcellus Bailey,
with whom he had served in the Civil War. He claimed he showed Gray's
patent caveat to Bailey. Wilber also claimed (after Bell arrived in
Washington D.C. from Boston) that he showed Gray's caveat to Bell and
that Bell paid him $100. Bell claimed they discussed the patent only in
general terms, although in a letter to Gray, Bell admitted that he
learned some of the technical details. Bell denied in a sworn affidavit
that he ever gave Wilber any money. Continuing
his experiments in Brantford, Bell brought home a working model of his
telephone. On August 3, 1876, from the telegraph office in Mount Pleasant five
miles (8 km) away from Brantford, Bell sent a tentative telegram
indicating that he was ready. With curious onlookers packed into the
office as witnesses, faint voices were heard replying. The following
night, he amazed guests as well as his family when a message was
received at the Bell home from Brantford, four miles (six km) distant
along an improvised wire strung up along telegraph lines and fences,
and laid through a tunnel. This time, guests at the household distinctly heard people in Brantford reading and singing. These
experiments clearly proved that the telephone could work over long
distances. Bell
and his partners, Hubbard and Sanders, offered to sell the patent
outright to Western Union for $100,000. The president of Western Union
balked, countering that the telephone was nothing but a toy. Two years
later, he told colleagues that if he could get the patent for $25
million he would consider it a bargain. By then, the Bell company no
longer wanted to sell the patent. Bell's
investors would become millionaires while he fared well from residuals
and at one point had assets of nearly one million dollars. Bell began a series of public demonstrations and lectures in order to introduce the new invention to the scientific community as well as the general public. Only one day after, his demonstration of an early telephone prototype at the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia made the telephone the featured headline worldwide. Influential visitors to the exhibition included Emperor Pedro II of Brazil, and later Bell had the opportunity to demonstrate the invention personally to William Thomson, a renowned Scottish scientist and even Queen Victoria who had requested a private audience at Osborne House, her Isle of Wight home; she called the demonstration "most extraordinary". The enthusiasm
surrounding Bell's public displays laid the groundwork for universal
acceptance of the revolutionary device. The Bell Telephone Company was
created in 1877, and by 1886, over 150,000 people in the U.S. owned
telephones. Bell company engineers made numerous other improvements to
the telephone, which emerged as one of the most successful products
ever. In 1879, the Bell company acquired Edison's patents for the carbon microphone from
Western Union. This made the telephone practical for long distances and
it was no longer necessary to shout to be heard at the receiving
telephone. In January 1915, Bell made the first ceremonial transcontinental telephone call. Calling from the AT&T head office at 15 Day Street in New York City, Bell was heard by Thomas Watson at 333 Grant Avenue in San Francisco. The New York Times reported: As
is sometimes common in scientific discoveries, simultaneous
developments can occur, as evidenced by a number of inventors who were
at work on the telephone. Over
a period of 18 years, the Bell Telephone Company faced over 600
lawsuits posing legal challenges concerning the rights to the
telephone, but none was successful in establishing priority over the
original Bell patent and the Bell Telephone Company never lost a case that had proceeded to a final trial stage. Bell's laboratory notes and family letters were the key to establishing a long lineage to his experiments. The Bell company lawyers successfully fought off myriad lawsuits generated initially around the challenges by Elisha Gray and Amos Dolbear.
In personal correspondence to Bell, both Gray and Dolbear had
acknowledged his prior work, which considerably weakened their later
claims. On
13 January 1887, the United States Government moved to annul the patent
issued to Bell on the grounds of fraud and misrepresentation. After a
series of decisions and reversals, the Bell company won a decision in the Supreme Court, though a couple of the original claims from the lower court cases were left undecided. By
the time that the trial wound its way through nine years of legal
battles, the U.S. prosecuting attorney had died and the two Bell
patents (No. 174,465 and dated 7 March 1876 and No. 186,787 dated
January 30, 1877) were no longer in effect, although the presiding
judges agreed to continue the proceedings due to the case's importance
as a "precedent." With a change in administration and charges of conflict of interest (on both sides) arising from the original trial, the U.S. Attorney General dropped the law suit on 30 November 1897 leaving several issues undecided on the merits. During a deposition filed for the 1887 trial, Italian inventor Antonio Meucci also
claimed to have created the first working model of a telephone in Italy
in 1834. In 1886, in the first of three cases in which he was involved,
Meucci took the stand as a witness in the hopes of establishing his
invention's priority. Meucci's evidence in this case was disputed due
to a lack of material evidence for his inventions as his working models
were purportedly lost at the laboratory of American District Telegraph (ADT) of New York, which later, in 1901, was incorporated as a subsidiary of Western Union. Meucci's
work, like many other inventors of the period, was based on earlier
acoustic principles and despite evidence of earlier experiments, the
final case involving Meucci was eventually dropped upon Meucci's death. However, due to the efforts of Congressman Vito Fossella, the U.S. House of Representatives on
11 June 2002 stated that Meucci's "work in the invention of the
telephone should be acknowledged", even though this did not put an end
to a still contentious issue. Some modern scholars do not agree with the claims that Bell's work on the telephone was influenced by Meucci's inventions. The
value of the Bell patent was acknowledged throughout the world, and
patent applications were made in most major countries, but when Bell
had delayed the German patent application, the electrical firm of Siemens & Halske (S&H) managed
to set up a rival manufacturer of Bell telephones under their own
patent. The Siemens company produced near-identical copies of the Bell
telephone without having to pay royalties. A
series of agreements in other countries eventually consolidated a
global telephone operation. The strain put on Bell by his constant
appearances in court, necessitated by the legal battles, eventually
resulted in his resignation from the company. On July 11, 1877, a few days after the Bell Telephone Company was established, Bell married Mabel Hubbard (1857 – 1923) at the Hubbard estate in Cambridge. His wedding present to his bride was to turn over 1,487 of his 1,497 shares in the newly created Bell Telephone Company. Shortly
thereafter, the newlyweds embarked on a year-long honeymoon in Europe.
During that excursion, Alec took a handmade model of his telephone with
him, making it a "working holiday". The courtship had begun years
earlier, however Alexander waited until he was more financially secure
before marrying. Although the telephone appeared to be an "instant"
success, it was not initially a profitable venture and Bell's main
sources of income were from lectures until after 1897. One unusual request exacted by his fiancée was that he use "Alec"
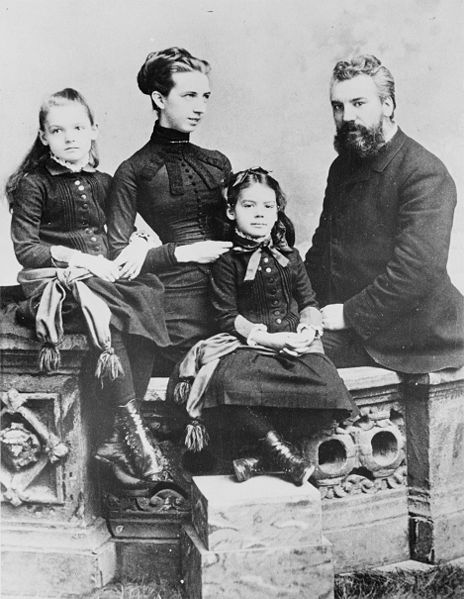
rather than the family's earlier familiar name of "Aleck." From 1876, he would sign his name "Alec Bell." They had four children: Elsie May Bell (1878 – 1964) who married Gilbert Grosvenor of National Geographic fame, Marian Hubbard Bell (1880 – 1962) who was referred to as "Daisy", and two sons who died in infancy. The Bell family home was located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, until 1880 when Bell's father-in-law bought a house in Washington, D.C.,
and later in 1882 in the same city for Bell's family, so that they
could be with him while he attended to the numerous court cases
involving patent disputes. Bell was a British subject throughout his early life in Scotland and later in Canada until 1882, when he became a naturalized citizen of the United States. In 1915, he characterized his status as: "I am not one of those hyphenated Americans who claim allegiance to two countries." Despite
this declaration, Bell has been proudly claimed as a "native son" by
all four countries he resided in: the United States, Canada, Scotland
and the United Kingdom. By 1885, a new summer retreat was contemplated. That summer, the Bells had a vacation on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, spending time at the small village of Baddeck. Returning in 1886, Bell started building an estate on a point across from Baddeck, overlooking Bras d'Or Lake. By 1889, a large house, christened The Lodge was completed and two years later, a larger complex of buildings, including a new laboratory, were begun that the Bells would name Beinn Bhreagh (Gaelic: beautiful mountain) after Alec's ancestral Scottish highlands. Bell
would spend his final, and some of his most productive, years in
residence in both Washington, D.C., where he and his family initially
resided for most of the year, and at Beinn Bhreagh. Until the end of his life, Bell and his family would alternate between the two homes, but Beinn Bhreagh would,
over the next 30 years, become more than a summer home as Bell became
so absorbed in his experiments that his annual stays lengthened. Both
Mabel and Alec became immersed in the Baddeck community and were
accepted by the villagers as "their own". The Bells were still in residence at Beinn Bhreagh when the Halifax Explosion occurred on 6 December 1917. Mabel and Alec mobilized the community to help victims in Halifax. Although
Alexander Graham Bell is most often associated with the invention of
the telephone, his interests were extremely varied. According to one of
his biographers, Charlotte Gray, Bell's work ranged "unfettered across the scientific landscape" and he often went to bed voraciously reading the Encyclopædia Britannica, scouring it for new areas of interest. The
range of Bell's inventive genius is represented only in part by the 18
patents granted in his name alone and the 12 he shared with his
collaborators. These included 14 for the telephone and telegraph, four
for the photophone, one for the phonograph, five for aerial vehicles, four for "hydroairplanes" and two for selenium cells. Bell's inventions spanned a wide range of interests and included a metal jacket to assist in breathing, the audiometer to
detect minor hearing problems, a device to locate icebergs,
investigations on how to separate salt from seawater, and work on
finding alternative fuels. Bell worked extensively in medical research and invented techniques for teaching speech to the deaf. During his Volta Laboratory period, Bell and his associates considered impressing a magnetic field on
a record as a means of reproducing sound. Although the trio briefly
experimented with the concept, they were unable to develop a workable
prototype. They abandoned the idea, never realizing they had glimpsed a
basic principle which would one day find its application in the tape recorder, the hard disc and floppy disc drive and other magnetic media. Bell's own home used a primitive form of air conditioning,
in which fans blew currents of air across great blocks of ice. He also
anticipated modern concerns with fuel shortages and industrial
pollution. Methane gas,
he reasoned, could be produced from the waste of farms and factories.
At his Canadian estate in Nova Scotia, he experimented with composting toilets and
devices to capture water from the atmosphere. In a magazine interview
published shortly before his death, he reflected on the possibility of
using solar panels to heat houses.
Bell is also credited with the invention of the metal detector in 1881. The device was quickly put together in an attempt to find the bullet in the body of U.S. President James Garfield.
The metal detector worked flawlessly in tests but did not find the
assassin's bullet partly because the metal bed frame on which the
President was lying disturbed the instrument, resulting in static. The
president's surgeons, who were skeptical of the device, ignored Bell's
requests to move the president to a bed not fitted with metal springs.
Alternatively, although Bell had detected a slight sound on his first
test, the bullet may have been lodged too deeply to be detected by the
crude apparatus. Bell gave a full account of his experiments in a paper read before the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in August 1882. The March 1906 Scientific American article by American hydrofoil pioneer William E. Meacham explained the basic principle of hydrofoils and hydroplanes.
Bell considered the invention of the hydroplane as a very significant
achievement. Based on information gained from that article he began to
sketch concepts of what is now called a hydrofoil boat. Bell and
assistant Frederick W. "Casey" Baldwin began
hydrofoil experimentation in the summer of 1908 as a possible aid to
airplane takeoff from water. Baldwin studied the work of the Italian
inventor Enrico Forlanini and began testing models. This led him and Bell to the development of practical hydrofoil watercraft. During
his world tour of 1910 – 1911, Bell and Baldwin met with Forlanini in
France. They had rides in the Forlanini hydrofoil boat over Lake Maggiore.
Baldwin described it as being as smooth as flying. On returning to
Baddeck, a number of initial concepts were built as experimental
models, including the Dhonnas Beag, the first self-propelled Bell-Baldwin hydrofoil. The experimental boats were essentially proof-of-concept prototypes that culminated in the more substantial HD-4, powered by Renault engines. A top speed of 54 miles per hour (87 km/h)
was achieved, with the hydrofoil exhibiting rapid acceleration, good
stability and steering along with the ability to take waves without
difficulty. In 1913, Dr. Bell hired Walter Pinaud, a Sydney yacht designer and builder as well as the proprietor of Pinaud's Yacht Yard in Westmount, Nova Scotia, to
work on the pontoons of the HD-4. Pinaud soon took over the boatyard at
Bell Laboratories on Beinn Bhreagh, Bell's estate near Baddeck, Nova Scotia. Pinaud's experience in boat-building enabled him to make useful design changes to the HD-4. After the First World War, work began again on the HD-4. Bell's report to the U.S. Navy permitted him to obtain two 350 horsepower (260 kW)
engines in July 1919. On 9 September 1919, the HD-4 set a world marine
speed record of 70.86 miles per hour (114.04 km/h), a record which stood for ten years. In 1891, Bell had begun experiments to develop motor-powered heavier-than-air aircraft.
The AEA was first formed as Bell shared the vision to fly with his
wife, who advised him to seek "young" help as Alexander was at the
graceful age of 60. In 1898, Bell experimented with tetrahedral box kites and wings constructed of multiple compound tetrahedral kites covered in silk. The tetrahedral wings were named Cygnet I, II and III, and were flown both unmanned and manned (Cygnet I crashed during a flight carrying Selfridge) in the period from 1907 – 1912. Some of Bell's kites are on display at the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site. Bell was a supporter of aerospace engineering research through the Aerial Experiment Association (AEA), officially formed at Baddeck, Nova Scotia, in October 1907 at the suggestion of his wife Mabel and with her financial support after she sold off a parcel of her land in Nova Scotia. The AEA was headed by Bell and the founding members were four young men: American Glenn H. Curtiss,
a motorcycle manufacturer at the time and who held the title "world's
fastest man", having ridden his self-constructed motor bicycle around
in the shortest time, and who was later awarded the Scientific American Trophy for the first official one kilometre flight in the Western hemisphere, and who later became a world renowned airplane manufacturer; Lieutenant Thomas Selfridge, an official observer from the U.S. government and the only person in the army who believed aviation was the future, Frederick W. Baldwin, the first Canadian and first British subject to pilot a public flight in Hammondsport, New York; and J.A.D. McCurdy;
both engineering students at University of Toronto. The
AEA's work progressed to heavier than air machines, applying their
knowledge of kites to gliders. Moving to Hammondsport, the group then
designed and built the Red Wing, framed in bamboo and covered in red silk and powered by a small air-cooled engine. On March 12, 1908, over Keuka Lake, the biplane lifted off on the first public flight in North America. The innovations that were incorporated into this design included a cockpit enclosure and tail rudder (later variations on the original design would add ailerons as a means of control). One of the AEA project's inventions, the aileron, is a standard component of aircraft today. (The aileron was also invented independently by Robert Esnault-Pelterie.) The White Wing and June Bug were
to follow and by the end of 1908, over 150 flights without mishap had
been accomplished. However, the AEA had depleted its initial reserves
and only a $10,000 grant from Mrs. Bell allowed it to continue with
experiments. Their final aircraft design, the Silver Dart embodied all of the advancements found in the earlier machines. On February 23, 1909, Bell was present as the Silver Dart flown
by J.A.D. McCurdy from the frozen ice of Bras d'Or, made the first
aircraft flight in Canada. Bell had worried that the flight was too
dangerous and had arranged for a doctor to be on hand. With the
successful flight, the AEA disbanded and the Silver Dart would
revert to Baldwin and McCurdy who began the Canadian Aerodrome Company
and would later demonstrate the aircraft to the Canadian Army.
Bell was connected with the eugenics movement in the United States. In his lecture Memoir upon the formation of a deaf variety of the human race presented to the National Academy of Sciences on
13 November 1883 he noted that congenitally deaf parents were more
likely to produce deaf children and tentatively suggested that couples
where both parties were deaf should not marry. However, it was his hobby of livestock breeding which led to his appointment to biologist David Starr Jordan's Committee on Eugenics, under the auspices of the American Breeders Association. The committee unequivocally extended the principle to man. From 1912 until 1918 he was the chairman of the board of scientific advisers to the Eugenics Record Office associated with Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory in New York, and regularly attended meetings. In 1921, he was the honorary president of the Second International Congress of Eugenics held under the auspices of the American Museum of Natural History in New York. Organisations such as these advocated passing laws (with success in some states) that established the compulsory sterilization of people deemed to be, as Bell called them, a "defective variety of the
human race". By the late 1930s, about half the states in the U.S. had
eugenics laws, and the California laws were used as a model for eugenics laws in Nazi Germany. Bell died of diabetes on August 2, 1922, at his private estate, Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, at age 75. Bell had also been afflicted with pernicious anemia. His last view of the earth he had inhabited was of the moon ascending over the beloved mountain on his estate at 2:00 A.M. While tending to her husband after a long illness, Mabel whispered, "Don't leave me." By way of reply, Bell traced the sign for no — and then he expired. On learning of Bell's death, Canadian Prime Minister Mackenzie King cabled Mrs. Bell, saying: [The
Government expresses] to you our sense of the world's loss in the death
of your distinguished husband. It will ever be a source of pride to our
country that the great invention, with which his name is immortally
associated, is a part of its history. On the behalf of the citizens of
Canada, may I extend to you an expression of our combined gratitude and
sympathy. Bell's coffin was constructed of Beinn Bhreagh pine
by his laboratory staff, lined with the same red silk fabric used in
his tetrahedral kite experiments. In order to help celebrate his life,
his wife asked guests not to wear black (the traditional funeral
colour) while attending his service, during which soloist Jean
MacDonald sang a verse of Robert Louis Stevenson's 'Requiem': Under a wide and starry sky, Upon the conclusion of Bell's funeral, "every
phone on the continent of North America was silenced in honor of the
man who had given to mankind the means for direct communication at a
distance". Dr.
Alexander Graham Bell was buried atop Beinn Bhreagh mountain, on his
estate where he had resided increasingly for the last 35 years of his
life, overlooking Bras d'Or Lake. He was survived by his wife Mabel and his two daughters, Elisa May and Marion.
Dig the grave and let me lie.
Glad did I live and gladly die
And I lay me down with a will.