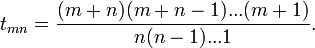<Back to Index>
- Mathematician and Physicist Blaise Pascal, 1623
PAGE SPONSOR



Blaise Pascal (19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662), was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer and Catholic philosopher. He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earliest work was in the natural and applied sciences where he made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clarified the concepts of pressure and vacuum by generalizing the work of Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal also wrote in defense of the scientific method.
In 1642, while still a teenager, he started some pioneering work on calculating machines, and after three years of effort and 50 prototypes he invented the mechanical calculator. He built twenty of these machines (called the Pascaline) in the following ten years. Pascal was a mathematician of the first order. He helped create two major new areas of research. He wrote a significant treatise on the subject of projective geometry at the age of sixteen, and later corresponded with Pierre de Fermat on probability theory, strongly influencing the development of modern economics and social science. Following Galileo and Torricelli, in 1646 he refuted Aristotle's followers who insisted that nature abhors a vacuum. His results caused many disputes before being accepted.
In 1646, he and his sister Jacqueline identified with the religious movement within Catholicism known by its detractors as Jansenism. His father died in 1651. Following a mystical experience in late 1654, he had his "second conversion", abandoned his scientific work, and devoted himself to philosophy and theology. His two most famous works date from this period: the Lettres provinciales and the Pensées, the former set in the conflict between Jansenists and Jesuits. In this year, he also wrote an important treatise on the arithmetical triangle. Between 1658 and 1659 he wrote on the cycloid and its use in calculating the volume of solids.
Pascal had poor health especially after his eighteenth year and his death came just two months after his 39th birthday.
Pascal was born in Clermont - Ferrand; he lost his mother, Antoinette Begon, at the age of three. His father, Étienne Pascal (1588 – 1651), who also had an interest in science and mathematics, was a local judge and member of the "Noblesse de Robe". Pascal had two sisters, the younger Jacqueline and the elder Gilberte.
In 1631, five years after the death of his wife, Étienne Pascal moved with his children to Paris. The newly arrived family soon hired Louise Delfault, a maid who eventually became an instrumental member of the family. Étienne, who never remarried, decided that he alone would educate his children, for they all showed extraordinary intellectual ability, particularly his son Blaise. The young Pascal showed an amazing aptitude for mathematics and science.
Particularly of interest to Pascal was a work of Desargues on conic sections. Following Desargues' thinking, the sixteen year old Pascal produced, as a means of proof, a short treatise on what was called the "Mystic Hexagram", Essai pour les coniques ("Essay on Conics") and sent it — his first serious work of mathematics — to Père Mersenne in Paris; it is known still today as Pascal's theorem. It states that if a hexagon is inscribed in a circle (or conic) then the three intersection points of opposite sides lie on a line (called the Pascal line).
Pascal's work was so precocious that Descartes was convinced that Pascal's father had written it. When assured by Mersenne that it was, indeed, the product of the son not the father, Descartes dismissed it with a sniff: "I do not find it strange that he has offered demonstrations about conics more appropriate than those of the ancients," adding, "but other matters related to this subject can be proposed that would scarcely occur to a sixteen year old child."
In
France at that time offices and positions could be — and were — bought and
sold. In 1631 Étienne sold his position as second president of the Cour des Aides for 65,665 livres. The money was invested in a government bond which
provided if not a lavish then certainly a comfortable income which
allowed the Pascal family to move to, and enjoy, Paris. But in 1638
Richelieu, desperate for money to carry on the Thirty Years' War,
defaulted on the government's bonds. Suddenly Étienne Pascal's
worth had dropped from nearly 66,000 livres to less than 7,300.
Like so many others, Étienne was eventually forced to flee Paris because of his opposition to the fiscal policies of Cardinal Richelieu, leaving his three children in the care of his neighbor Madame Sainctot, a great beauty with an infamous past who kept one of the most glittering and intellectual salons in all France. It was only when Jacqueline performed well in a children's play with Richelieu in attendance that Étienne was pardoned. In time Étienne was back in good graces with the cardinal, and in 1639 had been appointed the king's commissioner of taxes in the city of Rouen — a city whose tax records, thanks to uprisings, were in utter chaos.
In
1642, in an effort to ease his father's endless, exhausting
calculations, and recalculations, of taxes owed and paid, Pascal, not
yet nineteen, constructed a mechanical calculator capable of addition
and subtraction, called Pascal's calculator or the Pascaline. The Musée des Arts et Métiers in Paris and the Zwinger museum in Dresden, Germany, exhibit two of his original mechanical calculators. Though these machines are early forerunners to computer engineering, the calculator failed to be a great commercial success. Because it was extraordinarily expensive the Pascaline became little more than a toy, and status symbol,
for the very rich both in France and throughout Europe. However, Pascal
continued to make improvements to his design through the next decade
and built twenty machines in total.
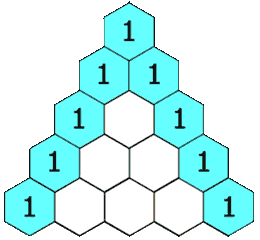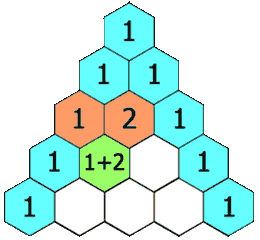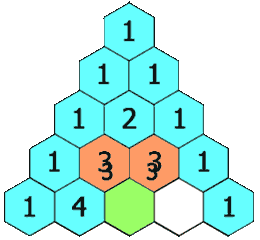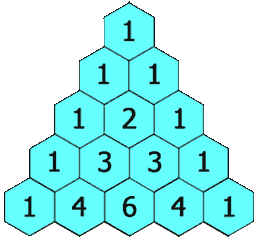
Pascal continued to influence mathematics throughout his life. His Traité du triangle arithmétique ("Treatise on the Arithmetical Triangle") of 1653 described a convenient tabular presentation for binomial coefficients, now called Pascal's triangle. The triangle can also be represented:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 4 | 10 | 20 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 15 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 6 | |||||
| 6 | 1 |
He defines the numbers in the triangle by recursion: Call the number in the (m+1)st row and (n+1)st column tmn. Then tmn = tm-1,n + tm,n-1, for m = 0, 1, 2... and n = 0, 1, 2... The boundary conditions are tm, −1 = 0, t−1, n for m = 1, 2, 3... and n = 1, 2, 3... The generator t00 = 1. Pascal concludes with the proof,
In 1654, prompted by a friend interested in gambling problems, he corresponded with Fermat on the subject, and from that collaboration was born the mathematical theory of probabilities. The friend was the Chevalier de Méré, and the specific problem was that of two players who want to finish a game early and, given the current circumstances of the game, want to divide the stakes fairly, based on the chance each has of winning the game from that point. From this discussion, the notion of expected value was introduced. Pascal later (in the Pensées) used a probabilistic argument, Pascal's Wager, to justify belief in God and a virtuous life. The work done by Fermat and Pascal into the calculus of probabilities laid important groundwork for Leibniz' formulation of the infinitesimal calculus.
After a religious experience in 1654, Pascal mostly gave up work in mathematics.
Pascal's major contribution to the philosophy of mathematics came with his De l'Esprit géométrique ("Of the Geometrical Spirit"), originally written as a preface to a geometry textbook for one of the famous "Petites - Ecoles de Port - Royal" ("Little Schools of Port - Royal"). The work was unpublished until over a century after his death. Here, Pascal looked into the issue of discovering truths, arguing that the ideal of such a method would be to found all propositions on already established truths. At the same time, however, he claimed this was impossible because such established truths would require other truths to back them up — first principles, therefore, cannot be reached. Based on this, Pascal argued that the procedure used in geometry was as perfect as possible, with certain principles assumed and other propositions developed from them. Nevertheless, there was no way to know the assumed principles to be true.
Pascal also used De l'Esprit géométrique to develop a theory of definition. He distinguished between definitions which are conventional labels defined by the writer and definitions which are within the language and understood by everyone because they naturally designate their referent. The second type would be characteristic of the philosophy of essentialism. Pascal claimed that only definitions of the first type were important to science and mathematics, arguing that those fields should adopt the philosophy of formalism as formulated by Descartes.
In De l'Art de persuader ("On the Art of Persuasion"), Pascal looked deeper into geometry's axiomatic method, specifically the question of how people come to be convinced of the axioms upon which later conclusions are based. Pascal agreed with Montaigne that
achieving certainty in these axioms and conclusions through human
methods is impossible. He asserted that these principles can only be
grasped through intuition, and that this fact underscored the necessity
for submission to God in searching out truths.
Pascal's work in the fields of the study of hydrodynamics and hydrostatics centered on the principles of hydraulic fluids. His inventions include the hydraulic press (using hydraulic pressure to multiply force) and the syringe. He has proven that hydrostatic pressure does not depend on the weight of the fluid but on the elevation difference. He demonstrated this principle by attaching a thin tube to a barrel full of water and filling the tube with water up to the level of the third floor of a building. The barrel started to leak. By 1646, Pascal had learned of Evangelista Torricelli's experimentation with barometers. Having replicated an experiment which involved placing a tube filled with mercury upside down in a bowl of mercury, Pascal questioned what force kept some mercury in the tube and what filled the space above the mercury in the tube. At the time, most scientists contended that, rather than a vacuum, some invisible matter was present. This was based on the Aristotelian notion that creation was a thing of substance, whether visible or invisible; and this substance was forever in motion. Furthermore, "Everything that is in motion must be moved by something," Aristotle declared. Therefore, to the Aristotelian trained scientists of Pascal's time, a vacuum was an impossibility. How so? As proof it was pointed out:
- Light passed through the so-called "vacuum" in the glass tube.
- Aristotle wrote how everything moved, and must be moved by something.
- Therefore, since there had to be an invisible "something" to move the light through the glass tube, there was no vacuum in the tube. Not in the glass tube or anywhere else. Vacuums — the absence of any and everything — were simply an impossibility.
Following more experimentation in this vein, in 1647 Pascal produced Experiences nouvelles touchant le vide ("New Experiments with the Vacuum"), which detailed basic rules describing to what degree various liquids could be supported by air pressure. It also provided reasons why it was indeed a vacuum above the column of liquid in a barometer tube.
On 19 September 1648, after many months of Pascal's friendly but insistent prodding, Florin Périer, husband of Pascal's elder sister Gilberte, was finally able to carry out the fact finding mission vital to Pascal's theory. The account, written by Périer, reads:
"The weather was chancy last Saturday... [but] around five o'clock that morning... the Puy - de - Dôme was visible... so I decided to give it a try. Several important people of the city of Clermont had asked me to let them know when I would make the ascent... I was delighted to have them with me in this great work... "...at eight o'clock we met in the gardens of the Minim Fathers, which has the lowest elevation in town.... First I poured sixteen pounds of quicksilver... into a vessel... then took several glass tubes... each four feet long and hermetically sealed at one end and opened at the other... then placed them in the vessel [of quicksilver]... I found the quick silver stood at 26" and 3½ lines above the quicksilver in the vessel... I repeated the experiment two more times while standing in the same spot... [they] produced the same result each time... "I attached one of the tubes to the vessel and marked the height of the quicksilver and... asked Father Chastin, one of the Minim Brothers... to watch if any changes should occur through the day... Taking the other tube and a portion of the quick silver... I walked to the top of Puy - de - Dôme, about 500 fathoms higher than the monastery, where upon experiment... found that the quicksilver reached a height of only 23" and 2 lines... I repeated the experiment five times with care... each at different points on the summit... found the same height of quicksilver... in each case..."
Pascal replicated the experiment in Paris by carrying a barometer up to the top of the bell tower at the church of Saint - Jacques - de - la - Boucherie, a height of about fifty meters. The mercury dropped two lines.
In the face of criticism that some invisible matter must exist in Pascal's empty space, Pascal, in his reply to Estienne Noel, gave one of the seventeenth century's major statements on the scientific method, which is a striking anticipation of the idea popularized by Karl Popper that scientific theories are characterized by their falsifiability: "In order to show that a hypothesis is evident, it does not suffice that all the phenomena follow from it; instead, if it leads to something contrary to a single one of the phenomena, that suffices to establish its falsity." His insistence on the existence of the vacuum also led to conflict with other prominent scientists, including Descartes.
Pascal introduced a primitive form of roulette and the roulette wheel in the 17th century in his search for a perpetual motion machine.
For after all what is man in nature? A nothing in relation to infinity, all in relation to nothing, a central point between nothing and all and infinitely far from understanding either. The ends of things and their beginnings are impregnably concealed from him in an impenetrable secret. He is equally incapable of seeing the nothingness out of which he was drawn and the infinite in which he is engulfed.
- Blaise Pascal, Pensées
In the winter of 1646, Pascal's 58 year old father broke his hip when he slipped and fell on an icy street of Rouen; given the man's age and the state of medicine in the 17th century, a broken hip could be a very serious condition, perhaps even fatal. Rouen was home to two of the finest doctors in France: Monsieur Doctor Deslandes and Monsieur Doctor de La Bouteillerie. The elder Pascal "would not let anyone other than these men attend him... It was a good choice, for the old man survived and was able to walk again..." But treatment and rehabilitation took three months, during which time La Bouteillerie and Deslandes had become household guests.
Both men were followers of Jean Guillebert, proponent of a splinter group from the main body of Catholic teaching known as Jansenism. This still fairly small sect was making surprising inroads into the French Catholic community at that time. It espoused rigorous Augustinism. Blaise spoke with the doctors frequently, and upon his successful treatment of Étienne, borrowed works by Jansenist authors from them. In this period, Pascal experienced a sort of "first conversion" and began to write on theological subjects in the course of the following year.
Pascal fell away from this initial religious engagement and experienced a few years of what some biographers have called his "worldly period" (1648 – 54). His father died in 1651 and left his inheritance to Pascal and Jacqueline, of which Pascal acted as her conservator. Jacqueline announced that she would soon become a postulant in the Jansenist convent of Port - Royal. Pascal was deeply affected and very sad, not because of her choice, but because of his chronic poor health; he too needed her.
"Suddenly there was war in the Pascal household. Blaise pleaded with Jacqueline not to leave, but she was adamant. He commanded her to stay, but that didn't work, either. At the heart of this was... Blaise's fear of abandonment... if Jacqueline entered Port - Royal, she would have to leave her inheritance behind... [but] nothing would change her mind."
By the end of October in 1651, a truce had been reached between brother and sister. In return for a healthy annual stipend, Jacqueline signed over her part of the inheritance to her brother. Gilberte had already been given her inheritance in the form of a dowry. In early January, Jacqueline left for Port - Royal. On that day, according to Gilberte concerning her brother, "He retired very sadly to his rooms without seeing Jacqueline, who was waiting in the little parlor..." In early June of 1653, after what must have seemed like endless badgering from Jacqueline, Pascal formally signed over the whole of his sister's inheritance to Port - Royal, which, to him, "had begun to smell like a cult." With two - thirds of his father's estate now gone, the 29 year old Pascal was now consigned to genteel poverty.
For a while, Pascal pursued the life of a bachelor. During visits to his sister at Port - Royal in 1654, he displayed contempt for affairs of the world but was not drawn to God.
Beginning in 1656, Pascal published his memorable attack on casuistry, a popular ethical method used by Catholic thinkers in the early modern period (especially the Jesuits, and in particular Antonio Escobar). Pascal denounced casuistry as the mere use of complex reasoning to justify moral laxity and all sorts of sins. The 18 letter series was published between 1656 and 1657 under the pseudonym Louis de Montalte and incensed Louis XIV. The king ordered that the book be shredded and burnt in 1660. In 1661, in the midsts of the formulary controversy, the Jansenist school at Port - Royal was condemned and closed down; those involved with the school had to sign a 1656 papal bull condemning the teachings of Jansen as heretical. The final letter from Pascal, in 1657, had defied Alexander VII himself. Even Pope Alexander, while publicly opposing them, nonetheless was persuaded by Pascal's arguments.
Aside from their religious influence, the Provincial Letters were popular as a literary work. Pascal's use of humor, mockery, and vicious satire in his arguments made the letters ripe for public consumption, and influenced the prose of later French writers like Voltaire and Jean - Jacques Rousseau. Wide praise has been given to the Provincial Letters.
Pascal's most influential theological work, referred to posthumously as the Pensées ("Thoughts"), was not completed before his death. It was to have been a sustained and coherent examination and defense of the Christian faith, with the original title Apologie de la religion Chrétienne ("Defense of the Christian Religion"). The first version of the numerous scraps of paper found after his death appeared in print as a book in 1669 titled Pensées de M. Pascal sur la religion, et sur quelques autres sujets ("Thoughts of M. Pascal on religion, and on some other subjects") and soon thereafter became a classic. One of the Apologie's main strategies was to use the contradictory philosophies of skepticism and stoicism, personalized by Montaigne on one hand, and Epictetus on the other, in order to bring the unbeliever to such despair and confusion that he would embrace God.
Pascal's Pensées is
widely considered to be a masterpiece, and a landmark in French prose.
When commenting on one particular section (Thought #72), Sainte - Beuve praised it as the finest pages in the French language. Will Durant, in his 11 volume, comprehensive The Story of Civilization series, hailed it as "the most eloquent book in French prose." In Pensées,
Pascal surveys several philosophical paradoxes: infinity and nothing,
faith and reason, soul and matter, death and life, meaning and
vanity — seemingly arriving at no definitive conclusions besides humility,
ignorance, and grace. Rolling these into one he develops Pascal's Wager.
T.S. Eliot described him during this phase of his life as "a man of the world among ascetics, and an ascetic among men of the world." Pascal's ascetic lifestyle derived from a belief that it was natural and necessary for a person to suffer. In 1659, Pascal fell seriously ill. During his last years, he frequently tried to reject the ministrations of his doctors, saying, "Sickness is the natural state of Christians."
Louis XIV suppressed the Jansenist movement at Port - Royal in 1661. In response, Pascal wrote one of his final works, Écrit sur la signature du formulaire ("Writ on the Signing of the Form"), exhorting the Jansenists not to give in. Later that year, his sister Jacqueline died, which convinced Pascal to cease his polemics on Jansenism. Pascal's last major achievement, returning to his mechanical genius, was inaugurating perhaps the first bus line, moving passengers within Paris in a carriage with many seats.
In 1662, Pascal's illness became more violent, and his emotional condition had severely worsened since his sister´s death, which happened the previous year. Aware that his health was fading quickly, he sought a move to the hospital for incurable diseases, but his doctors declared that he was too unstable to be carried. In Paris on 18 August 1662, Pascal went into convulsions and received extreme unction. He died the next morning, his last words being "May God never abandon me," and was buried in the cemetery of Saint - Étienne - du - Mont.
An autopsy performed after his death revealed grave problems with his stomach and other organs of his abdomen, along with damage to his brain. Despite the autopsy, the cause of his poor health was never precisely determined, though speculation focuses on tuberculosis, stomach cancer, or a combination of the two. The headaches which afflicted Pascal are generally attributed to his brain lesion.
In honor of his scientific contributions, the name Pascal has been given to the SI unit of pressure, to a programming language, and Pascal's law (an important principle of hydrostatics), and as mentioned above, Pascal's triangle and Pascal's wager still bear his name.
Pascal's development of probability theory was his most influential contribution to mathematics. Originally applied to gambling, today it is extremely important in economics, especially in actuarial science. John Ross writes, "Probability theory and the discoveries following it changed the way we regard uncertainty, risk, decision making, and an individual's and society's ability to influence the course of future events." However, it should be noted that Pascal and Fermat, though doing important early work in probability theory, did not develop the field very far. Christiaan Huygens, learning of the subject from the correspondence of Pascal and Fermat, wrote the first book on the subject. Later figures who continued the development of the theory include Abraham de Moivre and Pierre - Simon Laplace.
In literature, Pascal is regarded as one of the most important authors of the French Classical Period and is read today as one of the greatest masters of French prose. His use of satire and wit influenced later polemicists. The content of his literary work is best remembered for its strong opposition to the rationalism of René Descartes and simultaneous assertion that the main countervailing philosophy, empiricism, was also insufficient for determining major truths.
In France, prestigious annual awards, Blaise Pascal Chairs are given to outstanding international scientists to conduct their research in the Ile de France region. One of the Universities of Clermont - Ferrand, France – Université Blaise Pascal – is named after him. The University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, holds an annual math contest named in his honor.
Roberto Rossellini directed a filmed biopic (entitled Blaise Pascal) which originally aired on Italian television in 1971. Pascal was a subject of the first edition of the 1984 BBC Two documentary, Sea of Faith, presented by Don Cupitt.