<Back to Index>
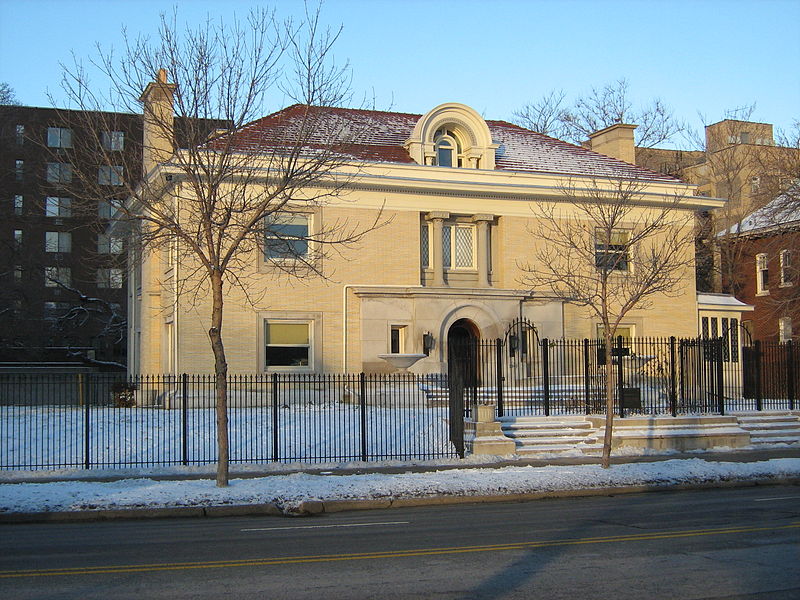
- Architect George Washington Maher, 1864
- Architect Dwight Heald Perkins, 1867
PAGE SPONSOR

George Washington Maher (December 25, 1864 – September 12, 1926) was a significant contributor to the Prairie School style of architecture during the first quarter of the 20th century. He also was known for blending the traditional with the Arts & Crafts style. According to architectural historian H. Allen Brooks, "His influence on the Midwest was profound and prolonged and, in its time, was certainly as great as was [Frank Lloyd] Wright's. Compared with the conventional architecture of the day, his work showed considerable freedom and originality, and his interiors were notable for their open and flowing ... space".
Maher was elected a Fellow of the American Institute of Architects in 1916.
George Maher was born in Mill Creek, West Virginia, but moved as a small boy with his family to New Albany, Indiana, where he attended public elementary school. While in his early teens, due to continuing financial pressures, the family moved to Chicago.
At the age of 13 he was apprenticed at the Chicago architectural firm of Augustus Bauer and Henry Hill. In 1887 he joined the office of architect Joseph L. Silsbee as a draftsman where he worked with Frank Lloyd Wright and George Grant Elmslie. In 1888 Maher formed a partnership with Charles Corwin which lasted for only a brief time before he began his own practice.
Maher married Elizabeth Brooks in 1893 and moved to Kenilworth, Illinois.
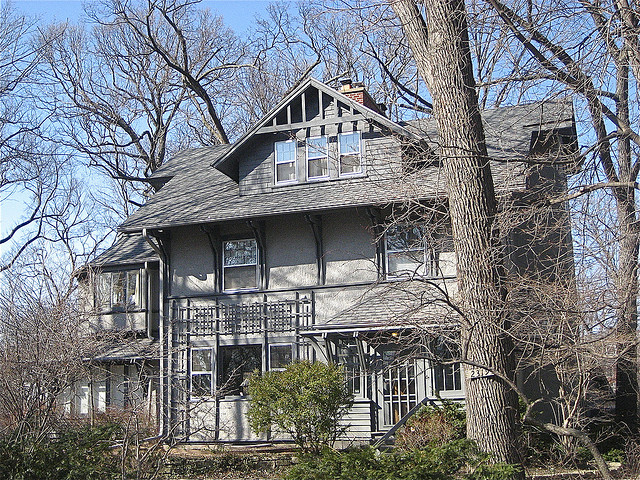
His own home, built there in 1893, which was only one of about 40 homes
he designed in Kenilworth. Along with the homes he also designed the
entrance to the village as well as a number of other public
embellishments. In addition to Kenilworth, one of the largest concentrations of his work is along Hutchinson Street, on Chicago's North Side lakefront.
From the start of his career, Maher wrote about his views on architecture and was active in organizations interested in exploring new ideas in architecture and design. In 1887 Inland Architect published a paper he had written titled “Originality in American Architecture,” one of the first of many he would write. In 1895 an interest in the English Arts and Crafts Movement lead him to become one of the founding members of The Chicago Arts and Crafts Society. During his career, he was involved as a leading figure in the meetings and exhibitions of the Chicago Architectural Club, a group that was at the center of activity of the Prairie movement in Chicago.
Maher’s early work during the 1890s reflected the influence of Silsbee and H.H. Richardson as well as Louis Sullivan and others of the Chicago School.
In 1893 Maher met J.L. Cochran who was developing the community of Edgewater which would ultimately become part of Chicago. During the next several years Maher designed a series of houses for Cochran which helped establish Maher's career and reputation.
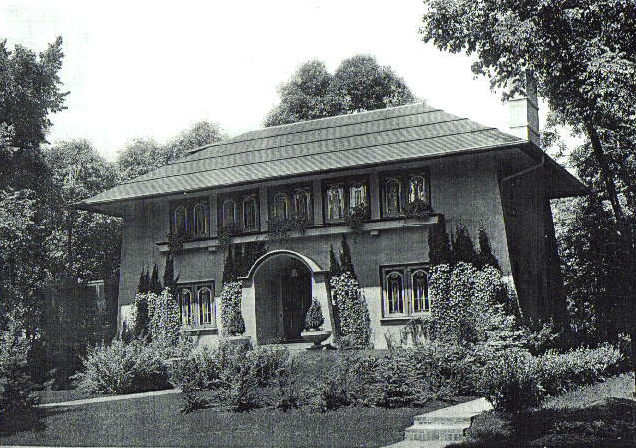
Commissioned in 1897, one of Maher's most important designs is the John Farson House in Oak Park, also known as Pleasant Home. In this house, Maher synthesized his own version of what would ultimately come to be called the Prairie School style of architecture. One of the earliest Prairie style buildings, its design concept proved to be extremely influential in its time and was widely copied throughout the Midwest.
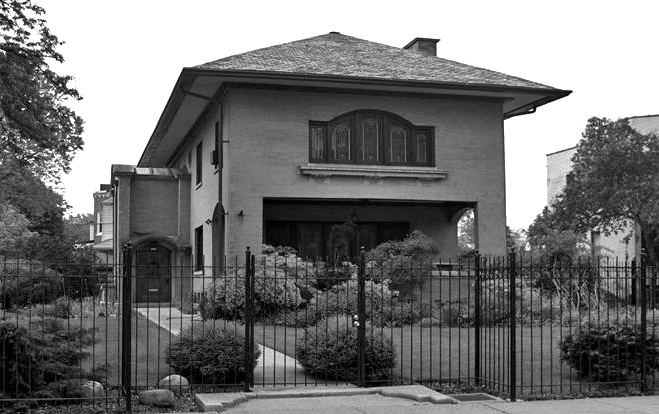
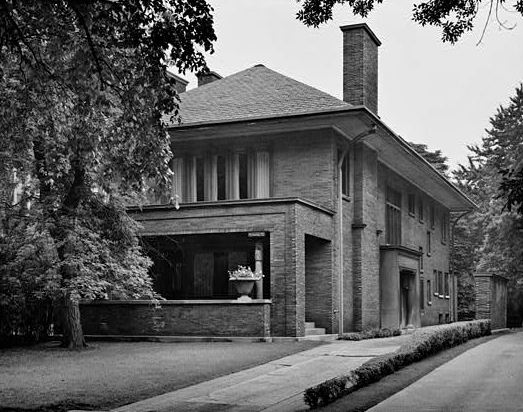
Over the years Maher designed numerous houses for clients ranging from middle class businessmen to wealthy society figures. The success of the Farson house led to a number of large commissions. Among his clients was James A. Patten for whom he built a large mansion in 1901. Patten was also responsible for getting Maher the commission to design the original Patten Gymnasium at Northwestern University where Maher also designed the Swift Hall of Engineering. Also in 1901, Maher was hired to remodel the Nickerson House which currently houses the Driehaus Muesum. These were followed by the design of a large estate for Harry Rubens that was built in Glencoe, Illinois, in 1903. Jens Jensen designed the landscaping for the Rubens estate. Other projects include the P.J. King House from 1901, the Rath House in 1907, and the Colvin House in 1909, all of which have been designated Chicago Landmarks by the city.
By the time of the Farson House commission, Maher was one of the first of the Prairie Style architects to have developed a personal style. By 1897, with almost a full decade behind him, his career was well established. With Wright’s Prairie houses still several years in the future, Maher's version of the Prairie style came at a time when Louis Sullivan’s work was still the dominant influence for the developing group of architects. While many of the others worked directly for Wright or Sullivan, Maher never did which may be part of the reason his design work would follow a more independent path throughout his career.
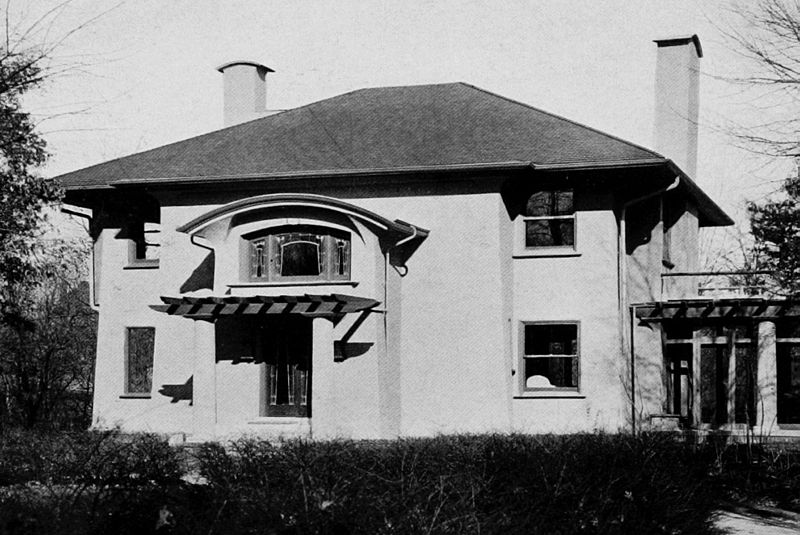
Around 1904 Maher’s designs started to show more of his interest in ideas derived from contemporary European design, especially the English Arts and Crafts movement and the Vienna Secession. Assimilating these influences into concepts of his own, he created designs that set his work apart at a time when Wright’s work was becoming increasingly influential among his contemporaries. Among these projects was the Corbin House in 1904 followed by houses such as the Erwin House (1905) , the Lackner House (1905) and the Schultz House (1907).
As
part of his design philosophy Maher developed what he call Motif - Rhythm
theory in an attempt to produce a design unity throughout the building
and its interior. This involved using a decorative element, often a
local flower, a geometric shape, or a combination of the two which would
be used repeatedly throughout the design to “bind the design together.” At “Rockledge”, the 12,000 square foot (1,100 m2)
summer house he designed in 1911 for Ernest and Grace King in Homer,
Minnesota, Maher was also commissioned to design the interior
furnishings for the house allowing him to use the Motif - Rhythm theory to
the fullest extent possible. Ultimately the house fell into disuse but
before the house was demolished the furniture, clocks, lamps, rugs, even
the tableware that Maher had designed were sold with many pieces ending
up in various museum collections as examples of Arts and Crafts design.
While Maher is known for his residential work, he also designed commercial and institutional buildings. His client James Patten was responsible for getting Maher the commission to design the most well known of these, the original Patten Gymnasium (1908 – 09) at Northwestern University where Maher also designed the Swift Hall of Engineering (1908). Other notable projects were several buildings for the J.R. Watkins Medical Company (1911) including their administrative headquarters in Winona, Minnesota. These were followed by the Winona Saving Bank which was designed and built in 1914 - 16.
The
momentum of the Prairie School movement began to rapidly decline in the
mid teens as clients' tastes and interests changed, forcing many of its
followers to turn in other directions. For some, including Maher, it
meant increasing pressure to design in the eclectic styles then in
vogue.
Throughout his career Maher was involved in organizations seeking to improve the architecture profession. In addition to the Chicago Architectural Club, he was active in the state chapter of the American Institute of Architects serving as state chapter president in 1918. Just as Maher had worked for Silsbee whose office had produced a number of architects that went on to have distinguished careers, Maher’s office also produced several notable architects including his son Phillip Brooks Maher and Robert Seyfarth.
After his World War l, his son joined the office as a partner and the firm became known as “George W. Maher & Son”. In the early 1920s Maher designed multiple buildings and landscapes throughout the Chicago area and in Gary, Indiana, where the firm produced a number of projects. His final work was commissioned by the Gary Heat, Light, and Water Company of Gary, Indiana. They requested him to design a new warehouse. This design embodied the last set of drawings to hold his name and architectural registration.
By
the time of his death he had designed over 270 projects; from houses to
parks to public buildings. In the fall of 1926 after several years of
declining health, including hospitalization for depression in 1924 - 25,
George W. Maher took his own life at the age of 61.
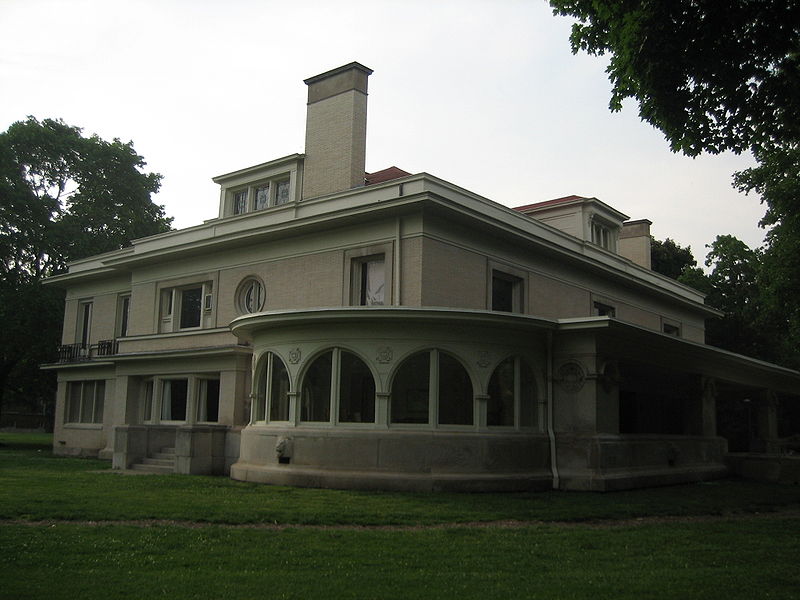
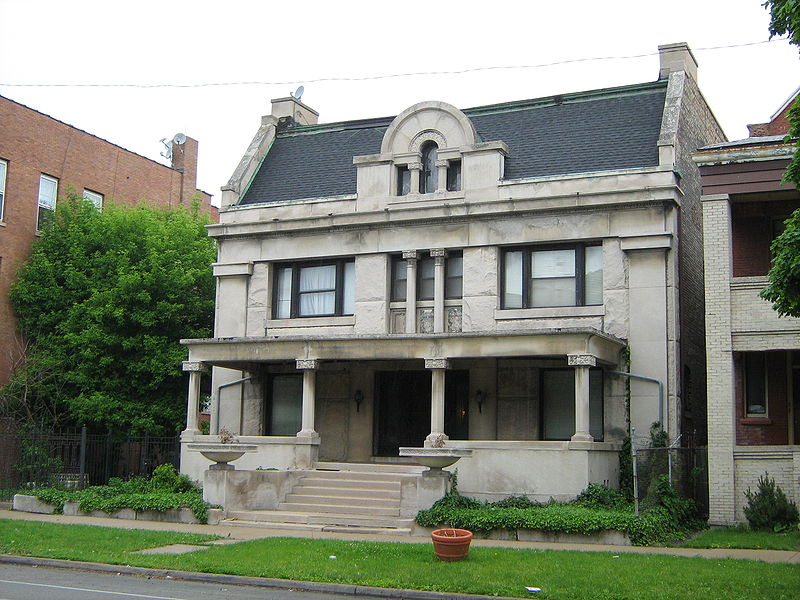
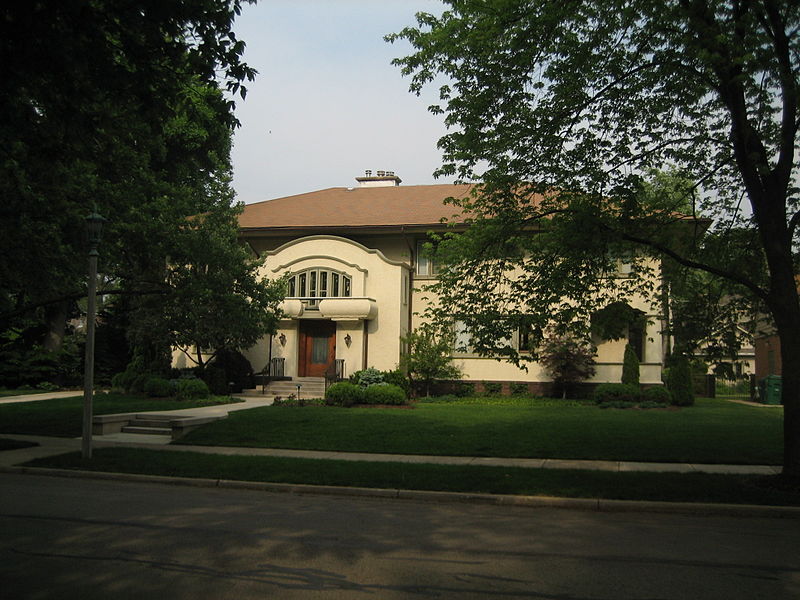










Dwight Heald Perkins (March 26, 1867 - November 2, 1941) was an American architect and planner.
Perkins was born in Memphis, Tennessee, and moved to Chicago with his family at age 4. His mother was widowed a few years after his family completed their move.
Perkins attended only 3 months of high school, having to find work to help support his family. He worked initially at the Chicago Stockyards and later at the architectural firms Wheelock & Clay and for a few months for Frederick Schock. He was accepted to study architecture at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1885. A family friend, Mrs. Charles Hitchcock, helped finance his education there.
He studied at MIT for two years and was so skilled that he was invited to serve as an instructor for a third year. Also while in Boston, he met Lucy Fitch, who would become his wife on August 18, 1891.
Perkins left Boston in late 1888. In January 1889 he interviewed at Burnham & Root in Chicago and was employed in early February of that year. He remained for 5 years, gradually assuming more and more responsibility. He left at the end of 1893 to form his own firm. It was during this period that Perkins was associated with a group called "The Eighteen" that included like minded architects such as Lawrence Buck and Frank Lloyd Wright.
On January 1, 1894, he opened the office after receiving his first major commission, with help from Daniel Burnham, the Stevens Point, Wisconsin, Normal School. In 1894 he was commissioned to design a new building for the Steinway Piano company. This building bore little resemblance to the work he would do later, often in the style which became known as "Prairie School" of architecture.
Perkins was offered the commission for Charles Hitchcock Hall as a result of his connection with the donor for the building, Mrs. Charles Hitchcock, who had previously helped fund his college education.
Perkins was appointed the Chief Architect for the Chicago Board of Education by Mayor Edward F. Dunne in 1905. He was responsible for the design of 40 public schools. Among these structures was Carl Schurz High School which was described by the American Institute of Architects as "the best and most important" of his designs, in addition to being his "masterpiece" and an "important example of early twentieth century architecture, utilizing elements of both the Chicago and Prairie Schools of Architecture."
His five year service in this role ended when he was accused of incompetence, inefficiency, and insubordination and was dismissed following a trial in which only the insubordination charge was upheld. However, it is generally accepted that the true reason for his firing was that he refused to bow down to the demands of the corrupt members of the Board of Education who insisted that he give contracts to their cronies.
Perkins had maintained a private practice with John L. Hamilton in addition to his service on the board. In 1911, with the addition of William K. Fellows, the firm of Perkins, Fellows, & Hamilton opened with offices in Chicago's loop. Perkins left the firm in c.1929 and joined what became Perkins, Chatten, and Hammond, which he left in 1933.
Perkins died in Lordsburg, New Mexico, in 1941 of a cerebral hemorrhage while traveling to his winter home in Pasedena, California.
Other works by Dwight Perkins firm include the Lincoln Park Zoo Lion House, the Alfred Nobel School, and many other residential homes.

