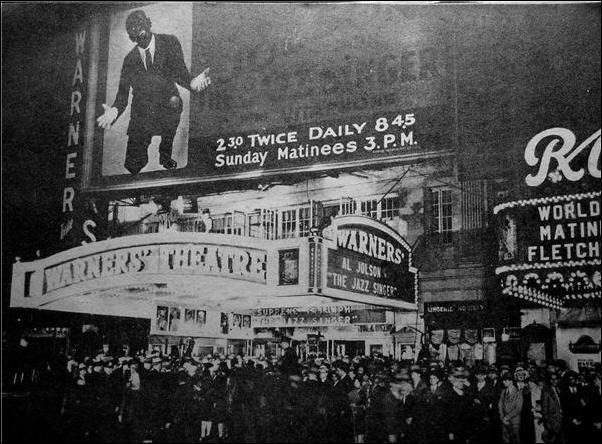<Back to Index>
- Al Jolson's The Jazz Singer, 1927
PAGE SPONSOR


The Jazz Singer is a 1927 American musical film. The first feature length motion picture with synchronized dialogue sequences, its release heralded the commercial ascendance of the "talkies" and the decline of the silent film era. Produced by Warner Bros. with its Vitaphone sound - on - disc system, the movie stars Al Jolson, who performs six songs. Directed by Alan Crosland, it is based on a play by Samson Raphaelson.
The
story begins with young Jakie Rabinowitz defying the traditions of his
devout Jewish family by singing popular tunes in a beer hall. Punished
by his father, a cantor,
Jakie runs away from home. Some years later, now calling himself Jack
Robin, he has become a talented jazz singer. He attempts to build a
career as an entertainer, but his professional ambitions ultimately come
into conflict with the demands of his home and heritage. On April 25, 1917, Samson Raphaelson, a native of New York City's Lower East Side and a University of Illinois undergraduate, attended a performance of the musical Robinson Crusoe, Jr. in Champaign, Illinois. The star of the show was a thirty year old singer, Al Jolson, a Russian born Jew who performed in blackface. In
a 1927 interview, Raphaelson described the experience: "I shall never
forget the first five minutes of Jolson — his velocity, the amazing
fluidity with which he shifted from a tremendous absorption in his
audience to a tremendous absorption in his song." He explained that he had seen emotional intensity like Jolson's only among synagogue cantors. A
few years later, pursuing a professional literary career, Raphaelson
wrote "The Day of Atonement", a short story about a young Jew named
Jakie Rabinowitz, based on Jolson's real life. The story was published
in January 1922 in Everybody's Magazine. Raphaelson later adapted the story into a stage play, The Jazz Singer. A straight drama, all the singing in Raphaelson's version takes place offstage. With George Jessel in the lead role, the show premiered on Broadway in September 1925 and became a hit. Warner Bros. acquired the movie rights to the play on June 4, 1926, and signed Jessel to a contract. Moving Picture World published a story in February 1927 announcing that production on the film would begin with Jessel on May 1. But
the plans to make the film with Jessel would fall through, for multiple
reasons. Jessel's contract with Warner Bros. had not anticipated that
the movie they had particularly signed him for would be made with sound
(he'd made a modestly budgeted, silent comedy in the interim). When
Warners had hits with two Vitaphone, though dialogue - less, features in
late 1926, The Jazz Singer production had been reconceived. Jessel asked for a bonus or a new contract, but was rebuffed. According to Jessel's description in his autobiography, Harry Warner "was
having a tough time with the financing of the company.... He talked
about taking care of me if the picture was a success. I did not feel
that was enough." In
fact, around the beginning of 1927, Harry Warner — the eldest of the
brothers who ran the eponymous studio — had sold $4 million of his
personal stock to keep the studio solvent Then came another major issue. According to Jessel, a first read of screenwriter Alfred A. Cohn's
adaptation "threw me into a fit. Instead of the boy's leaving the
theatre and following the traditions of his father by singing in the
synagogue, as in the play, the picture scenario had him return to the Winter Garden as a blackface comedian, with his mother wildly applauding in the box. I raised hell. Money or no money, I would not do this." According to performer Eddie Cantor, as negotiations between Warner Bros. and Jessel foundered, Jack Warner and the studio's production chief, Darryl Zanuck,
called to see if he was interested in the part. Cantor, a friend of
Jessel's, responded that he was sure any differences with the actor
could be worked out and offered his assistance. Cantor
was not invited to participate in the Jessel talks; instead, the role
was then offered to Jolson, who had inspired it in the first place.
Describing Jolson as the production's best choice for its star, film
historian Donald Crafton wrote, "The entertainer, who sang jazzed - up
minstrel numbers in blackface, was at the height of his phenomenal
popularity. Anticipating the later stardom of crooners and rock stars,
Jolson electrified audiences with the vitality and sex appeal of his
songs and gestures, which owed much to African - American sources." As
described by historian Robert L. Carringer, "Jessel was a vaudeville
comedian and master of ceremonies with one successful play and one
modestly successful film to his credit. Jolson was a superstar." Jolson
took the part, signing a $ 75,000 contract on May 26, 1927, for eight
weeks of services beginning in July. There have been several claims but no proof that Jolson invested some of his own money in the film. Jessel
and Jolson, also friends, did not speak for some time after — on the one
hand, Jessel had been confiding his problems with the Warners to Jolson;
on the other, Jolson had signed with them without telling Jessel of his
plans. In his autobiography, Jessel wrote that, in the end, Jolson
"must not be blamed, as the Warners had definitely decided that I was
out."
While many earlier sound films had dialogue, all were short subjects. D.W. Griffith's feature Dream Street (1921)
was shown in New York with a single singing sequence and crowd noises.
It was preceded by a program of sound shorts, including a sequence with
Griffith speaking directly to the audience, but the feature itself had
no talking scenes. Similarly, the first Warner Bros. Vitaphone features, Don Juan (premiered August 1926) and The Better 'Ole (premiered
October 1926), like two more that followed in early 1927, had only a
synchronized instrumental score and sound effects. The Jazz Singer contains
those, as well as numerous synchronized singing sequences and some
synchronized speech: Two popular tunes are performed by the young Jakie
Rabinowitz, the future Jazz Singer; his father, a cantor, performs the
devotional Kol Nidre; the famous cantor Yossele Rosenblatt,
appearing as himself, sings another religious melody. As the adult Jack
Robin, Jolson performs six songs, five popular "jazz" tunes and the Kol
Nidre. The sound for the film was recorded by British born George Groves, who had also worked on Don Juan. To direct, the studio chose Alan Crosland, who already had two Vitaphone films to his credit: Don Juan and Old San Francisco, which opened while The Jazz Singer was in production. Jolson's first vocal performance, about fifteen minutes into the picture, is of "Dirty Hands, Dirty Face," with music by James V. Monaco and lyrics by Edgar Leslie and
Grant Clarke. The first synchronized speech, uttered by Jack to a
cabaret crowd and to the piano player in the band that accompanies him,
occurs directly after that performance, beginning at the 17:25 mark of
the film. Jack's first spoken words — "Wait a minute, wait a minute, you
ain't heard nothin' yet" — were well established stage patter of Jolson's.
He had even spoken very similar lines in a 1926 short, Al Jolson in "A Plantation Act." The
line had developed as something of an in-joke. In November 1918, during
a gala concert celebrating the end of World War I, Jolson ran onstage
amid the applause for the preceding performer, the great operatic tenor Enrico Caruso, and exclaimed, "Folks, you ain't heard nothin' yet." The following year, he recorded the song "You Ain't Heard Nothin' Yet". In a later scene, Jack talks with his mother, played by Eugenie Besserer, in the family parlor; his father enters and pronounces one very
conclusive word. In total, the movie contains barely two minutes worth
of synchronized talking, much or all of it improvised. The rest of the
dialogue is presented through the caption cards, or intertitles, standard in silent movies of the era. While Jolson was touring with a stage show during June 1927, production on The Jazz Singer began
with the shooting of exterior scenes. In late June, Alan Crosland
headed to New York City to shoot the Lower East Side and Winter Garden
exteriors on location. Jolson joined the production in mid July (his
contract specified July 11). Filming with Jolson began with his silent
scenes; the more complex Vitaphone sequences were primarily done in
late August. Both
Jolson and Zanuck would later take credit for thinking up the ad - libbed
dialogue sequence between Jack and his mother; another story had it
that Sam Warner was
impressed by Jolson's brief ad - libbing in the cabaret scene and had
screenwriter Alfred Cohn come up with some lines on the spot. On September 23, Motion Picture News reported that production on the film had been completed. The production cost for The Jazz Singer was $ 422,000 — a
large sum, especially for Warner Bros., which rarely spent more than
$ 250,000. It was by no means a record for the studio, however; two
features starring John Barrymore had been costlier: The Sea Beast (1926), a loose and entirely silent adaptation of Moby - Dick, at $ 503,000 and Don Juan at $ 546,000. Nonetheless,
the outlay constituted a major gamble in light of the studio's
financial straits: Harry Warner had stopped taking a salary and his
daughter Doris "recalled that Harry had pawned his wife's jewelry and
moved the family into a small apartment at the time The Jazz Singer was in production." The
premiere was set for October 6, 1927, at Warner Bros.' flagship theater
in New York City. The choice of date was pure show business — the
following day was Yom Kippur, the Jewish holiday around which much of the movie's plot revolves. The
buildup to the premiere was tense. Besides Warner Bros.' precarious
financial position, the physical presentation of the film itself was
remarkably complex: Each
of Jolson's musical numbers was mounted on a separate reel with a
separate accompanying sound disc. Even though the film was only eighty
- nine minutes long... there were fifteen reels and fifteen discs to
manage, and the projectionist had to be able to thread the film and cue
up the Vitaphone records very quickly. The least stumble, hesitation,
or human error would result in public and financial humiliation for the
company. None of the Warner brothers were able to attend: Sam Warner — among
them, the strongest advocate for Vitaphone — had died the previous day of
pneumonia, and the surviving brothers had returned to California for
his funeral. According
to Doris Warner, who was in attendance, about halfway through the film
she began to feel that something exceptional was taking place. Jolson's
"Wait a minute" line had prompted a loud, positive response from the
audience. Applause followed each of his songs. Excitement built, and
when Jolson and Eugenie Besserer began their dialogue scene, "the
audience became hysterical." After
the show, the audience turned into a "milling, battling, mob", in one
journalist's description, chanting "Jolson, Jolson, Jolson!" Among those who reviewed the film, the critic who foresaw most clearly what it presaged for the future of cinema was Life magazine's Robert E. Sherwood.
He described the spoken dialogue scene between Jolson and Besserer as
"fraught with tremendous significance.... I for one suddenly realized
that the end of the silent drama is in sight". Critical reaction was generally, though far from universally, positive. New York Times critic Mordaunt Hall, reviewing the film's premiere, declared that not since the first presentation of Vitaphone features, more than a year ago [i.e., Don Juan],
has anything like the ovation been heard in a motion picture
theatre.... The Vitaphoned songs and some dialogue have been introduced
most adroitly. This in itself is an ambitious move, for in the
expression of song the Vitaphone vitalizes the production enormously.
The dialogue is not so effective, for it does not always catch the
nuances of speech or inflections of the voice so that one is not aware
of the mechanical features. Variety called it "[u]ndoubtedly the best thing Vitaphone has ever put on the screen...[with] abundant power and appeal." Richard Watts, Jr. of the New York Herald Tribune called
it a "pleasantly sentimental orgy dealing with a struggle between
religion and art.... [T]his is not essentially a motion picture, but
rather a chance to capture for comparative immortality the sight and
sound of a great performer." The Exhibitors Herald's
take was virtually identical: "scarcely a motion picture. It should be
more properly labeled an enlarged Vitaphone record of Al Jolson in half a
dozen songs." The film received favorable reviews in both the Jewish press and in African American newspapers such as the Baltimore Afro - American, the New York Amsterdam News, and the Pittsburgh Courier. The headline of the Los Angeles Times review
told a somewhat different story: "'Jazz Singer' Scores a Hit — Vitaphone
and Al Jolson Responsible, Picture Itself Second Rate." Photoplay dismissed Jolson as "no movie actor. Without his Broadway reputation he wouldn't rate as a minor player." The film developed into a major hit, demonstrating the profit potential of feature length "talkies",
but Donald Crafton has shown that the reputation the film later
acquired for being one of Hollywood's most enormous successes to date
was inflated. The movie did well, but not astonishingly so, in the
major cities where it was first released, garnering much of its
impressive profits with long, steady runs in population centers large
and small all around the country. As conversion of movie theaters to
sound was still in its early stages, the film actually arrived at many
of those secondary venues in a silent version. On the other hand,
Crafton's statement that The Jazz Singer "was
in a distinct second or third tier of attractions compared to the most
popular films of the day and even other Vitaphone talkies" is also
incorrect. In
fact, the film was easily the biggest earner in Warner Bros. history,
and would remain so until it was surpassed a year later by The Singing Fool,
another Jolson feature. In the larger scope of Hollywood, among films
originally released in 1927, available evidence suggests that The Jazz Singer was among the three biggest box office hits, trailing only Wings and, perhaps, The King of Kings. One
of the keys to the film's success was an innovative marketing scheme
conceived by Sam Morris, Warner Bros.' sales manager. In Crafton's
description: [A] special clause in Warners' Vitaphone exhibition contract virtually guaranteed long runs. Theaters had to book The Jazz Singer for
full rather than split weeks. Instead of the traditional flat rental
fee, Warners took a percentage of the gate. A sliding scale meant that
the exhibitor's take increased the longer the film was held over. The
signing of this contract by the greater New York Fox circuit was
regarded as a headline - making precedent. Similar
arrangements, based on a percentage of the gross rather than flat
rental fees, would soon become standard for the U.S. film industry's
high end or "A" product. Though in retrospect, the success of The Jazz Singer signaled the end of the silent motion picture era,
this was not immediately apparent. Mordaunt Hall, for example, praised
Warner Bros. for "astutely realiz[ing] that a film conception of The Jazz Singer was one of the few subjects that would lend itself to the use of the Vitaphone." In
historian Richard Koszarski's words, "Silent films did not disappear
overnight, nor did talking films immediately flood the theaters....
Nevertheless, 1927 remains the year that Warner Bros. moved to close the
book on the history of silent pictures, even if their original goal had
been somewhat more modest." The
film had other effects that were more immediate. George Jessel, who was
in his third season touring with the stage production of The Jazz Singer,
later described what happened to his show — perhaps anticipating how
sound would soon cement Hollywood's dominance of the American
entertainment industry: "A week or two after the Washington engagement
the sound - and - picture version of The Jazz Singer with
Al Jolson was sweeping the country, and I was swept out of business. I
couldn't compete with a picture theatre across the street showing the
first great sound picture in the world ... for fifty cents, while the
price at my theatre was $ 3.00." Crafton
points to the January 1928 national release of the film's sound version
as the truly pivotal event: two months later, Warners announced that The Jazz Singer was playing at a record 235 theaters (though many could still show it only silently). In May, a consortium including the leading Hollywood studios signed up with Western Electric's licensing division, ERPI, for sound conversion. In July, Warner Bros. released the first all - talking feature, Lights of New York, a musical crime melodrama. On September 27, The Jazz Singer became
the first feature length talking picture to be shown in Europe when it
premiered at London's Piccadilly Theatre. The movie "created a
sensation", according to British film historian Rachael Low. "The Jazz Singer was a turning point [for the introduction of sound]. The Bioscope greeted it with, 'We are inclined to wonder why we ever called them Living Pictures.'" The Paris sound premiere followed in January 1929. By
mid 1929, Hollywood was producing almost exclusively sound films; by
the end of the following year, the same was true in much of Western
Europe. Jolson went on to make a series of movies for Warners, including The Singing Fool, a part - talkie, and the all - talking features Say It with Songs (1929), Mammy (1930), and Big Boy (1930). Three subsequent screen versions of The Jazz Singer have been produced: a 1952 remake, starring Danny Thomas and Peggy Lee; a 1959 television remake, starring Jerry Lewis; and a 1980 remake starring Neil Diamond, Lucie Arnaz, and Laurence Olivier. The Jazz Singer was adapted as a one hour radio play on two broadcasts of Lux Radio Theater, both starring Al Jolson, reprising his screen role. The first aired August 10, 1936; the second on June 2, 1947. Among the many references to The Jazz Singer in popular culture, perhaps the most notable is that of the classic MGM musical Singin' in the Rain (1952). The story, set in 1927, revolves around efforts to change a silent film production, The Dueling Cavalier, into a talking picture in response to The Jazz Singer's success. The plot of the Simpsons episode "Like Father, Like Clown"
(1991) parallels the tale of Jakie Rabinowitz / Jack Robin. Krusty the
Clown's rabbi father disapproves of his son's choice to be a comedian,
telling him, "If you were a musician or a jazz singer, this I could
forgive." According to film historian Krin Gabbard, The Jazz Singer "provides
the basic narrative for the lives of jazz and popular musicians in the
movies. If this argument means that sometime after 1959 the narrative
must belong to pop rockers, it only proves the power of the original
1927 film to determine how Hollywood tells the stories of popular
musicians." More broadly, he also suggests that this "seemingly unique film" has "become a paradigm for American success stories." More specifically, he examines a cycle of biopics of white jazz musicians stretching from The Birth of the Blues (1941) to The Five Pennies (1959) that trace their roots to The Jazz Singer. In 1996, The Jazz Singer was selected for preservation in the American National Film Registry of
"culturally, historically or aesthetically significant" motion
pictures. In 1998, the film was chosen in voting conducted by the American Film Institute as one of the best American films of all time, ranking at number ninety. In
2007, a three disc deluxe DVD edition of the film was released. The
supplemental material includes Jolson's 1926 Vitaphone short, A Plantation Act. Jack Robin's use of blackface in his Broadway stage act is the primary focus of many Jazz Singer studies. Its crucial and unusual role is described by scholar Corin Willis: In contrast to the racial jokes and innuendo brought out in its subsequent persistence in early sound film, blackface imagery in The Jazz Singer is
at the core of the film's central theme, an expressive and artistic
exploration of the notion of duplicity and ethnic hybridity within
American identity. Of the more than seventy examples of blackface in
early sound film 1927 – 53 that I have viewed (including the nine
blackface appearances Jolson subsequently made), The Jazz Singer is unique in that it is the only film where blackface is central to the narrative development and thematic expression. The
function and meaning of blackface in the film is intimately involved
with Jack's own Jewish heritage and his desire to make his mark in mass
American culture — much as the ethnically Jewish Jolson and the Warner
brothers were doing themselves. Jack Robin "compounds both tradition and
stardom. The Warner Brothers thesis is that, really to succeed, a man
must first acknowledge his ethnic self," argues W.T. Lhamon. "[T]he
whole film builds toward the blacking - up scene at the dress rehearsal.
Jack Robin needs the blackface mask as the agency of his compounded
identity. Blackface will hold all the identities together without
freezing them in a singular relationship or replacing their parts." Seymour
Stark's view is less sanguine. In describing Jolson's extensive
experience performing in blackface in stage musicals, he asserts, "The
immigrant Jew as Broadway star ... works within a blackface minstrel
tradition that obscures his Jewish pedigree, but proclaims his white
identity. Jolson's slight Yiddish accent was hidden by a Southern
veneer." Arguing that The Jazz Singer actually
avoids honestly dealing with the tension between American assimilation
and Jewish identity, he claims that its "covert message ... is that the
symbol of blackface provides the Jewish immigrant with the same rights
and privileges accorded to earlier generations of European immigrants
initiated into the rituals of the minstrel show." Lisa
Silberman Brenner contradicts this view. She returns to the intentions
expressed by Samson Raphaelson, on whose play the film's script was
closely based: "For Raphaelson, jazz is prayer, American style, and the
blackface minstrel the new Jewish cantor. Based on the author's own
words, the play is not about blackface as a means for Jews to become
White, but about blackface as a means for Jews to express a new kind of
Jewishness, that of the modern American Jew." She
observes that during the same period, the Jewish press was noting with
pride that Jewish performers were adopting aspects of African American
music. According
to Scott Eyman, the film "marks one of the few times Hollywood Jews
allowed themselves to contemplate their own central cultural myth, and the conundrums that go with it. The Jazz Singer implicitly celebrates the ambition and drive needed to escape the shtetls of
Europe and the ghettos of New York, and the attendant hunger for
recognition. Jack, Sam, and Harry [Warner] let Jack Robin have it all:
the satisfaction of taking his father's place and of
conquering the Winter Garden. They were, perhaps unwittingly,
dramatizing some of their own ambivalence about the debt
first - generation Americans owed their parents." Cantor Rabinowitz wants his son to carry on the generations old family tradition and become a cantor at the synagogue in the Jewish ghetto of
Manhattan's Lower East Side. But down at the beer garden,
thirteen year old Jakie Rabinowitz is performing popular, so-called
jazz, tunes. Moisha Yudelson spots the boy and tells Jakie's father, who
drags him home. Jakie clings to his mother, Sara, as his father
declares, "I'll teach him better than to debase the voice God gave him!"
Jakie threatens: "If you whip me again, I'll run away — and never come back!" After the whipping, Jakie kisses his mother goodbye and, true to his word, runs away. At the Yom Kippur service,
Rabinowitz mournfully tells a fellow celebrant, "My son was to stand at
my side and sing tonight — but now I have no son." As the sacred Kol Nidre is sung, Jakie sneaks back home to retrieve a picture of his loving mother. Approximately
ten years later, Jakie has changed his name to the more assimilated
Jack Robin. Jack is called up from his table at a cabaret to perform on
stage. He belts out "'Dirty Hands, Dirty Face," which is
enthusiastically received, then addresses the crowd with the
live recorded, spoken words that made motion picture history: Jack
wows the crowd with his energized rendition. Afterward, he is
introduced to the beautiful Mary Dale, a musical theater dancer. "There
are lots of jazz singers, but you have a tear in your voice," she says, offering to help with his budding career. Back
at the family home Jack left long ago, the elder Rabinowitz instructs a
young student in the traditional cantorial art. Jack's visibly aged
mother receives a letter that Yudleson reads to her: Dear
Mama: I'm getting along great, making $ 250.00 a week. A wonderful girl,
Mary Dale, got me my big chance. Write me c/o State Theatre in Chicago.
Last time you forgot and addressed me Jakie Rabinowitz. Jack Robin is my name now. Your loving son, Jakie. His mother wonders if he has become romantically involved with a "shiksa", another step away from his religious roots. When Sara shows her husband the letter, he is furious: "We have no son!" Sara weeps. With
Mary's help, Jack has gained a place on the vaudeville circuit and now
travels constantly around the country. For one glorious week, their
paths have crossed in Chicago. Now they must part for an indefinite
period as Mary has won a lead role in a Broadway show. Jack attends a
concert of sacred songs performed by renowned cantor Yossele Rosenblatt and
is reminded poignantly of his father. About to board a train for the
next stop on the circuit, Jack learns that he's won a shot at the big
time: a spot in a Broadway revue, which will bring him close to both
Mary and his treasured mother. At
the Rabinowitz home, Sara organizes presents that have arrived in
celebration of her husband's sixtieth birthday. It is also the day of
Jack's return, and he surprises his mother with an expensive piece of
jewelry. At his father's piano, he sings and plays Irving Berlin's "Blue Skies"
for her. Then, as Jack continues to tinkle on the piano with his left
hand throughout, comes the first true dialogue sequence ever heard in a
feature length film (Sara's lines, for the most part, are not fully
enunciated, and at times are difficult to understand amid her frequent
giggles): Sara: Yes... Jack: I'm glad of it. I'd rather please you than anybody I know of. Oh, darlin', will you gimme something? Sara: What? Jack:
You'll never guess. Shut your eyes, Mama. Shut 'em for little Jakie
[pronounced "Jack-ee," not "Jayk-ee"]. Haw, I'm gonna steal something
[he kisses her]. Ha, ha, ha, ha, ha, ha! Sara: Oh, Jakie, oh... Jack:
I'll give it back to you someday too, you see if I don't. Mama darling,
if I'm a success in this show, well, we're gonna move from here. Sara: Oh, no. Jack:
Oh yes, we're gonna move up in the Bronx. A lot of nice green grass up
there, and a whole lot of people you know. There's the Ginsbergs, the
Guttenbergs, and the Goldbergs. Oh, a whole lot of Bergs. I don't know
'em all. And I'm gonna buy you a nice black silk dress, Mama. Sara: Ohh... Jack: You'll see, Mrs. Friedman, the butcher's wife, she'll be jealous of you. Sara: Oh, no... Jack: Yes she will. You'll see if she isn't. And I'm going to get you a nice pink dress that will go with your brown eyes. Sara: Oh, no, Jakie, no. I...I... Jack: What do you mean, "no"? Sara: Oh, no, dear. Jack:
Who, who is tellin' ya? What do you mean, "no"? Yes, you'll wear pink
or else. Or else you'll wear pink. Hm, hm, hm, hm. And darlin', ohh, I'm
gonna take you to Coney Island. Sara: Yeah? Jack: Yes, you're gonna ride on the shoot-the-chute. Sara: Oh ho... Jack: And you know the dark mill. Sara: Yeah? Jack: Ever been in the dark mill? Sara: Oh, no, I wouldn't. Jack:
Well, with me it's alright. I'll kiss ya and hug ya—you'll see if I
don't. Now Mama, Mama, stop now, you're gettin' kittenish. Mama, listen,
I'm gonna sing this like I will if I go on the stage, you know, with
the show. I'm gonna sing it jazzy. Now get this. Having
performed a relatively straightforward version of the song, Jack now
demonstrates for his mother the energetic method with which he plans to
perform it on Broadway. In the middle of the song, he interjects,
referring to his flamboyant piano style, Jack's
father enters and watches Jack perform for a few moments. Stunned, he
shouts the last recorded line of speech in the movie: Jack tries to explain his modern point of view, but the appalled cantor banishes him: "I never want to see you again — you jazz singer!"
As he leaves, Jack makes a prediction: "I came home with a heart full
of love, but you don't want to understand. Some day you'll understand,
the same as Mama does." Sara fears Jack will never return: "He came back
once, Papa, but — he'll never come back again." The cantor slumps
defeatedly. Two weeks after Jack's expulsion from the family home and twenty - four hours before opening night of April Follies on
Broadway, Jack's father falls gravely ill. Jack is asked to choose
between the show and duty to his family and faith: in order to sing the
Kol Nidre for Yom Kippur in his father's place, he will have to miss the
big premiere. That
evening, the eve of Yom Kippur, Yudleson tells the Jewish elders, "For
the first time, we have no Cantor on the Day of Atonement." Lying in his
bed, weak and gaunt, Cantor Rabinowitz tells Sara that he cannot
perform on the most sacred of holy days: "My son came to me in my dreams
— he sang Kol Nidre so beautifully. If he would only sing like that
tonight — surely he would be forgiven." As
Jack prepares for a dress rehearsal by applying blackface makeup, he
and Mary discuss his career aspirations and the family pressures they
agree he must resist. Sara and Yudleson comes to Jack's dressing room to
plea for him to come to his father and sing in his stead. Jack is torn.
He delivers his blackface performance ("Mother of Mine, I Still Have
You"), and Sara sees her son onstage for the first time. She has a
tearful revelation: "Here he belongs. If God wanted him in His house, He
would have kept him there. He's not my boy anymore — he belongs to the whole world now." Afterward,
Jack returns to the Rabinowitz home. He kneels at his father's bedside
and the two converse fondly: "My son — I love you." Sara suggests that
it may help heal his father if Jack takes his place at the Yom Kippur
service. Mary arrives with the producer, who warns Jack that he'll
never work on Broadway again if he fails to appear on opening night.
Jack can't decide. Mary challenges him: "Were you lying when you said
your career came before everything?" Jack is unsure if he even can
replace his father: "I haven't sung Kol Nidre since I was a little boy."
His mother tells him, "Do what is in your heart, Jakie — if you sing
and God is not in your voice — your father will know." The producer
cajoles Jack: "You're a jazz singer at heart!" At
the theater, the opening night audience is told that there will be no
performance. Jack sings the Kol Nidre in his father's place. His father
listens from his deathbed to the nearby ceremony and speaks his last,
forgiving words: "Mama, we have our son again." The spirit of Jack's
father is shown at his side in the synagogue. Mary has come to listen.
She sees how Jack has reconciled the division in his soul: "a jazz
singer — singing to his God." "The
season passes — and time heals — the show goes on." Jack, as "The Jazz
Singer," is now appearing at the Winter Garden theater, apparently as the featured performer opening for a show called Back Room. In the front row of the packed theater, his mother sits alongside Yudleson. Jack, in blackface, performs the song "My Mammy" for her and for the world.
“ Wait
a minute, wait a minute, you ain't heard nothin' yet. Wait a minute I
tell ya, you ain't heard nothin'. You wanna hear "Toot, Toot, Tootsie"?
Alright. Hold on. Hold on. [turning to the band's piano player] Lou,
listen. Play "Toot, Toot, Tootsie" — three choruses, you understand? In
the third chorus, I whistle. Now give it to 'em hard and heavy. Go
right ahead. ”
“ Jack: Did you like that, Mama? ” “ You like that slapping business? ” “ Stop! ”