<Back to Index>
- Philosopher and Mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, 1646
- Mathematician Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstraß, 1815
PAGE SPONSOR
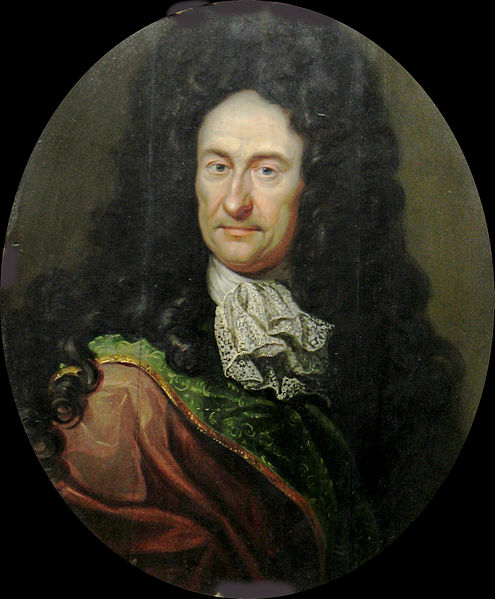
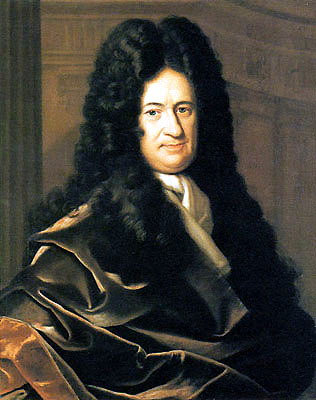


Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (July 1, 1646 – November 14, 1716) was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin (~40%), French (~30%) and German (~15%).
Leibniz occupies a prominent place in the history of mathematics and the history of philosophy. He developed the infinitesimal calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and Leibniz's mathematical notation has been widely used ever since it was published. He became one of the most prolific inventors in the field of mechanical calculators. While working on adding automatic multiplication and division to Pascal's calculator, he was the first to describe a pinwheel calculator in 1685 and invented the Leibniz wheel, used in the arithmometer, the first mass produced mechanical calculator. He also refined the binary number system, which is at the foundation of virtually all digital computers. In philosophy, Leibniz is mostly noted for his optimism, e.g., his conclusion that our Universe is, in a restricted sense, the best possible one that God could have created. Leibniz, along with René Descartes and Baruch Spinoza, was one of the three great 17th century advocates of rationalism. The work of Leibniz anticipated modern logic and analytic philosophy, but his philosophy also looks back to the scholastic tradition, in which conclusions are produced by applying reason to first
principles or prior definitions rather than to empirical evidence.
Leibniz made major contributions to physics and technology, and anticipated notions that surfaced much later in biology, medicine, geology, probability theory, psychology, linguistics, and information science. He wrote works on politics, law, ethics, theology, history, philosophy, and philology. Leibniz's contributions to this vast array of subjects were scattered in various learned journals,
in tens of thousands of letters, and in unpublished manuscripts. As of
2011, there is no complete gathering of the writings of Leibniz.
Gottfried Leibniz was born on July 1, 1646 in Leipzig, Saxony (at the end of the Thirty Years' War), to Friedrich Leibnütz (Leibniz changed his name) and Catherina Schmuck. Friedrich noted in his family journal: "On Sunday 21 June [NS: 1 July] 1646, my son Gottfried Wilhelm is born into the world after six in the evening, ¾ to seven [ein Viertel uff sieben], Aquarius rising." His father, who was of Sorbian ancestry, died when Leibniz was six years old, and from that point on he was raised by his mother. Her teachings influenced Leibniz's philosophical thoughts in his later life.
Leibniz's father had been a Professor of Moral Philosophy at the University of Leipzig and Leibniz inherited his father's personal library. He was given free access to this from the age of seven. While Leibniz's schoolwork focused on a small canon of authorities, his father's library enabled him to study a wide variety of advanced philosophical and theological works – ones that he would not have otherwise been able to read until his college years. Access to his father's library, largely written in Latin, also led to his proficiency in the Latin language. Leibniz was proficient in Latin by the age of 12, and he composed three hundred hexameters of Latin verse in a single morning for a special event at school at the age of 13.
He enrolled in his father's former university at age 15, and he completed his bachelor's degree in philosophy in December of 1662. He defended his Disputatio Metaphysica de Principio Individui, which addressed the Principle of individuation, on June 9, 1663. Leibniz earned his master's degree in philosophy on February 7, 1664. He published and defended a dissertation Specimen Quaestionum Philosophicarum ex Jure collectarum, arguing for both a theoretical and a pedagogical relationship between philosophy and law, in December 1664. After one year of legal studies, he was awarded his bachelor's degree in Law on September 28, 1665.
In 1666, (at age 20), Leibniz published his first book, On the Art of Combinations, the first part of which was also his habilitation thesis in philosophy. His next goal was to earn his license and doctorate in Law, which normally required three years of study then. In 1666, the University of Leipzig turned down Leibniz's doctoral application and refused to grant him a doctorate in law, most likely due to his relative youth (he was 21 years old at the time). Leibniz subsequently left Leipzig.
Leibniz then enrolled in the University of Altdorf, and almost immediately he submitted a thesis, which he had probably been working on earlier in Leipzig. The title of his thesis was Disputatio de Casibus perplexis in Jure. Leibniz earned his license to practice law and his Doctorate in Law in November of 1666. He next declined the offer of an academic appointment at Altdorf, saying that "my thoughts were turned in an entirely different direction.
As
an adult, Leibniz often introduced himself as "Gottfried von Leibniz".
Also many posthumously published editions of his writings presented his name on the title page as "Freiherr G.
W. von Leibniz." However, no document has ever been found from any
contemporary government that stated his appointment to any form of nobility.
Leibniz's first position was as a salaried alchemist in Nuremberg, even though he knew nothing about the subject. He soon met Johann Christian von Boineburg (1622 – 1672), the dismissed chief minister of the Elector of Mainz, Johann Philipp von Schönborn. Von Boineburg hired Leibniz as an assistant, and shortly thereafter reconciled with the Elector and introduced Leibniz to him. Leibniz then dedicated an essay on law to the Elector in the hope of obtaining employment. The stratagem worked; the Elector asked Leibniz to assist with the redrafting of the legal code for his Electorate. In 1669, Leibniz was appointed Assessor in the Court of Appeal. Although von Boineburg died late in 1672, Leibniz remained under the employment of his widow until she dismissed him in 1674.
Von Boineburg did much to promote Leibniz's reputation, and the latter's memoranda and letters began to attract favorable notice. Leibniz's service to the Elector soon followed a diplomatic role. He published an essay, under the pseudonym of a fictitious Polish nobleman, arguing (unsuccessfully) for the German candidate for the Polish crown. The main European geopolitical reality during Leibniz's adult life was the ambition of Louis XIV of France, backed by French military and economic might. Meanwhile, the Thirty Years' War had left German speaking Europe exhausted, fragmented, and economically backward. Leibniz proposed to protect German speaking Europe by distracting Louis as follows. France would be invited to take Egypt as a stepping stone towards an eventual conquest of the Dutch East Indies. In return, France would agree to leave Germany and the Netherlands undisturbed. This plan obtained the Elector's cautious support. In 1672, the French government invited Leibniz to Paris for discussion, but the plan was soon overtaken by the outbreak of the Franco - Dutch War and became irrelevant. Napoleon's failed invasion of Egypt in 1798 can be seen as an unwitting implementation of Leibniz's plan.
Thus, Leibniz began several years in Paris. Soon after arriving, he met Dutch physicist and mathematician Christiaan Huygens and
realized that his own knowledge of mathematics and physics was patchy.
With Huygens as mentor, he began a program of self study that soon
pushed him to making major contributions to both subjects, including
inventing his version of the differential and integral calculus. He met Nicolas Malebranche and Antoine Arnauld, the leading French philosophers of the day, and studied the writings of Descartes and Pascal, unpublished as well as published. He befriended a German mathematician, Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus; they corresponded for the rest of their lives. In 1675 he was admitted as a foreign honorary member of the French Academy of Sciences, which he continued to follow mostly by correspondence.
When it became clear that France would not implement its part of Leibniz's Egyptian plan, the Elector sent his nephew, escorted by Leibniz, on a related mission to the English government in London, early in 1673. There Leibniz came into acquaintance of Henry Oldenburg and John Collins. After demonstrating a calculating machine he had been designing and building since 1670 to the Royal Society, the first such machine that could execute all four basic arithmetical operations, the Society made him an external member. The mission ended abruptly when news reached it of the Elector's death, whereupon Leibniz promptly returned to Paris and not, as had been planned, to Mainz.
The
sudden deaths of Leibniz's two patrons in the same winter meant that
Leibniz had to find a new basis for his career. In this regard, a 1669 invitation from the Duke of Brunswick to visit Hanover proved fateful. Leibniz declined the invitation, but began corresponding with the Duke in 1671. In 1673, the Duke offered
him the post of Counselor which Leibniz very reluctantly accepted two
years later, only after it became clear that no employment in Paris,
whose intellectual stimulation he relished, or with the Habsburg imperial court was forthcoming.
Leibniz managed to delay his arrival in Hanover until the end of 1676 after making one more short journey to London, where he was later accused by Newton of being shown some of Newton's unpublished work on the calculus. This fact was deemed evidence supporting the accusation, made decades later, that he had stolen the calculus from Newton. On the journey from London to Hanover, Leibniz stopped in The Hague where he met Leeuwenhoek, the discoverer of microorganisms. He also spent several days in intense discussion with Spinoza, who had just completed his masterwork, the Ethics. Leibniz respected Spinoza's powerful intellect, but was dismayed by his conclusions that contradicted both Christian and Jewish orthodoxy.
In 1677, he was promoted, at his request, to Privy Counselor of Justice, a post he held for the rest of his life. Leibniz served three consecutive rulers of the House of Brunswick as historian, political adviser, and most consequentially, as librarian of the ducal library. He thenceforth employed his pen on all the various political, historical, and theological matters involving the House of Brunswick; the resulting documents form a valuable part of the historical record for the period.
Among the few people in north Germany to accept Leibniz were the Electress Sophia of Hanover (1630 – 1714), her daughter Sophia Charlotte of Hanover (1668 – 1705), the Queen of Prussia and his avowed disciple, and Caroline of Ansbach, the consort of her grandson, the future George II. To each of these women he was correspondent, adviser, and friend. In turn, they all approved of Leibniz more than did their spouses and the future king George I of Great Britain.
The population of Hanover was only about 10,000, and its provinciality eventually grated on Leibniz. Nevertheless, to be a major courtier to the House of Brunswick was quite an honor, especially in light of the meteoric rise in the prestige of that House during Leibniz's association with it. In 1692, the Duke of Brunswick became a hereditary Elector of the Holy Roman Empire. The British Act of Settlement 1701 designated the Electress Sophia and her descent as the royal family of England, once both King William III and his sister - in - law and successor, Queen Anne, were dead. Leibniz played a role in the initiatives and negotiations leading up to that Act, but not always an effective one. For example, something he published anonymously in England, thinking to promote the Brunswick cause, was formally censured by the British Parliament.
The Brunswicks tolerated the enormous effort Leibniz devoted to intellectual pursuits unrelated to his duties as a courtier, pursuits such as perfecting the calculus, writing about other mathematics, logic, physics, and philosophy, and keeping up a vast correspondence. He began working on the calculus in 1674; the earliest evidence of its use in his surviving notebooks is 1675. By 1677 he had a coherent system in hand, but did not publish it until 1684. Leibniz's most important mathematical papers were published between 1682 and 1692, usually in a journal which he and Otto Mencke founded in 1682, the Acta Eruditorum. That journal played a key role in advancing his mathematical and scientific reputation, which in turn enhanced his eminence in diplomacy, history, theology, and philosophy.
The Elector Ernest Augustus commissioned Leibniz to write a history of the House of Brunswick, going back to the time of Charlemagne or earlier, hoping that the resulting book would advance his dynastic ambitions. From 1687 to 1690, Leibniz traveled extensively in Germany, Austria, and Italy, seeking and finding archival materials bearing on this project. Decades went by but no history appeared; the next Elector became quite annoyed at Leibniz's apparent dilatoriness. Leibniz never finished the project, in part because of his huge output on many other fronts, but also because he insisted on writing a meticulously researched and erudite book based on archival sources, when his patrons would have been quite happy with a short popular book, one perhaps little more than a genealogy with commentary, to be completed in three years or less. They never knew that he had in fact carried out a fair part of his assigned task: when the material Leibniz had written and collected for his history of the House of Brunswick was finally published in the 19th century, it filled three volumes.
In 1708, John Keill, writing in the journal of the Royal Society and with Newton's presumed blessing, accused Leibniz of having plagiarized Newton's calculus. Thus began the calculus priority dispute which darkened the remainder of Leibniz's life. A formal investigation by the Royal Society (in which Newton was an unacknowledged participant), undertaken in response to Leibniz's demand for a retraction, upheld Keill's charge. Historians of mathematics writing since 1900 or so have tended to acquit Leibniz, pointing to important differences between Leibniz's and Newton's versions of the calculus.
In 1711, while traveling in northern Europe, the Russian Tsar Peter the Great stopped in Hanover and met Leibniz, who then took some interest in Russian matters for the rest of his life. In 1712, Leibniz began a two year residence in Vienna, where he was appointed Imperial Court Councillor to the Habsburgs. On the death of Queen Anne in 1714, Elector George Louis became King George I of Great Britain, under the terms of the 1701 Act of Settlement. Even though Leibniz had done much to bring about this happy event, it was not to be his hour of glory. Despite the intercession of the Princess of Wales, Caroline of Ansbach, George I forbade Leibniz to join him in London until he completed at least one volume of the history of the Brunswick family his father had commissioned nearly 30 years earlier. Moreover, for George I to include Leibniz in his London court would have been deemed insulting to Newton, who was seen as having won the calculus priority dispute and whose standing in British official circles could not have been higher. Finally, his dear friend and defender, the Dowager Electress Sophia, died in 1714.
Leibniz died in Hanover in 1716: at the time, he was so out of favor that neither George I (who happened to be near Hanover at the time) nor any fellow courtier other than his personal secretary attended the funeral. Even though Leibniz was a life member of the Royal Society and the Berlin Academy of Sciences, neither organization saw fit to honor his passing. His grave went unmarked for more than 50 years. Leibniz was eulogized by Fontenelle, before the Academie des Sciences in Paris, which had admitted him as a foreign member in 1700. The eulogy was composed at the behest of the Duchess of Orleans, a niece of the Electress Sophia.
Leibniz
never married. He complained on occasion about money, but the fair sum
he left to his sole heir, his sister's stepson, proved that the
Brunswicks had, by and large, paid him well. In his diplomatic
endeavors, he at times verged on the unscrupulous, as was all too often
the case with professional diplomats of his day. On several occasions,
Leibniz backdated and altered personal manuscripts, actions which put
him in a bad light during the calculus controversy. On the other hand,
he was charming, well mannered, and not without humor and imagination. He had many friends and admirers all over Europe.
Leibniz's philosophical thinking appears fragmented, because his philosophical writings consist mainly of a multitude of short pieces: journal articles, manuscripts published long after his death, and many letters to many correspondents. He wrote only two philosophical treatises, of which only the Théodicée of 1710 was published in his lifetime.
Leibniz dated his beginning as a philosopher to his Discourse on Metaphysics, which he composed in 1686 as a commentary on a running dispute between Nicolas Malebranche and Antoine Arnauld. This led to an extensive and valuable correspondence with Arnauld; it and the Discourse were not published until the 19th century. In 1695, Leibniz made his public entrée into European philosophy with a journal article titled "New System of the Nature and Communication of Substances". Between 1695 and 1705, he composed his New Essays on Human Understanding, a lengthy commentary on John Locke's 1690 An Essay Concerning Human Understanding, but upon learning of Locke's 1704 death, lost the desire to publish it, so that the New Essays were not published until 1765. The Monadologie, composed in 1714 and published posthumously, consists of 90 aphorisms.
Leibniz met Spinoza in 1676, read some of his unpublished writings, and has since been suspected of appropriating some of Spinoza's ideas. While Leibniz admired Spinoza's powerful intellect, he was also forthrightly dismayed by Spinoza's conclusions, especially when these were inconsistent with Christian orthodoxy.
Unlike Descartes and Spinoza, Leibniz had a thorough university education in philosophy. His lifelong scholastic and Aristotelian turn of mind betrayed the strong influence of one of his Leipzig professors, Jakob Thomasius, who also supervised his BA thesis in philosophy. Leibniz also eagerly read Francisco Suárez, a Spanish Jesuit respected even in Lutheran universities. Leibniz was deeply interested in the new methods and conclusions of Descartes, Huygens, Newton, and Boyle,
but viewed their work through a lens heavily tinted by scholastic
notions. Yet it remains the case that Leibniz's methods and concerns
often anticipate the logic, and analytic and linguistic philosophy of the 20th century.
Leibniz variously invoked one or another of seven fundamental philosophical Principles:
- Identity/contradiction. If a proposition is true, then its negation is false and vice versa.
- Identity of indiscernibles. Two things are identical if and only if they share the same and only the same properties. Frequently invoked in modern logic and philosophy. The "identity of indiscernibles" is often referred to as Leibniz's Law. It has attracted the most controversy and criticism, especially from corpuscular philosophy and quantum mechanics.
- Sufficient reason. "There must be a sufficient reason [often known only to God] for anything to exist, for any event to occur, for any truth to obtain."
- Pre-established harmony. "[T]he appropriate nature of each substance brings it about that what happens to one corresponds to what happens to all the others, without, however, their acting upon one another directly." (Discourse on Metaphysics, XIV) A dropped glass shatters because it "knows" it has hit the ground, and not because the impact with the ground "compels" the glass to split.
- Law of Continuity. Natura non saltum facit. A mathematical analog to this principle would proceed as follows: if a function describes a transformation of something to which continuity applies, then its domain and range are both dense sets.
- Optimism. "God assuredly always chooses the best."
- Plenitude. "Leibniz believed that the best of all possible worlds would actualize every genuine possibility, and argued in Théodicée that this best of all possible worlds will contain all possibilities, with our finite experience of eternity giving no reason to dispute nature's perfection."
Leibniz would on occasion give a speech for a specific principle, but more often took them for granted.
Leibniz's best known contribution to metaphysics is his theory of monads, as exposited in Monadologie. According to Leibniz, monads are elementary particles with blurred perception of each other, this theory can be viewed as early version of Many - Minds Quantum Mechanics. Monads can also be compared to the corpuscles of the Mechanical Philosophy of René Descartes and others. Monads are the ultimate elements of the universe. The monads are "substantial forms of being" with the following properties: they are eternal, indecomposable, individual, subject to their own laws, un-interacting, and each reflecting the entire universe in a pre-established harmony (a historically important example of panpsychism). Monads are centers of force; substance is force, while space, matter, and motion are merely phenomenal.
The ontological essence of a monad is its irreducible simplicity. Unlike atoms, monads possess no material or spatial character. They also differ from atoms by their complete mutual independence, so that interactions among monads are only apparent. Instead, by virtue of the principle of pre-established harmony, each monad follows a preprogrammed set of "instructions" peculiar to itself, so that a monad "knows" what to do at each moment. (These "instructions" may be seen as analogs of the scientific laws governing subatomic particles.) By virtue of these intrinsic instructions, each monad is like a little mirror of the universe. Monads need not be "small"; e.g., each human being constitutes a monad, in which case free will is problematic. God, too, is a monad, and the existence of God can be inferred from the harmony prevailing among all other monads; God wills the pre-established harmony.
Monads are purported to having gotten rid of the problematic:
- Interaction between mind and matter arising in the system of Descartes;
- Lack of individuation inherent to the system of Spinoza, which represents individual creatures as merely accidental.
(Note that the word "optimism" here is used in the classic sense of optimal, not in the mood - related sense, as being positively hopeful.)
The Theodicy tries to justify the apparent imperfections of the world by claiming that it is optimal among all possible worlds. It must be the best possible and most balanced world, because it was created by an all powerful and all knowing God, who would not choose to create an imperfect world if a better world could be known to him or possible to exist. In effect, apparent flaws that can be identified in this world must exist in every possible world, because otherwise God would have chosen to create the world that excluded those flaws.
Leibniz asserted that the truths of theology (religion) and philosophy cannot contradict each other, since reason and faith are both "gifts of God" so that their conflict would imply God contending against himself. The Theodicy is Leibniz's attempt to reconcile his personal philosophical system with his interpretation of the tenets of Christianity. This project was motivated in part by Leibniz's belief, shared by many conservative philosophers and theologians during the Enlightenment, in the rational and enlightened nature of the Christian religion, at least as this was defined in tendentious comparisons between Christian and non Western or "primitive" religious practices and beliefs. It was also shaped by Leibniz's belief in the perfectibility of human nature (if humanity relied on correct philosophy and religion as a guide), and by his belief that metaphysical necessity must have a rational or logical foundation, even if this metaphysical causality seemed inexplicable in terms of physical necessity (the natural laws identified by science).
Because reason and faith must be entirely reconciled, any tenet of faith which could not be defended by reason must be rejected. Leibniz then approached one of the central criticisms of Christian theism: if God is all good, all wise and all powerful, how did evil come into the world? The answer (according to Leibniz) is that, while God is indeed unlimited in wisdom and power, his human creations, as creations, are limited both in their wisdom and in their will (power to act). This predisposes humans to false beliefs, wrong decisions and ineffective actions in the exercise of their free will. God does not arbitrarily inflict pain and suffering on humans; rather he permits both moral evil (sin) and physical evil (pain and suffering) as the necessary consequences of metaphysical evil (imperfection), as a means by which humans can identify and correct their erroneous decisions, and as a contrast to true good.
Further, although human actions flow from prior causes that ultimately arise in God, and therefore are known as a metaphysical certainty to God, an individual's free will is exercised within natural laws, where choices are merely contingently necessary, to be decided in the event by a "wonderful spontaneity" that provides individuals an escape from rigorous predestination.
This theory drew controversy and refutations, that are collected in the article Best of all possible worlds.
Leibniz believed that much of human reasoning could be reduced to calculations of a sort, and that such calculations could resolve many differences of opinion:
The only way to rectify our reasonings is to make them as tangible as those of the Mathematicians, so that we can find our error at a glance, and when there are disputes among persons, we can simply say: Let us calculate [calculemus], without further ado, to see who is right.
Leibniz's calculus ratiocinator, which resembles symbolic logic, can be viewed as a way of making such calculations feasible. Leibniz wrote memoranda that can now be read as groping attempts to get symbolic logic — and thus his calculus — off the ground. But Gerhard and Couturat did not publish these writings until modern formal logic had emerged in Frege's Begriffsschrift and in writings by Charles Sanders Peirce and his students in the 1880s, and hence well after Boole and De Morgan began that logic in 1847.
Leibniz thought symbols were important for human understanding. He attached so much importance to the invention of good notations that he attributed all his discoveries in mathematics to this. His notation for the infinitesimal calculus is an example of his skill in this regard. C.S. Peirce, a 19th-century pioneer of semiotics, shared Leibniz's passion for symbols and notation, and his belief that these are essential to a well running logic and mathematics.
But Leibniz took his speculations much further. Defining a character as any written sign, he then defined a "real" character as one that represents an idea directly and not simply as the word embodying the idea. Some real characters, such as the notation of logic, serve only to facilitate reasoning. Many characters well known in his day, including Egyptian hieroglyphics, Chinese characters, and the symbols of astronomy and chemistry, he deemed not real. Instead, he proposed the creation of a characteristica universalis or "universal characteristic", built on an alphabet of human thought in which each fundamental concept would be represented by a unique "real" character:
It is obvious that if we could find characters or signs suited for expressing all our thoughts as clearly and as exactly as arithmetic expresses numbers or geometry expresses lines, we could do in all matters insofar as they are subject to reasoning all that we can do in arithmetic and geometry. For all investigations which depend on reasoning would be carried out by transposing these characters and by a species of calculus.
Complex thoughts would be represented by combining characters for simpler thoughts. Leibniz saw that the uniqueness of prime factorization suggests a central role for prime numbers in the universal characteristic, a striking anticipation of Gödel numbering. Granted, there is no intuitive or mnemonic way to number any set of elementary concepts using the prime numbers. Leibniz's idea of reasoning through a universal language of symbols and calculations however remarkably foreshadows great 20th century developments in formal systems, such as Turing completeness, where computation was used to define equivalent universal languages (Turing degree).
Because Leibniz was a mathematical novice when he first wrote about the characteristic, at first he did not conceive it as an algebra but rather as a universal language or script. Only in 1676 did he conceive of a kind of "algebra of thought", modeled on and including conventional algebra and its notation. The resulting characteristic included a logical calculus, some combinatorics, algebra, his analysis situs (geometry of situation), a universal concept language, and more.
What Leibniz actually intended by his characteristica universalis and calculus ratiocinator, and the extent to which modern formal logic does justice to the calculus, may never be established.
Leibniz is the most important logician between Aristotle and 1847, when George Boole and Augustus De Morgan each published books that began modern formal logic. Leibniz enunciated the principal properties of what we now call conjunction, disjunction, negation, identity, set inclusion, and the empty set. The principles of Leibniz's logic and, arguably, of his whole philosophy, reduce to two:
- All our ideas are compounded from a very small number of simple ideas, which form the alphabet of human thought.
- Complex ideas proceed from these simple ideas by a uniform and symmetrical combination, analogous to arithmetical multiplication.
The formal logic that emerged early in the 20th century also requires, at minimum, unary negation and quantified variables ranging over some universe of discourse.
Leibniz
published nothing on formal logic in his lifetime; most of what he
wrote on the subject consists of working drafts. In his book History of Western Philosophy, Bertrand Russell went
so far as to claim that Leibniz had developed logic in his unpublished
writings to a level which was reached only 200 years later.
Although the mathematical notion of function was implicit in trigonometric and logarithmic tables, which existed in his day, Leibniz was the first, in 1692 and 1694, to employ it explicitly, to denote any of several geometric concepts derived from a curve, such as abscissa, ordinate, tangent, chord, and the perpendicular. In the 18th century, "function" lost these geometrical associations.
Leibniz was the first to see that the coefficients of a system of linear equations could be arranged into an array, now called a matrix, which can be manipulated to find the solution of the system, if any. This method was later called Gaussian elimination.
Leibniz is credited, along with Sir Isaac Newton, with the inventing of infinitesimal calculus (that comprises differential and integral calculus). According to Leibniz's notebooks, a critical breakthrough occurred on November 11, 1675, when he employed integral calculus for the first time to find the area under the graph of a function y = ƒ(x). He introduced several notations used to this day, for instance the integral sign ∫ representing an elongated S, from the Latin word summa and the d used for differentials, from the Latin word differentia. This cleverly suggestive notation for the calculus is probably his most enduring mathematical legacy. Leibniz did not publish anything about his calculus until 1684. The product rule of differential calculus is still called "Leibniz's law". In addition, the theorem that tells how and when to differentiate under the integral sign is called the Leibniz integral rule.
Leibniz's approach to the calculus fell well short of later standards of rigor (the same can be said of Newton's). We now see a Leibniz proof as being in truth mostly a heuristic argument mainly grounded in geometric intuition. Leibniz also freely invoked mathematical entities he called infinitesimals, manipulating them in ways suggesting that they had paradoxical algebraic properties. George Berkeley, in a tract called The Analyst and elsewhere, ridiculed this and other aspects of the early calculus, pointing out that natural science grounded in the calculus required just as big of a leap of faith as theology grounded in Christian revelation.
Leibniz was the first to use the term analysis situs, later used in the 19th century to refer to what is now known as topology. There are two takes on this situation. On the one hand, Mates, citing a 1954 paper in German by Jacob Freudenthal, argues:
Although for Leibniz the situs of a sequence of points is completely determined by the distance between them and is altered if those distances are altered, his admirer Euler, in the famous 1736 paper solving the Königsberg Bridge Problem and its generalizations, used the term geometria situs in such a sense that the situs remains unchanged under topological deformations. He mistakenly credits Leibniz with originating this concept. ...it is sometimes not realized that Leibniz used the term in an entirely different sense and hence can hardly be considered the founder of that part of mathematics.
But Hideaki Hirano argues differently, quoting Mandelbrot:
To sample Leibniz' scientific works is a sobering experience. Next to calculus, and to other thoughts that have been carried out to completion, the number and variety of premonitory thrusts is overwhelming. We saw examples in 'packing,'... My Leibniz mania is further reinforced by finding that for one moment its hero attached importance to geometric scaling. In "Euclidis Prota" ..., which is an attempt to tighten Euclid's axioms, he states,...: 'I have diverse definitions for the straight line. The straight line is a curve, any part of which is similar to the whole, and it alone has this property, not only among curves but among sets.' This claim can be proved today.
Thus the fractal geometry promoted by Mandelbrot drew on Leibniz's notions of self - similarity and the principle of continuity: natura non facit saltus. We also see that when Leibniz wrote, in a metaphysical vein, that "the straight line is a curve, any part of which is similar to the whole", he was anticipating topology by more than two centuries. As for "packing", Leibniz told to his friend and correspondent Des Bosses to imagine a circle, then to inscribe within it three congruent circles with maximum radius; the latter smaller circles could be filled with three even smaller circles by the same procedure. This process can be continued infinitely, from which arises a good idea of self - similarity. Leibniz's improvement of Euclid's axiom contains the same concept.
Leibniz's
writings are currently discussed, not only for their anticipations and
possible discoveries not yet recognized, but as ways of advancing
present knowledge. Much of his writing on physics is included in
Gerhardt's Mathematical Writings.
Leibniz contributed a fair amount to the statics and dynamics emerging about him, often disagreeing with Descartes and Newton. He devised a new theory of motion (dynamics) based on kinetic energy and potential energy, which posited space as relative, whereas Newton felt strongly space was absolute. An important example of Leibniz's mature physical thinking is his Specimen Dynamicum of 1695.
Until the discovery of subatomic particles and the quantum mechanics governing them, many of Leibniz's speculative ideas about aspects of nature not reducible to statics and dynamics made little sense. For instance, he anticipated Albert Einstein by arguing, against Newton, that space, time and motion are relative, not absolute. Leibniz's rule is an important, if often overlooked, step in many proofs in diverse fields of physics. The principle of sufficient reason has been invoked in recent cosmology, and his identity of indiscernibles in quantum mechanics, a field some even credit him with having anticipated in some sense. Those who advocate digital philosophy, a recent direction in cosmology, claim Leibniz as a precursor.
Leibniz's vis viva (Latin for living force) is mv2, twice the modern kinetic energy. He realized that the total energy would be conserved in certain mechanical systems, so he considered it an innate motive characteristic of matter. Here too his thinking gave rise to another regrettable nationalistic dispute. His vis viva was seen as rivaling the conservation of momentum championed by Newton in England and by Descartes in France; hence academics in those countries tended to neglect Leibniz's idea. In reality, both energy and momentum are conserved, so the two approaches are equally valid.
By proposing that the earth has a molten core, he anticipated modern geology. In embryology, he was a preformationist, but also proposed that organisms are the outcome of a combination of an infinite number of possible microstructures and of their powers. In the life sciences and paleontology, he revealed an amazing transformist intuition, fueled by his study of comparative anatomy and fossils. One of his principal works on this subject, Protogaea, unpublished in his lifetime, has recently been published in English for the first time. He worked out a primal organismic theory. In medicine, he exhorted the physicians of his time — with some results — to ground their theories in detailed comparative observations and verified experiments, and to distinguish firmly scientific and metaphysical points of view.
In psychology, he anticipated the distinction between conscious and unconscious states. In public health, he advocated establishing a medical administrative authority, with powers over epidemiology and veterinary medicine. He worked to set up a coherent medical training program, oriented towards public health and preventive measures. In economic policy, he proposed tax reforms and a national insurance scheme, and discussed the balance of trade. He even proposed something akin to what much later emerged as game theory. In sociology he laid the ground for communication theory.
In
1906, Garland published a volume of Leibniz's writings bearing on his
many practical inventions and engineering work. To date, few of these
writings have been translated into English. Nevertheless, it is well
understood that Leibniz was a serious inventor, engineer, and applied
scientist, with great respect for practical life. Following the motto theoria cum praxis, he urged that theory be combined with practical application, and thus has been claimed as the father of applied science.
He designed wind driven propellers and water pumps, mining machines to
extract ore, hydraulic presses, lamps, submarines, clocks, etc. With Denis Papin, he invented a steam engine.
He even proposed a method for desalinating water. From 1680 to 1685, he
struggled to overcome the chronic flooding that afflicted the ducal silver mines in the Harz Mountains, but did not succeed.
Leibniz may have been the first computer scientist and information theorist. Early in life, he documented the binary numeral system (base 2), then revisited that system throughout his career. He anticipated Lagrangian interpolation and algorithmic information theory. His calculus ratiocinator anticipated aspects of the universal Turing machine. In 1934, Norbert Wiener claimed to have found in Leibniz's writings a mention of the concept of feedback, central to Wiener's later cybernetic theory.
In 1671, Leibniz began to invent a machine that could execute all four arithmetical operations, gradually improving it over a number of years. This "Stepped Reckoner" attracted fair attention and was the basis of his election to the Royal Society in 1673. A number of such machines were made during his years in Hanover, by a craftsman working under Leibniz's supervision. It was not an unambiguous success because it did not fully mechanize the operation of carrying. Couturat reported finding an unpublished note by Leibniz, dated 1674, describing a machine capable of performing some algebraic operations.
Leibniz was groping towards hardware and software concepts worked out much later by Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace.
In 1679, while mulling over his binary arithmetic, Leibniz imagined a
machine in which binary numbers were represented by marbles, governed by
a rudimentary sort of punched cards. Modern
electronic digital computers replace Leibniz's marbles moving by
gravity with shift registers, voltage gradients, and pulses of
electrons, but otherwise they run roughly as Leibniz envisioned in 1679.
While serving as librarian of the ducal libraries in Hanover and Wolfenbuettel, Leibniz effectively became one of the founders of library science. The latter library was enormous for its day, as it contained more than 100,000 volumes, and Leibniz helped design a new building for it, believed to be the first building explicitly designed to be a library. He also designed a book indexing system in ignorance of the only other such system then extant, that of the Bodleian Library at Oxford University. He also called on publishers to distribute abstracts of all new titles they produced each year, in a standard form that would facilitate indexing. He hoped that this abstracting project would eventually include everything printed from his day back to Gutenberg. Neither proposal met with success at the time, but something like them became standard practice among English language publishers during the 20th century, under the aegis of the Library of Congress and the British Library.
He called for the creation of an empirical database as a way to further all sciences. His characteristica universalis, calculus ratiocinator, and a "community of minds" — intended, among other things, to bring political and religious unity to Europe — can be seen as distant unwitting anticipations of artificial languages (e.g., Esperanto and its rivals), symbolic logic, even the World Wide Web.
Leibniz emphasized that research was
a collaborative endeavor. Hence he warmly advocated the formation of
national scientific societies along the lines of the British Royal
Society and the French Academie Royale des Sciences. More specifically,
in his correspondence and travels he urged the creation of such
societies in Dresden, Saint Petersburg, Vienna, and Berlin. Only one
such project came to fruition; in 1700, the Berlin Academy of Sciences was
created. Leibniz drew up its first statutes, and served as its first
President for the remainder of his life. That Academy evolved into the
German Academy of Sciences, the publisher of the ongoing critical
edition of his works.
With the possible exception of Marcus Aurelius, no philosopher has ever had as much experience with practical affairs of state as Leibniz. Leibniz's writings on law, ethics, and politics were long overlooked by English speaking scholars, but this has changed of late.
While Leibniz was no apologist for absolute monarchy like Hobbes, or for tyranny in any form, neither did he echo the political and constitutional views of his contemporary John Locke, views invoked in support of democracy, in 18th century America and later elsewhere. The following excerpt from a 1695 letter to Baron J.C. Boineburg's son Philipp is very revealing of Leibniz's political sentiments:
As for.. the great question of the power of sovereigns and the obedience their peoples owe them, I usually say that it would be good for princes to be persuaded that their people have the right to resist them, and for the people, on the other hand, to be persuaded to obey them passively. I am, however, quite of the opinion of Grotius, that one ought to obey as a rule, the evil of revolution being greater beyond comparison than the evils causing it. Yet I recognize that a prince can go to such excess, and place the well - being of the state in such danger, that the obligation to endure ceases. This is most rare, however, and the theologian who authorizes violence under this pretext should take care against excess; excess being infinitely more dangerous than deficiency.
In 1677, Leibniz called for a European confederation, governed by a council or senate, whose members would represent entire nations and would be free to vote their consciences; in doing so, he anticipated the European Union. He believed that Europe would adopt a uniform religion. He reiterated these proposals in 1715.
Leibniz devoted considerable intellectual and diplomatic effort to what would now be called ecumenical endeavor, seeking to reconcile first the Roman Catholic and Lutheran churches, later the Lutheran and Reformed churches. In this respect, he followed the example of his early patrons, Baron von Boineburg and the Duke John Frederick — both
cradle Lutherans who converted to Catholicism as adults — who did what
they could to encourage the reunion of the two faiths, and who warmly
welcomed such endeavors by others. (The House of Brunswick remained Lutheran because the Duke's children did not follow their father.)
These efforts included corresponding with the French bishop Jacques - Bénigne Bossuet,
and involved Leibniz in a fair bit of theological controversy. He
evidently thought that the thoroughgoing application of reason would
suffice to heal the breach caused by the Reformation.
Leibniz the philologist was an avid student of languages, eagerly latching on to any information about vocabulary and grammar that came his way. He refuted the belief, widely held by Christian scholars in his day, that Hebrew was the primeval language of the human race. He also refuted the argument, advanced by Swedish scholars in his day, that a form of proto - Swedish was the ancestor of the Germanic languages. He puzzled over the origins of the Slavic languages, was aware of the existence of Sanskrit, and was fascinated by classical Chinese.
He published the princeps editio (first modern edition) of the late medieval Chronicon Holtzatiae, a Latin chronicle of the County of Holstein.
Leibniz was perhaps the first major European intellect to take a close interest in Chinese civilization, which he knew by corresponding with, and reading other works by, European Christian missionaries posted in China. Having read Confucius Sinicus Philosophus on the first year of its publication, he concluded that Europeans could learn much from the Confucian ethical tradition. He mulled over the possibility that the Chinese characters were an unwitting form of his universal characteristic. He noted with fascination how the I Ching hexagrams correspond to the binary numbers from 0 to 111111, and concluded that this mapping was evidence of major Chinese accomplishments in the sort of philosophical mathematics he admired.
Leibniz's attraction to Chinese philosophy originates from his perception that Chinese philosophy was similar to his own. The
historian E.R. Hughes suggests that Leibniz's ideas of "simple
substance" and "pre-established harmony" were directly influenced by Confucianism, pointing to the fact that they were conceived during the period that he was reading Confucius Sinicus Philosophus.
While making his grand tour of European archives to research the Brunswick family history that he never completed, Leibniz stopped in Vienna between May 1688 and February 1689, where he did much legal and diplomatic work for the Brunswicks. He visited mines, talked with mine engineers, and tried to negotiate export contracts for lead from the ducal mines in the Harz mountains. His proposal that the streets of Vienna be lit with lamps burning rapeseed oil was implemented. During a formal audience with the Austrian Emperor and in subsequent memoranda, he advocated reorganizing the Austrian economy, reforming the coinage of much of central Europe, negotiating a Concordat between the Habsburgs and the Vatican, and creating an imperial research library, official archive, and public insurance fund. He wrote and published an important paper on mechanics.
Leibniz also wrote a short paper, first published by Louis Couturat in 1903, summarizing his views on metaphysics.
The paper is undated; that he wrote it while in Vienna was determined
only in 1999, when the ongoing critical edition finally published
Leibniz's philosophical writings for the period 1677 – 90. Couturat's
reading of this paper was the launching point for much 20th century
thinking about Leibniz, especially among analytic philosophers.
When Leibniz died, his reputation was in decline. He was remembered for only one book, the Théodicée, whose supposed central argument Voltaire lampooned in his Candide. Voltaire's depiction of Leibniz's ideas was so influential that many believed it to be an accurate description. Thus Voltaire and his Candide bear some of the blame for the lingering failure to appreciate and understand Leibniz's ideas. Leibniz had an ardent disciple, Christian Wolff, whose dogmatic and facile outlook did Leibniz's reputation much harm. He also influenced David Hume who read his Théodicée and used some of his ideas. In any event, philosophical fashion was moving away from the rationalism and system building of the 17th century, of which Leibniz had been such an ardent proponent. His work on law, diplomacy, and history was seen as of ephemeral interest. The vastness and richness of his correspondence went unrecognized.
Much of Europe came to doubt that Leibniz had discovered the calculus independently of Newton, and hence his whole work in mathematics and physics was neglected. Voltaire, an admirer of Newton, also wrote Candide at least in part to discredit Leibniz's claim to having discovered the calculus and Leibniz's charge that Newton's theory of universal gravitation was incorrect. The rise of relativity and subsequent work in the history of mathematics has put Leibniz's stance in a more favorable light.
Leibniz's long march to his present glory began with the 1765 publication of the Nouveaux Essais, which Kant read closely. In 1768, Dutens edited the first multi - volume edition of Leibniz's writings, followed in the 19th century by a number of editions, including those edited by Erdmann, Foucher de Careil, Gerhardt, Gerland, Klopp, and Mollat. Publication of Leibniz's correspondence with notables such as Antoine Arnauld, Samuel Clarke, Sophia of Hanover, and her daughter Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, began.
In 1900, Bertrand Russell published a critical study of Leibniz's metaphysics. Shortly thereafter, Louis Couturat published an important study of Leibniz, and edited a volume of Leibniz's heretofore unpublished writings, mainly on logic. They made Leibniz somewhat respectable among 20th century analytical and linguistic philosophers in the English speaking world (Leibniz had already been of great influence to many Germans such as Bernhard Riemann). For example, Leibniz's phrase salva veritate, meaning interchangeability without loss of or compromising the truth, recurs in Willard Quine's writings. Nevertheless, the secondary English language literature on Leibniz did not really blossom until after World War II. This is especially true of English speaking countries; in Gregory Brown's bibliography fewer than 30 of the English language entries were published before 1946. American Leibniz studies owe much to Leroy Loemker (1904 – 85) through his translations and his interpretive essays in LeClerc (1973).
Nicholas Jolley has surmised that Leibniz's reputation as a philosopher is now perhaps higher than at any time since he was alive. Analytic and contemporary philosophy continue to invoke his notions of identity, individuation, and possible worlds, while the doctrinaire contempt for metaphysics, characteristic of analytic and linguistic philosophy, has faded. Work in the history of 17th and 18th century ideas has revealed more clearly the 17th century "Intellectual Revolution" that preceded the better known Industrial and commercial revolutions of the 18th and 19th centuries. The 17th and 18th century belief that natural science, especially physics, differs from philosophy mainly in degree and not in kind, is no longer dismissed out of hand. That modern science includes a "scholastic" as well as a "radical empiricist" element is more accepted now than in the early 20th century. Leibniz's thought is now seen as a major prolongation of the mighty endeavor begun by Plato and Aristotle: the universe and man's place in it are amenable to human reason.
In 1985, the German government created the Leibniz Prize, offering an annual award of 1.55 million euros for experimental results and 770,000 euros for theoretical ones. It is the world's largest prize for scientific achievement.
The collection of manuscript papers of Leibniz at the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Bibliothek – Niedersächische Landesbibliothek were inscribed on UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register in 2007.
Leibniz-Keks,
a popular brand of biscuits in Germany, are named after Gottfried
Leibniz. These biscuits honor Leibniz because he was a resident of
Hanover, where the company is based.
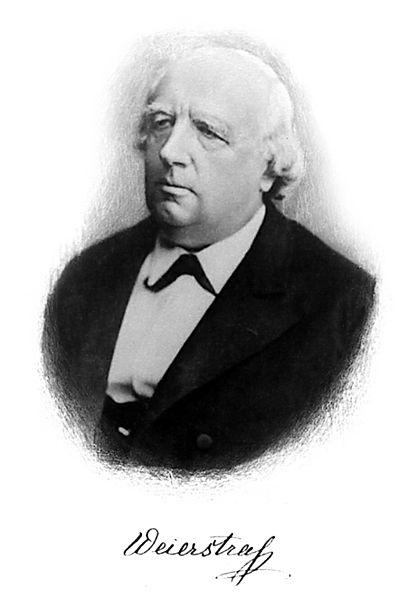



Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass (German: Weierstraß; October 31, 1815 – February 19, 1897) was a German mathematician who is often cited as the "father of modern analysis".
Weierstrass was born in Ostenfelde, part of Ennigerloh, Province of Westphalia.
Weierstrass was the eldest son of Wilhelm Weierstrass, a government official, and Theodora Vonderforst. The family soon moved to Westernkotten in Westphalia, where Weierstrass' three siblings, Peter, Klara, and Elise, were born; none of whom married. Shortly after Elise's birth in 1826, Weierstrass' mother died, and a year later his father remarried. His interest in mathematics began while he was a Gymnasium student at Theodorianum in Paderborn. He was sent to the University of Bonn upon graduation to prepare for a government position. Because his studies were to be in the fields of law, economics, and finance, he was immediately in conflict with his hopes to study mathematics. He resolved the conflict by paying little heed to his planned course of study, but continued private study in mathematics. The outcome was to leave the university without a degree. After that he studied mathematics at the University of Münster (which was even at this time very famous for mathematics) and his father was able to obtain a place for him in a teacher training school in Münster. Later he was certified as a teacher in that city. During this period of study, Weierstrass attended the lectures of Christoph Gudermann and became interested in elliptic functions. In 1843 he taught in Deutsch - Krone in Westprussia and since 1848 he taught at the Lyceum Hosianum in Braunsberg. Besides mathematics he also taught physics, botanics and gymnastics.
After
1850 Weierstrass suffered from a long period of illness, but was able
to publish papers that brought him fame and distinction. He took a chair at the Technical University of Berlin, then known as the Gewerbeinstitut. He was immobile for the last three years of his life, and died in Berlin from pneumonia.
Weierstrass was interested in the soundness of calculus. At the time, there were somewhat ambiguous definitions regarding the foundations of calculus, and hence important theorems could not be proven with sufficient rigor. While Bolzano had developed a reasonably rigorous definition of a limit as early as 1817 (and possibly even earlier) his work remained unknown to most of the mathematical community until years later, and many had only vague definitions of limits and continuity of functions.
Cauchy gave a form of the (ε, δ)-definition of limit, in the context of formally defining the derivative, in the 1820s, but did not correctly distinguish between continuity at a point versus uniform continuity on an interval, due to insufficient rigor. Notably, in his 1821 Cours d'analyse, Cauchy gave a famously incorrect proof that the (pointwise) limit of (pointwise) continuous functions was itself (pointwise) continuous. The correct statement is rather that the uniform limit of uniformly continuous functions is uniformly continuous. This required the concept of uniform convergence, which was first observed by Weierstrass's advisor, Christoph Gudermann, in an 1838 paper, where Gudermann noted the phenomenon but did not define it or elaborate on it. Weierstrass saw the importance of the concept, and both formalized it and applied it widely throughout the foundations of calculus.
The (ε, δ)-definition of limit, as formulated by Weierstrass, is as follows:
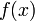 is continuous at
is continuous at 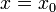 if
if 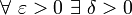 such that
such that 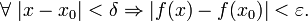
Using this definition and the concept of uniform convergence, Weierstrass was able to write proofs of several then unproven theorems such as the intermediate value theorem (for which Bolzano had already given a rigorous proof), the Bolzano – Weierstrass theorem, and Heine – Borel theorem.
Weierstrass also made significant advancements in the field of calculus of variations. Using the apparatus of analysis that he helped to develop, Weierstrass was able to give a complete reformulation of the theory which paved the way for the modern study of the calculus of variations. Among several significant results, Weierstrass established a necessary condition for the existence of strong extrema of variational problems. He also helped devise the Weierstrass – Erdmann condition which give sufficient conditions for an extremal to have a corner.