<Back to Index>
- Mineralogist Johann Gottlieb Lehmann, 1719
- Landscape Architect Roberto Burle Marx, 1909
- Prime Minister of Yugoslavia Milan Stojadinović, 1888
PAGE SPONSOR
Johann Gottlieb Lehmann (4 August 1719, Langenhennersdorf, Saxony, – 22 January 1767, Saint Petersburg, Russia) was a German mineralogist and geologist noted for his work and research contributions to the geologic record leading to the development of stratigraphy.
He attended the University of Wittenberg, from which he received an M.D. in 1741, and then established a practice in Dresden. Living in Saxony, he developed an interest in the local mining industry, and published on the chemical composition of ore deposits. In 1750 the Royal Prussian Academy of Sciences commissioned him to study mining practices throughout Prussia.
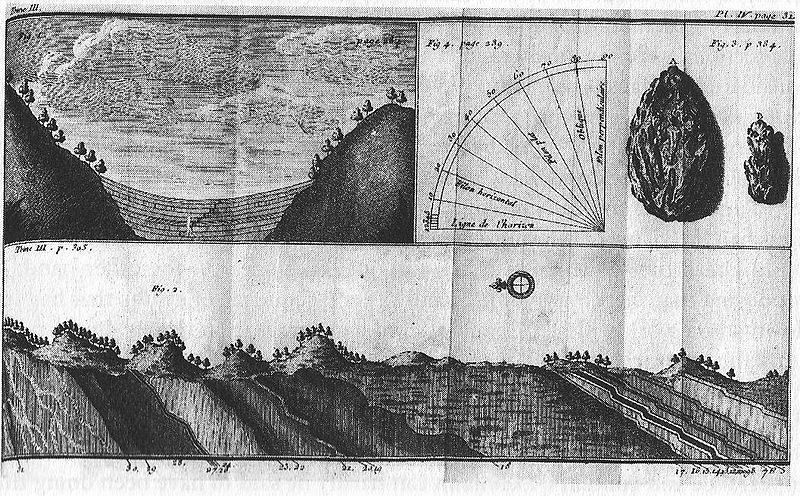
In 1761 the Russian Imperial Academy of Sciences invited him to St Petersburg, where he became professor of chemistry and director of the imperial museum there. At the Beryozovskoye deposit in the Urals he discovered a lead ore with a reddish - orange mineral (PbCrO4), which he named "Rotbleierz" (red lead ore); today in English its name is crocoite.
Lehmann, Georg Christian Füchsel, and Giovanni Arduino were founders of stratigraphy. "The chief merit of Lehmann is his accurate description of the stratified rocks (Flötzgebirge). He distinguished thirty successive bands of rock in the stratified system of Ilfeld and Mansfeld, and set forth the geological structure of that district in an accompanying series of diagrams and sections. Many of the terms in his description of the Thuringian deposits were adopted by him from the miners, and have been retained in geological literature; for example, Zechstein or mine - stone, corresponding to the Magnesian Limestone and shales or Upper Dyassic group in England; and rothes Todtliegendes (Rothliegende) or red underlayer, the unproductive basement beds below the ore - bearing, and the equivalent of the Lower Dyassic." Lehmann died in St Petersburg from injuries caused by the explosion of a retort filled with arsenic.