<Back to Index>
- Minister President of Bavaria Kurt Eisner, 1867
- 11th Chancellor of Germany Gustav Adolf Bauer, 1870
PAGE SPONSOR
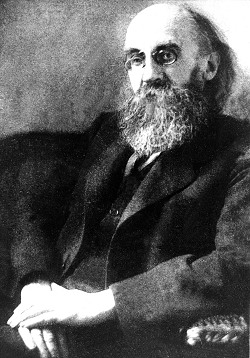


Kurt Eisner (14 May 1867 – 21 February 1919) was a Bavarian politician and journalist. As a German socialist journalist and statesman, he organized the Socialist Revolution that overthrew the Wittelsbach monarchy in Bavaria in November 1918. He is used as an example of charismatic authority by Max Weber.
Kurt Eisner was born in Berlin at 10:15 p.m. on 14 May 1867 to Emanuel Eisner and Hedwig Levenstein, both Jewish. He was married to painter Elisabeth Hendrich from 1892, with whom he had five children, but they eventually divorced in 1917 and Eisner then married Elise Belli, an editor. With her, he had two daughters.
Eisner studied philosophy, but then became a journalist in Marburg. From 1890 to 1895, he was contributing editor of the Frankfurter Zeitung, during which time he wrote an article attacking Kaiser Wilhelm II, and for which he spent nine months in prison. Eisner was always an open Republican as well as a Social Democrat, joining the SPD in 1898, whereas for tactical reasons German Social Democracy, particularly in its later stages, rather cold shouldered anything in the shape of Republican propaganda as being unnecessary and included in general Social Democratic aims. Consequently he fought actively for political democracy as well as Social Democracy. He became editor of Vorwärts after the death of Wilhelm Liebknecht in 1900, but was subsequently called upon to resign from that position. After his withdrawal from Vorwärts in 1905, his activities were confined in the main to Bavaria, though he toured other parts of Germany. He was chief editor for the Fränkische Tagespost in Nuremberg from 1907 to 1910 and afterwards became a freelance journalist in Munich.
He joined the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany in 1917, at the height of World War I, and was convicted of treason in 1918 for his role in inciting a strike of munitions workers. He spent 9 months in Cell 70 of Stadelheim Prison, after which he was released during the General Amnesty in October of that year.
After his release from prison, he organized the revolution that overthrew the monarchy in Bavaria (German Revolution). He declared Bavaria to be a free state and republic on 8 November 1918, becoming the first republican premier of Bavaria. On 23 November 1918, he leaked documents from the Bavarian plenipotentiary at
Berlin in July / August 1914 he thought proved the war was caused by "a
small horde of mad Prussian military" men as well as "allied"
industrialists, capitalists, politicians, and princes. At the Berne Conference of Socialists,
held at Berne, Switzerland, he attacked the moderate German socialists
because of their refusal to acknowledge Germany's guilt in bringing
about World War I.
For this speech and for his uncompromising hostility to Prussia, he
became bitterly hated by large sections of the German people.
Due to the inability of the new government to provide basic services as a result of the Treaty of Versailles as well as the antisemitic stab - in - the - back legend originating in Austria, Eisner's Independent Social Democrats were defeated in the January 1919 election by the Bavarian People's Party.
Eisner was assassinated in Munich when German nationalist Anton Graf von Arco auf Valley shot Eisner in the back on 21 February 1919. Eisner was on his way to present his resignation to the Bavarian parliament. His assassination resulted in the establishment of the brief Bavarian Soviet Republic and parliament and government fleeing Munich.
In
1989 a monument at the site of his assassination was built. It reads,
"Kurt Eisner, der am 9. November 1918 die Bayerische Republik ausrief,
nachmaliger Ministerpräsident des Volksstaates Bayern, wurde an
dieser Stelle am 21. Februar 1919 ermordet." ("Kurt Eisner, who
proclaimed the Bavarian republic on 8 November 1918 – later Prime
Minister of the Republic of Bavaria – was murdered here on 21 February
1919.")
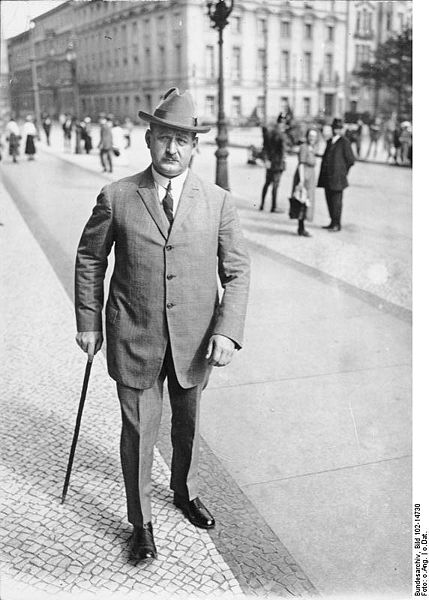


Gustav Adolf Bauer (6 January 1870 – 16 September 1944) was a German Social Democratic Party leader and Chancellor of Germany from 1919 to 1920.
Born in Darkehmen (now Ozyorsk, Kaliningrad Oblast) near Königsberg in East Prussia, Bauer, who rose to notice through his leadership of a white collar trade union, served from 1908 to 1918 as chairman of the General Commission of Trade Unions for all of Germany. A member of the Reichstag, Bauer entered Prince Max of Baden's government in October 1918 as Minister of Labor, a role which he continued to hold in the government of Philipp Scheidemann after the war. When Scheidemann resigned in June 1919 to protest the Treaty of Versailles, Bauer became Chancellor, serving until March 1920, when he resigned shortly after the failure of the Kapp Putsch.
Bauer resigned from the Social Democratic Party and the Reichstag in disgrace in February 1925, after it appeared that he had accepted improper payments in the Barmat Scandal and then lied about it, but was reinstated in 1926.
Bauer later served in the governments of Hermann Müller and Joseph Wirth.