<Back to Index>
- Statesman Solon of Athens (Σόλων ο Αθηναίος), 638 B.C.
PAGE SPONSOR



Solon (ancient Greek: Σόλων, c. 638 BC – 558 BC) was an Athenian statesman, lawmaker, and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in archaic Athens. His reforms failed in the short term, yet he is often credited with having laid the foundations for Athenian democracy.
Knowledge of Solon is limited by the lack of documentary and archeological evidence covering Athens in the early 6th century BC. He wrote poetry for pleasure, as patriotic propaganda, and in defence of his constitutional reforms. His works only survive in fragments. They appear to feature interpolations by later authors and it is possible that fragments have been wrongly attributed to him. Ancient authors such as Herodotus and Plutarch are
the main source of information, yet they wrote about Solon hundreds of
years after his death, at a time when history was by no means an
academic discipline. Fourth century orators, such as Aeschines, tended to attribute to Solon all the laws of their own, much later times. Archaeology
reveals glimpses of Solon's period in the form of fragmentary
inscriptions but little else. For some scholars, our 'knowledge' of
Solon and his times is largely a fictive construct based on insufficient
evidence while others believe a substantial body of real knowledge is still attainable. Solon
and his times can appear particularly interesting to students of
history as a test of the limits and nature of historical argument.
During Solon's time, many Greek city - states had seen the emergence of tyrants, opportunistic noblemen who had grabbed power on behalf of sectional interests. In Sicyon, Cleisthenes had usurped power on behalf of an Ionian minority. In Megara, Theagenes had come to power as an enemy of the local oligarchs. The son - in - law of Theagenes, an Athenian nobleman named Cylon, made an unsuccessful attempt to seize power in Athens in 632 BC. Solon, on the other hand, appears to have been temporarily awarded autocratic powers by his fellow citizens on the grounds that he had the wisdom to sort out their differences for them in a peaceful and equitable manner. According to ancient sources, he obtained these powers when he was elected eponymous archon (594/3 BC). Some modern scholars believe these powers were in fact granted some years after Solon had been archon, when he would have been a member of the Areopagus and probably a more respected statesman by his (aristocratic) peers.
The
social and political upheavals that characterised Athens in Solon's
time have been variously interpreted by historians from ancient times to
the present day. Two contemporary historians have identified three
distinct historical accounts of Solon's Athens, emphasizing quite
different rivalries: economic and ideological rivalry, regional rivalry
and rivalry between aristocratic clans. These different accounts provide a convenient basis for an overview of the issues involved.
- Economic and ideological rivalry is a common theme in ancient sources. This sort of account emerges from Solon's poems,
in which he casts himself in the role of a noble mediator between two
intemperate and unruly factions. This same account is substantially
taken up about three centuries later by the author of the Athenaion Politeia but with an interesting variation:
"...there was conflict between the nobles and the common people for an extended period. For the constitution they were under was oligarchic in every respect and especially in that the poor, along with their wives and children, were in slavery to the rich... All the land was in the hands of a few. And if men did not pay their rents, they themselves and their children were liable to be seized as slaves. The security for all loans was the debtor's person up to the time of Solon. He was the first champion of the people."
Here Solon is presented as a partisan in a democratic cause whereas, judged from the viewpoint of his own poems, he was instead a mediator between rival factions. A still more significant variation in the ancient historical account appears in the writing of Plutarch in the late 1st - early 2nd century AD:
'Athens was torn by recurrent conflict about the constitution. The city was divided into as many parties as there were geographical divisions in its territory. For the party of the people of the hills was most in favour of democracy, that of the people of the plain was most in favour of oligarchy, while the third group, the people of the coast, which preferred a mixed form of constitution somewhat between the other two, formed an obstruction and prevented the other groups from gaining control.'
The ancient historical account here demonstrates a more sophisticated understanding of political process - what were two sides in Solon's account have now become three parties, each with a regional base and a constitutional platform. Plutarch then goes on to repeat the usual ancient account with its brutal landlords on one side and wretched tenants on the other. But how does this melodramatic struggle between haves and have-nots fit into a picture of three regional groupings? - Regional rivalry is a theme commonly found among modern scholars.
'The new picture which emerged was one of strife between regional groups, united by local loyalties and led by wealthy landowners. Their goal was control of the central government at Athens and with it dominance over their rivals from other districts of Attika.'
Regional factionalism was inevitable in a relatively large territory such as Athens possessed. In most Greek city states, a farmer could conveniently reside in town and travel to and from his fields every day. According to Thucydides, on the other hand, most Athenians continued to live in rural settlements right up until the Peloponnesian War. The effects of regionalism in a large territory could be seen in Laconia, where Sparta had gained control through intimidation and resettlement of some of its neighbours and enslavement of the rest. Attika in Solon's time seemed to be moving towards a similarly ugly solution with many citizens in danger of being reduced to the status of helots. - Rivalry between clans is a theme recently developed by some scholars, based on an appreciation of the political significance of kinship groupings. According to this account, bonds of kinship rather than local loyalties were the decisive influence on events in archaic Athens. An Athenian belonged not only to a phyle or tribe and one of its subdivisions, the phatry or brotherhood, but also to an extended family, clan or genos. It has been argued that these interconnecting units of kinship reinforced a hierarchic structure with aristocratic clans at the top. Thus rivalries between aristocratic clans could engage all levels of society irrespective of any regional ties. In that case, the struggle between rich and poor was the struggle between powerful aristocrats and the weaker affiliates of their rivals or perhaps even with their own rebellious affiliates.
The
historical account of Solon's Athens has evolved over many centuries
into a set of contradictory stories or a complex story that might be
interpreted in a variety of ways. As further evidence accumulates, and
as historians continue to debate the issues, Solon's motivations and the
intentions behind his reforms will continue to attract speculation.
Solon's laws were inscribed on large wooden slabs or cylinders attached to a series of axles that stood upright in the Prytaneum. These axones appear to have operated on the same principle as a Lazy Susan, allowing both convenient storage and ease of access. Originally the axones recorded laws enacted by Draco in the late 7th Century (traditionally 621 BC). Nothing of Draco's codification has survived except for a law relating to homicide, yet there is consensus among scholars that it did not amount to anything like a constitution. Solon repealed all Draco's laws except those relating to homicide. Fragments of the axones were still visible in Plutarch's time but today the only records we have of Solon's laws are fragmentary quotes and comments in literary sources such as those written by Plutarch himself. Moreover, the language of his laws was archaic even by the standards of the fifth century and this caused interpretational problems for ancient commentators. Modern scholars doubt the reliability of these sources and our knowledge of Solon's legislation is therefore actually very limited in its details.
Generally,
Solon's reforms appear to have been constitutional, economic and moral
in their scope. This distinction, though somewhat artificial, does at
least provide a convenient framework within which to consider the laws
that have been attributed to Solon. Some short term consequences of his
reforms are considered at the end of the section.
Previous to Solon's reforms, the Athenian state was administered by nine archons appointed or elected annually by the Areopagus on the basis of noble birth and wealth. The Areopagus comprised former archons and it therefore had, in addition to the power of appointment, extraordinary influence as a consultative body. The nine archons took the oath of office while ceremonially standing on a stone in the agora, declaring their readiness to dedicate a golden statue if they should ever be found to have violated the laws. There was an assembly of Athenian citizens (the Ekklesia) but the lowest class (the Thetes) was not admitted and its deliberative procedures were controlled by the nobles. There therefore seemed to be no means by which an archon could be called to account for breach of oath unless the Areopagus favoured his prosecution.
According to Aristotle, Solon legislated for all citizens to be admitted into the Ekklesia and for a court (the Heliaia) to be formed from all the citizens. The Heliaia appears to have been the Ekklesia, or some representative portion of it, sitting as a jury. By giving common people the power not only to elect officials but also to call them to account, Solon appears to have established the foundations of a true democracy. However some scholars have doubted whether Solon actually included the Thetes in the Ekklesia, this being considered too bold a move for any aristocrat in the archaic period. Ancient sources credit Solon with the creation of a Council of Four Hundred, drawn from the four Athenian tribes to serve as a steering committee for the enlarged Ekklesia. However, many modern scholars have doubted this also.
There
is consensus among scholars that Solon broadened the financial and
social qualifications required for election to public office. The
Solonian constitution divided citizens into four political classes
defined according to assessable property a classification that might previously have served the state for military or taxation purposes only. The standard unit for this assessment was one medimnos (approximately
12 gallons) of cereals and yet the kind of classification set out below
might be considered too simplistic to be historically accurate.
- Pentacosiomedimnoi valued at 500 medimnoi of cereals annually; eligible to serve as Strategoi (Generals)
- Hippeis valued at 300 medimnoi production annually; approximating to the mediaeval class of knights, they had enough wealth to equip themselves for the Cavalry
- Zeugitai valued at a 200 medimnoi production annually; approximating to the mediaeval class of Yeoman, they had enough wealth to equip themselves for the infantry (Hoplite)
- Thetes valued 199 medimnoi annually or less; manual workers or sharecroppers, they served voluntarily in the role of batman, or as auxiliaries armed for instance with the sling or as rowers in the Navy.
According to Aristotle, only the Pentacosiomedimnoi were eligible for election to high office as archons and therefore only they gained admission into the Areopagus. A modern view affords the same privilege to the hippeis. The top three classes were eligible for a variety of lesser posts and only the Thetes were excluded from all public office.
Depending
on how we interpret the historical facts known to us, Solon's
constitutional reforms were either a radical anticipation of democratic
government, or they merely provided a plutocratic flavour to a
stubbornly aristocratic regime, or else the truth lies somewhere between
these two extremes.
Solon's economic reforms need to be understood in the context of the primitive, subsistence economy that prevailed both before and after his time. Most Athenians were still living in rural settlements right up to the Peloponnesian War. Opportunities for trade even within the Athenian borders were limited. The typical farming family, even in classical times, barely produced enough to satisfy its own needs. Opportunities for international trade were minimal. It has been estimated that, even in Roman times, goods rose 40% in value for every 100 miles they were carried over land, but only 1.3% for the same distance were they carried by ship and yet there is no evidence that Athens possessed any merchant ships until around 525 BC. Until then, the narrow warship doubled as a cargo vessel. Athens, like other Greek city states in the 7th Century BC, was faced with increasing population pressures and by about 525 BC it was able to feed itself only in 'good years'.
Solon's
reforms can thus be seen to have taken place at a crucial period of
economic transition, when a subsistence rural economy increasingly
required the support of a nascent commercial sector. The specific
economic reforms credited to Solon are these:
- Fathers were encouraged to find trades for their sons; if they did not, there would be no legal requirement for sons to maintain their fathers in old age.
- Foreign tradesmen were encouraged to settle in Athens; those who did would be granted citizenship, provided they brought their families with them.
- Cultivation of olives was encouraged; the export of all other produce was prohibited.
- Competitiveness of Athenian commerce was promoted through revision of weights and measures, possibly based on successful standards already in use elsewhere, such as Aegina or Euboia or, according to the ancient account but unsupported by modern scholarship, Argos.
It is generally assumed, on the authority of ancient commentators that Solon also reformed the Athenian coinage. However, recent numismatic studies now lead to the conclusion that Athens probably had no coinage until around 560 BC, well after Solon's reforms.
Solon's economic reforms succeeded in stimulating foreign trade. Athenian black - figure pottery was exported in increasing quantities and good quality throughout the Aegean between 600 BC and 560 BC, a success story that coincided with a decline in trade in Corinthian pottery. The ban on the export of grain might be understood as a relief measure for the benefit of the poor. However, the encouragement of olive production for export could actually have led to increased hardship for many Athenians since it would have led to a reduction in the amount of land dedicated to grain. Moreover an olive produces no fruit for the first six years. The real motives behind Solon's economic reforms are therefore as questionable as his real motives for constitutional reform. Were the poor being forced to serve the needs of a changing economy, or was the economy being reformed to serve the needs of the poor?
In his poems, Solon portrays Athens as being under threat from the unrestrained greed and arrogance of its citizens. Even the earth (Gaia), the mighty mother of the gods, had been enslaved. The visible symbol of this perversion of the natural and social order was a boundary marker called a horos,
a wooden or stone pillar indicating that a farmer was in debt or under
contractual obligation to someone else, either a noble patron or a
creditor. Up until Solon's time, land was the inalienable property of a family or clan and
it could not be sold or mortgaged. This was no disadvantage to a clan
with large landholdings since it could always rent out farms in a sharecropping system.
A family struggling on a small farm however could not use the farm as
security for a loan even if it owned the farm. Instead the farmer would
have to offer himself and his family as security, providing some form of
slave labour in lieu of repayment. Equally, a family might voluntarily
pledge part of its farm income or labour to a powerful clan in return
for its protection. Farmers subject to these sorts of arrangements were
loosely known as hektemoroi indicating that they either paid or kept a sixth of a farm's annual yield. In the event of 'bankruptcy', or failure to honour the contract stipulated by the horoi, farmers and their families could in fact be sold into slavery.
Solon's reform of these injustices was later known and celebrated among Athenians as the Seisachtheia (shaking off of burdens). As with all his reforms, there is considerable scholarly debate about its real significance. Many scholars are content to accept the account given by the ancient sources, interpreting it as a cancellation of debts, while others interpret it as the abolition of a type of feudal relationship, and some prefer to explore new possibilities for interpretation. The reforms included:
- annulment of all contracts symbolised by the horoi.
- prohibition on a debtor's person being used as security for a loan.
- release of all Athenians who had been enslaved.
The removal of the horoi clearly provided immediate economic relief for the most oppressed group in Attica, and it also brought an immediate end to the enslavement of Athenians by their countrymen. Some Athenians had already been sold into slavery abroad and some had fled abroad to escape enslavement - Solon proudly records in verse the return of this diaspora. It has been cynically observed, however, that few of these unfortunates were likely to have been recovered. It has been observed also that the seisachtheia not only removed slavery and accumulated debt, it also removed the ordinary farmer's only means of obtaining further credit.
The seisachtheia however was merely one set of reforms within a broader agenda of moral reformation. Other reforms included:
- the abolition of extravagant dowries.
- legislation against abuses within the system of inheritance, specifically with relation to the epikleros (i.e., a female who had no brothers to inherit her father's property and who was traditionally required to marry her nearest paternal relative in order to produce an heir to her father's estate).
- entitlement of any citizen to take legal action on behalf of another.
- the disenfranchisement of any citizen who might refuse to take up arms in times of civil strife, a measure that was intended to counteract dangerous levels of political apathy.
The personal modesty and frugality of the rich and powerful men of Athens in the city's subsequent golden age have been attested to by Demosthenes. Perhaps Solon, by both personal example and legislated reform, established a precedent for this decorum. A heroic sense of civic duty later united Athenians against the might of the Persians. Perhaps this public spirit was instilled in them by Solon and his reforms.
After completing his work of reform, Solon surrendered his extraordinary authority and left the country. According to Herodotus the country was bound by Solon to maintain his reforms for 10 years, whereas according to Plutarch and the author of Athenaion Politeia (reputedly Aristotle) the contracted period was instead 100 years. A modern scholar considers
the time span given by Herodotus to be historically accurate because it
fits the 10 years that Solon was said to have been absent from the
country. Within
4 years of Solon's departure, the old social rifts re-appeared, but
with some new complications. There were irregularities in the new
governmental procedures, elected officials sometimes refused to stand
down from their posts and sometimes important posts were left vacant. It
has even been said that some people blamed Solon for their troubles. Eventually one of Solon's relatives, Pisistratus, ended the factionalism by force, thus instituting an unconstitutionally gained tyranny. In Plutarch's account, Solon accused Athenians of stupidity and cowardice for allowing this to happen.
Solon was the first of the Athenian poets whose work has survived to the present day. His verses have come down to us in fragmentary quotations by ancient authors such as Plutarch and Demosthenes who used them to illustrate their own arguments. It is possible that some fragments have been wrongly attributed to him and some scholars have detected interpolations by later authors.
The literary merit of Solon's verse is generally considered unexceptional. Solon the poet can be said to appear 'self - righteous' and 'pompous' at times and he once composed an elegy with moral advice for a more gifted elegiac poet, Mimnermus. Most of the extant verses show him writing in the role of a political activist determined to assert personal authority and leadership. According to Plutarch however, Solon originally wrote poetry for amusement, discussing pleasure in a popular rather than philosophical way. Solon's elegiac style is said to have been influenced by the example of Tyrtaeus. He also wrote iambic and trochaic verses which, according to one modern scholar, are more lively and direct than his elegies and possibly paved the way for the iambics of Athenian drama.
Solon's verses are mainly significant for historical rather than aesthetic reasons, as a personal record of his reforms and attitudes. However, poetry is not an ideal genre for communicating facts and very little detailed information can be derived from the surviving fragments. According to Solon the poet, Solon the reformer was a voice for political moderation in Athens at a time when his fellow citizens were increasingly polarized by social and economic differences:
πολλοὶ γὰρ πλουτεῦσι κακοί, ἀγαθοὶ δὲ πένονται:
ἀλλ' ἡμεῖς αὐτοῖς οὐ διαμειψόμεθα
τῆς ἀρετῆς τὸν πλοῦτον: ἐπεὶ τὸ μὲν ἔμπεδον αἰεί,
χρήματα δ' ἀνθρώπων ἄλλοτε ἄλλος ἔχει.Some wicked men are rich, some good are poor;
We will not change our virtue for their store:
Virtue's a thing that none can take away,
But money changes owners all the day.
Here translated by the English poet John Dryden, Solon's words define a 'moral high ground' where differences between rich and poor can be reconciled or maybe just ignored. His poetry indicates that he attempted to use his extraordinary legislative powers to establish a peaceful settlement between the country's rival factions:
ἔστην δ' ἀμφιβαλὼν κρατερὸν σάκος ἀμφοτέροισι:
νικᾶν δ' οὐκ εἴασ' οὐδετέρους ἀδίκως.Before them both I held my shield of might
And let not either touch the other's right.
His attempts evidently were misunderstood:
χαῦνα μὲν τότ' ἐφράσαντο, νῦν δέ μοι χολούμενοι
λοξὸν ὀφθαλμοῖς ὁρῶσι πάντες ὥστε δήϊον.Formerly they boasted of me vainly; with averted eyes
Now they look askance upon me; friends no more but enemies.
Solon gave voice to Athenian 'nationalism', particularly in the city state's struggle with Megara, its neighbour and rival in the Saronic Gulf. Plutarch professes admiration of Solon's elegy urging Athenians to recapture the island of Salamis from Megarian control. The same poem was said by Diogenes Laertios to have stirred Athenians more than any other verses that Solon wrote:
Let us go to Salamis to fight for the island
We desire, and drive away our bitter shame!
It is possible that Solon backed up this poetic bravado with true valour on the battlefield.
As a regulator of Athenian society, Solon, according to some authors, also formalized its sexual mores. According to a surviving fragment from a work ("Brothers") by the comic playwright Philemon, Solon established publicly funded brothels at Athens in order to "democratize" the availability of sexual pleasure. While the veracity of this comic account is open to doubt, at least one modern author considers it significant that in Classical Athens, three hundred or so years after the death of Solon, there existed a discourse that associated his reforms with an increased availability of heterosexual pleasure.
Ancient authors also say that Solon regulated pederastic relationships in Athens; this has been presented as an adaption of custom to the new structure of the polis. According to various authors, ancient lawgivers (and therefore Solon by implication) drew up a set of laws that were intended to promote and safeguard the institution of pederasty and to control abuses against freeborn boys. In particular, the orator Aeschines cites laws excluding slaves from wrestling halls and forbidding them to enter pederastic relationships with the sons of citizens. Accounts of Solon's laws by 4th Century orators like Aeschines, however, are considered unreliable for a number of reasons;
Attic pleaders did not hesitate to attribute to him (Solon) any law which suited their case, and later writers had no criterion by which to distinguish earlier from later works. Nor can any complete and authentic collection of his statutes have survived for ancient scholars to consult.
Besides the alleged legislative aspect of Solon's involvement with pederasty, there were also suggestions of personal involvement. According to some ancient authors Solon had taken the future tyrant Peisistratus as his eromenos. Aristotle, writing around 330 BC, attempted to refute that belief, claiming that "those are manifestly talking nonsense who pretend that Solon was the lover of Peisistratus, for their ages do not admit of it," as Solon was about thirty years older than Peisistratus. Nevertheless the tradition persisted. Four centuries later Plutarch ignored Aristotle's skepticism and recorded the following anecdote, supplemented with his own conjectures:
And they say Solon loved [Peisistratus]; and that is the reason, I suppose, that when afterwards they differed about the government, their enmity never produced any hot and violent passion, they remembered their old kindnesses, and retained "Still in its embers living the strong fire" of their love and dear affection.
A century after Plutarch, Aelian also said that Peistratus had been Solon's eromenos.
Despite its persistence, however, it is not known whether the account
is historical or fabricated. It has been suggested that the tradition
presenting a peaceful and happy coexistence between Solon and
Peisistratus was cultivated during the latter's dominion, in order to
legitimize his own rule, as well as that of his sons. Whatever its
source, later generations lent credence to the narrative. Solon's
presumed pederastic desire was thought in antiquity to have found
expression also in his poetry, which is today represented only in a few
surviving fragments. The
authenticity of all the poetic fragments attributed to Solon is however
uncertain - in particular, pederastic aphorisms ascribed by some
ancient sources to Solon have been ascribed by other sources to Theognis instead.
Details about Solon's personal life have been passed down to us by ancient authors such as Plutarch and Herodotus. Herodotus is sometimes referred to both as 'the father of history' and 'the father of lies'. Plutarch, by his own admission, did not write histories so much as biographies; he believed that a jest or a phrase could reveal more about a person's character than could a battle that cost thousands of lives. A battle of course is a matter of historical record; a jest or a phrase is not.
According to Plutarch, Solon was related to the tyrant Pisistratus (their mothers were cousins). Solon's father Execestides could trace his ancestry back to Codrus, the last King of Athens. Solon's family belonged to a noble or Eupatrid clan yet it possessed only moderate wealth. and Solon was therefore drawn into an unaristocratic pursuit of commerce. According to Diogenes Laertius, he had a brother named Dropidas and was an ancestor (six generations removed) of Plato.
Solon was given leadership of the Athenian war against Megara on the strength of a poem he wrote about Salamis Island. Supported by Pisistratus, he defeated the Megarians either by means of a cunning trick or more directly through heroic battle. The Megarians however refused to give up their claim to the island. The dispute was referred to the Spartans, who eventually awarded possession of the island to Athens on the strength of the case that Solon put to them.
When he was archon, Solon discussed his intended reforms with some friends. Knowing that he was about to cancel all debts, these friends took out loans and promptly bought some land. Suspected of complicity, Solon complied with his own law and released his own debtors, amounting to 5 talents (or 15 according to some sources). His friends never repaid their debts.
After
he had finished his reforms, he travelled abroad for ten years, so that
the Athenians could not induce him to repeal any of his laws. His first
stop was Egypt. There, according to Herodotus he visited the Pharaoh of
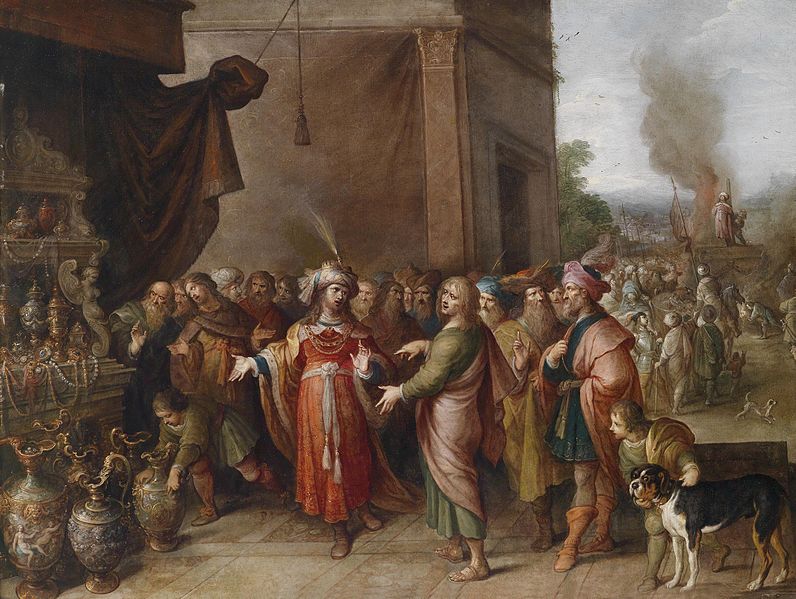
Egypt Amasis II. According to Plutarch, he spent some time and discussed philosophy with two Egyptian priests, Psenophis of Heliopolis and Sonchis of Sais. According to Plato's dialogues Timaeus and Critias, he visited Neith's temple at Sais and received from the priests there an account of the history of Atlantis. Next Solon sailed to Cyprus, where he oversaw the construction of a new capital for a local king, in gratitude for which the king named it Soloi.
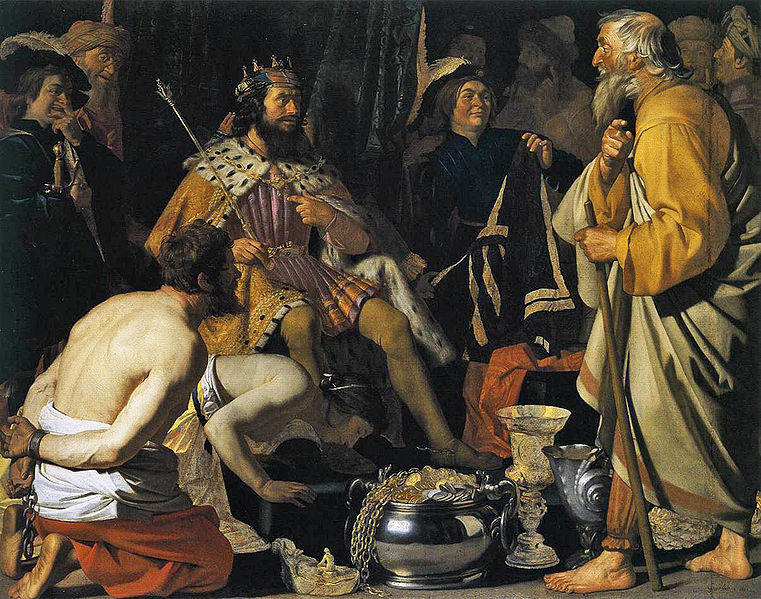
Solon's travels finally brought him to Sardis, capital of Lydia. According to Herodotus and Plutarch, he met with Croesus and gave the Lydian king advice, which however Croesus failed to appreciate until it was too late. Croesus had considered himself to be the happiest man alive and Solon had advised him, "Count no man happy until he be dead", because at any minute, fortune might turn on even the happiest man and make his life miserable. It was only after he had lost his kingdom to the Persian king Cyrus, while awaiting execution, that Croesus acknowledged the wisdom of Solon's advice.
After his return to Athens, Solon became a staunch opponent of Pisistratus. In protest and as an example to others, Solon stood outside his own home in full armour, urging all who passed to resist the machinations of the would - be tyrant. But his efforts were in vain. Solon died shortly after Pisistratus usurped by force the autocratic power that Athens had once freely bestowed upon him. According to one account, he died in Cyprus and, in accordance with his will, his ashes were scattered around Salamis, the island where he was born.
The travel writer, Pausanias, listed Solon among the seven sages whose aphorisms adorned Apollo's temple in Delphi. Stobaeus in the Florilegium relates a story about a symposium, where Solon's young nephew was singing a poem of Sappho's;
Solon, upon hearing the song, asked the boy to teach him to sing it.
When someone asked, "Why should you waste your time on it?" Solon
replied ἵνα μαθὼν αὐτὸ ἀποθάνω, "So that I may learn it then die." Ammianus Marcellinus however told a similar story about Socrates and the poet Stesichorus, quoting the philosopher's rapture in almost identical terms: "ut aliquid sciens amplius e vita discedam".