<Back to Index>
- Anatomist Hieronymus Fabricius, 1537
- Painter Francis Cotes, 1726
- Defense and Foreign Minister of Israel Moshe Dayan, 1915
PAGE SPONSOR
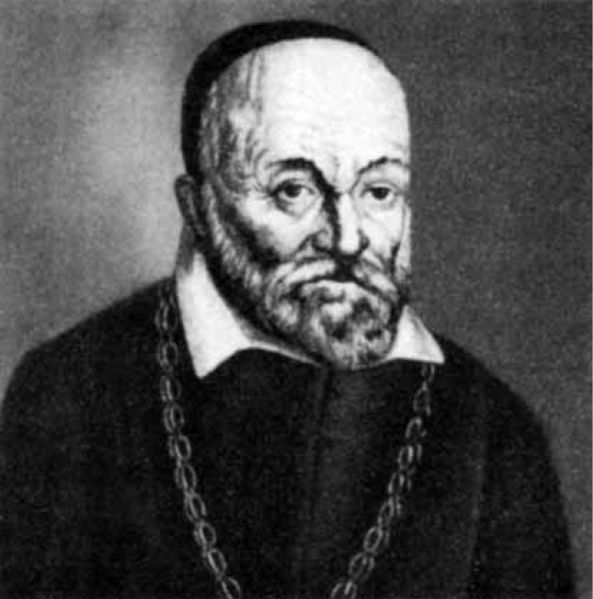

Hieronymus Fabricius or Girolamo Fabrizio or by his Latin name Fabricus ab Aquapendende also Girolamo Fabrizi d'Acquapendente (1537 – 1619) was a pioneering anatomist and surgeon known in medical science as "The Father of Embryology."
Born in Acquapendente, Latium, Fabricius studied at the University of Padua, receiving a Doctor of Medicine degree in 1559 under the guidance of Gabriele Falloppio. He became professor of anatomy and surgery at Padua from 1562, a position which he held until 1604. In 1565, Fabricius succeeded Falloppio as chairman of the department of anatomy.
In 1594 he revolutionized the teaching of anatomy when he designed the first permanent theater for public anatomical dissections. Julius Casserius (1561 – 1616) of Piacenza was among Fabricius' students. William Harvey (1578 – 1657) and Adriaan van den Spiegel (1578 – 1625) also studied under Fabricius, beginning around 1598. Julius Casserius would later succeed Fabricius as Professor of Anatomy at the University of Padua in 1604, and Adriaan van den Spiegel succeeded Casserius in that position in 1615.
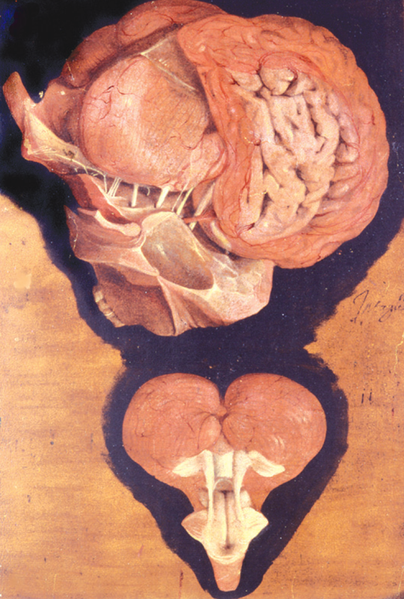
By dissecting animals, Fabricius investigated the formation of the fetus, the structure of the esophagus, stomach and intestines, and the peculiarities of the eye, the ear, and the larynx. He was the first to describe the membranous folds that he called "valves" in the interior of veins. These valves are now understood to prevent retrograde flow of blood within the veins, thus facilitating antegrade flow of blood towards the heart, though Fabricius did not understand their role at that time.
In his Tabulae Pictae, first published in 1600, Fabricius described the cerebral fissure separating the temporal lobe from the frontal lobe. However, Fabricius' discovery was not recognized until recently. Instead, Danish anatomist Caspar Bartholini credits Franciscus Sylvius with the discovery, and Bartholin's son Thomas named it the Sylvian fissure in the 1641 edition of the textbook Institutiones anatomicae.
The Bursa of Fabricius (the site of hematopoiesis in birds) is named after Fabricius. A manuscript entitled De Formatione Ovi et Pulli, found among his lecture notes after his death, was published in 1621. It contains the first description of the bursa.
Fabricius contributed much to the field of surgery. Though he never actually performed a tracheotomy, his writings include descriptions of the surgical technique. He favored using a vertical incision and was the first to introduce the idea of a tracheostomy tube. This was a straight, short cannula that incorporated wings to prevent the tube from disappearing into the trachea. He recommended the operation only as a last resort, to be used in cases of airway obstruction by foreign bodies or secretions. Fabricius' description of the tracheotomy procedure is similar to that used today.
Julius Casserius published his own writings regarding technique and equipment for tracheotomy. Casserius recommended using a curved silver tube with several holes in it. Marco Aurelio Severino (1580 – 1656), a skilful surgeon and anatomist, performed at least one tracheotomy during a diphtheria epidemic in Naples in 1610, using the vertical incision technique recommended by Fabricius.