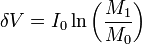<Back to Index>
- Rocket Scientist Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky, 1857
- Writer Gottlieb Wilhelm Rabener, 1714
- 2nd President of Sri Lanka Junius Richard Jayewardene, 1906
PAGE SPONSOR



Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (17 September [O.S. 5 September] 1857 – 19 September 1935) was an Imperial Russian and Soviet rocket scientist and pioneer of the astronautic theory. Along with the German Hermann Oberth and the American Robert H. Goddard, he is considered to be one of the founding fathers of rocketry and astronautics. His works later inspired leading Soviet rocket engineers such as Sergey Korolyov and Valentin Glushko and contributed to the early success of the Soviet space program.
Tsiolkovsky spent most of his life in a log house on the outskirts of Kaluga, about 200 km (125 miles) southwest of Moscow. A recluse by nature, he appeared strange and bizarre to his fellow town-folk.
He was born in Izhevskoye (now in Spassky District, Ryazan Oblast), in the Russian Empire, to a middle class family. His father, Edward Tsiolkovsky (in Polish: Ciołkowski), was Polish; his mother, Maria Yumasheva, was an educated Russian woman of Tartar descent. His father was a Polish patriot deported to Russia as a result of his revolutionary political activities. At the age of 9, Konstantin caught scarlet fever and became hard of hearing. He was not admitted to elementary schools because of his hearing problem, so he was self-taught.
After falling behind in his studies, Tsiolkovsky spent 3 years attending a library where Russian cosmism proponent Nikolai Fyodorov worked. He later came to believe that colonizing space would lead to the perfection of the human race, with immortality and a carefree existence. Additionally, inspired by the fiction of Jules Verne, Tsiolkovsky theorized many aspects of space travel and rocket propulsion. He is considered the father of spaceflight and the first man to conceive the space elevator, becoming inspired in 1895 by the newly constructed Eiffel Tower in Paris.
Tsiolkovsky worked as a high school mathematics teacher until retiring in 1920. He did not particularly flourish under a communist system, in particular Tsiolkovsky's support of eugenics made him politically unpopular. However, from the mid 1920s onwards the importance of his other work was acknowledged, and he was honoured for it. He died on 19 September 1935 in Kaluga and was buried in state.
Tsiolkovsky stated that he developed the theory of rocketry only as a supplement to its philosophical researches. He wrote more than 400 works, most of which are little known to the general reader because of their questionable value.
During his lifetime he published over 88 works on space travel and related subjects. Among his works are designs for rockets with steering thrusters, multi-stage boosters, space stations, airlocks for exiting a spaceship into the vacuum of space, and closed cycle biological systems to provide food and oxygen for space colonies.
The first scientific study of Tsiolkovsky refers to the year 1880 - 1881. Unaware of the discoveries already made, he wrote a paper called "Theory of Gases," in which he outlined the basis of the kinetic theory of gases. His second work - "The mechanics of the animal organism" received favorable feedback and Tsiolkovsky was inducted in to the Russian Physico - Chemical Society. The main works of Tsiolkovsky after 1884 were on four major areas: the scientific rationale for the all-metal balloon (Airship), the streamlined airplane, trains, hovercrafts, and rockets for interplanetary travel.
Tsiolkovsky developed the first aerodynamic laboratory in Russia in his apartment. In 1897, he built the first Russian wind tunnel with an open test section, developed a method to experiment in it and in 1900 on a grant by the Academy of Sciences he determined the drag coefficient of the ball, flat plates, cylinders, cones and other bodies. Tsiolkovsky's work in the field of aerodynamics was a source of ideas for Zhukovsky. Tsiolkovsky described the flow air stream of bodies of different geometric shapes.
Tsiolkovsky
studied the mechanics of powered flight, which were designed
"dirigibles" (the word "airship" had not yet been invented). Tsiolkovsky
first proposed the idea of an all-metal dirigible, and built its
model. The first printed work on the airship was "Managed Metallic
Balloon" (1892), in which was given the scientific and technical
rationale for the design of an airship with metal sheath. Progressive
for its time, Tsiolkovsky was not supported on the airship project: the
author was refused a grant to build the model. An appeal to the General
Aviation Staff of the Russian army also had no success. In 1892, he
turned to the new and unexplored field of aircraft heavier than air.
Tsiolkovsky's idea was to build an airplane with a metal frame. In the
article "An airplane or a birdlike (aircraft) flying machine" (1894)
are the descriptions and drawings of a monoplane, which by its
appearance and aerodynamics was the design of an anticipated
construction aircraft that would emerge over 15 – 18 years.
Since 1896 Tsiolkovsky systematically studied the theory of motion of jet apparatus. Thoughts on the use of the rocket principle in the cosmos were expressed as early as 1883 by Tsiolkovsky. But a rigorous theory of jet propulsion described them in 1896. Tsiolkovsky derived the formula (it was called "Formula of Aviation"), establishing the relationship between:
- speed of a rocket at any moment
- specific impulse fuel
- mass of the rocket in the initial and final time
In the same year (1897) the formula for the motion of the body of variable mass was published in the thesis of the Russian mathematician I.V. Meshchersky ("Dynamics of a point of variable mass," IV Meshchersky, St. Petersburg., 1897).
His most important work, published in 1903, was The Exploration of Cosmic Space by Means of Reaction Devices (Russian: Исследование мировых пространств реактивными приборами). Tsiolkovsky calculated, with the Tsiolkovsky equation, that the horizontal speed required for a minimal orbit around the Earth is 8,000 m/s (5 miles per second) and that this could be achieved by means of a multistage rocket fueled by liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen.
In 1903 he published an article "Investigation of outer space rocket appliances", in which for the first time it was proved that a rocket could perform space flight. In this article, and its subsequent sequels (1911 and 1914), he developed some ideas of missiles and the use of liquid rocket engine.
The impact of the first publication was not the one expected by Tsiolkovsky. No foreign scientists appreciated the research, which today has evolved to an entire scientific discipline. He was simply ahead of his time. In 1911 he published the second part of the work "The study of outer space rocket appliances." Tsiolkovsky evaluates the work needed to overcome the force of gravity, determines the speed needed to exit the device into the solar system ("escape velocity") and the flight time. At this time the article of Tsiolkovsky had a definite impact on the scientific world. Tsiolkovsky found many supporters in the world of science.
In 1926 — 1929 Tsiolkovsky solved the practical problem: how to get fuel into the rocket to get the separation speed and leave the Earth. It turned out that the finite speed of the rocket depends on the rate of gas flowing from it and on how many times the weight of the fuel exceeds the empty weight of the rocket.
Tsiolkovsky came up with a number of ideas that have been used in rockets. He proposed: gas rudders (graphite) for the rocket flight control and for changing the trajectory of its center of mass, the use of components of the fuel to cool the outer shell of the spacecraft (during re-entry to the Earth), the walls of the combustion chamber and nozzle, a pump system feeding the fuel components, the optimal descent trajectory of the spacecraft while returning from space, etc. In the field of rocket propellants Tsiolkovsky studied a large number of different oxidizing and combustible fuel recommended couples: liquid oxygen and hydrogen and oxygen with hydrocarbons. Tsiolkovsky did much fruitful work on the creation of the theory of jet aircraft and has invented his chart Gas Turbine Engine; In 1927 he published the theory and design of a train on an air cushion. He first proposed a "bottom of the retractable body" chassis. Tsiolkovsky had been developing the idea of the air cushion since 1921, publishing a fundamental paper on it in 1927, entitled "Air Resistance and the Express Train" (Russian: Сопротивление воздуха и скорый поезд). In 1929 Tsiolkovsky proposed the construction of multistage rockets in his book Space Rocket Trains (Russian: Космические ракетные поезда).
Tsiolkovsky championed the idea of the diversity of life in Universe, was the first theorist and advocate of human space exploration.
Hearing problems did not prevent the scientist a good understanding of music. There is his work "The Origin of music and its essence."
Tsiolkovsky never built a rocket; he apparently did not expect many of his theories to ever be implemented. Only late in his lifetime was Tsiolkovsky honoured for his pioneering work. He supported the Bolshevik Revolution, and the new Soviet government wished to identify itself with technology. In 1918 he was elected as a member of the Socialist Academy, and in 1921 received a lifetime pension.
Although many called his ideas impractical, Tsiolkovsky influenced later rocket scientists throughout Europe, like Wernher von Braun. Russian search teams at Peenemünde found a German translation of a book by Tsiolkovsky of which "almost every page... was embellished by von Braun's comments and notes." Leading Russian rocket engine designer Valentin Glushko and rocket designer Sergey Korolyov studied Tsiolkovsky's works as youths, and both sought to turn Tsiolkovsky's theories into reality. In particular, Korolyov saw traveling to Mars as the more important priority, until in 1964 he decided to compete with the American Project Apollo for the moon.
Tsiolovsky
wrote a book called "The Will of the Universe. The Unknown
Intelligence" in 1928 in which he propounded a philosophy of panpsychism. He believed humans would eventually colonize the Milky Way galaxy.