<Back to Index>
- Chemist Friedrich August Kekulé von Stradonitz, 1829
- Chemist Julius Lothar von Meyer, 1830
PAGE SPONSOR
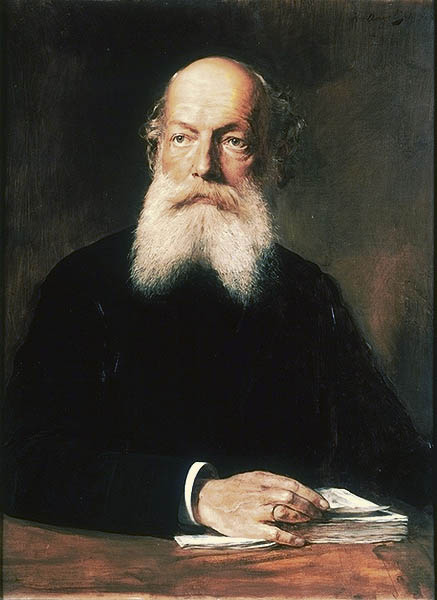


Friedrich August Kekule von Stradonitz (also August Kekulé) (7 September 1829 – 13 July 1896) was a German organic chemist. From the 1850s until his death, Kekule was one of the most prominent chemists in Europe, especially in theoretical chemistry. He was the principal founder of the theory of chemical structure.
Kekulé never used his first given name; he was known throughout his life as August Kekulé. After he was ennobled by the Kaiser in 1895, he adopted the name August Kekule von Stradonitz, without the French acute accent over the second "e". The French accent had apparently been added to the name by Kekulé's father during the Napoleonic occupation of Hesse by France, in order to ensure that French speakers pronounced the third syllable.
Kekulé was born in Darmstadt, the son of a civil servant. After graduating from secondary school, in 1847 he entered the University of Giessen, with the intention of studying architecture. After hearing the lectures of Justus von Liebig he decided to study chemistry. Following his education in Giessen, he took postdoctoral fellowships in Paris (1851 – 52), in Chur, Switzerland (1852 – 53), and in London (1853 – 55), where he was decisively influenced by Alexander Williamson.
In 1856 Kekulé became Privatdozent at the University of Heidelberg. In 1858 he was hired as full professor at the University of Ghent, then in 1867 he was called to Bonn, where he remained for the rest of his career. Basing his ideas on those of predecessors such as Williamson, Edward Frankland, William Odling, Auguste Laurent, Charles Adolphe Wurtz and others, Kekulé was the principal formulator of the theory of chemical structure (1857 – 58). This theory proceeds from the idea of atomic valence, especially the tetravalence of carbon (which Kekulé announced late in 1857) and the ability of carbon atoms to link to each other (announced in a paper published in May 1858), to the determination of the bonding order of all of the atoms in a molecule. Archibald Scott Couper independently arrived at the idea of self - linking of carbon atoms (his paper appeared in June 1858), and provided the first molecular formulas where lines symbolize bonds connecting the atoms.
For organic chemists, the theory of structure provided dramatic new clarity of understanding, and a reliable guide to both analytic and especially synthetic work. As a consequence, the field of organic chemistry developed explosively from this point. Among those who were most active in pursuing early structural investigations were, in addition to Kekulé and Couper, Frankland, Wurtz, Alexander Crum Brown, Emil Erlenmeyer, and Aleksandr Mikhailovich Butlerov.
Kekulé's idea of assigning certain atoms to certain positions within the molecule, and schematically connecting them using what he called their "Verwandtschaftseinheiten" ("affinity units", now called "valences" or "bonds"), was based largely on evidence from chemical reactions, rather than on instrumental methods that could peer directly into the molecule, such as X-ray crystallography. Such physical methods of structural determination had not yet been developed, so chemists of Kekulé's day had to rely almost entirely on so-called "wet" chemistry. Some chemists, notably Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe, heavily criticized the use of structural formulas that were offered, as he thought, without proof. However, most chemists followed Kekulé's lead in pursuing and developing what some have called "classical" structure theory, which was modified after the discovery of electrons (1897) and the development of quantum mechanics (in the 1920s).
The idea that the number of valences of a given element was invariant
was a key component of Kekulé's version of structural chemistry. This
generalization suffered from many exceptions, and was subsequently
replaced by the suggestion that valences were fixed at certain oxidation
states. For example, periodic acid
according to Kekuléan structure theory could be represented by the
chain structure I-O-O-O-O-H. By contrast, the modern structure of (meta)
periodic acid has all four oxygen atoms surrounding the iodine in a tetrahedral geometry.
Kekulé's most famous work was on the structure of benzene. In 1865 Kekulé published a paper in French (for he was then still in Francophone Belgium) suggesting that the structure contained a six - membered ring of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds. The next year he published a much longer paper in German on the same subject. The empirical formula for benzene had been long known, but its highly unsaturated structure was a challenge to determine. Archibald Scott Couper in 1858 and Joseph Loschmidt in 1861 suggested possible structures that contained multiple double bonds or multiple rings, but the study of aromatic compounds was in its earliest years, and too little evidence was then available to help chemists decide on any particular structure.
More evidence was available by 1865, especially regarding the relationships of aromatic isomers. Kekulé argued for his proposed structure by considering the number of isomers observed for derivatives of benzene. For every monoderivative of benzene (C6H5X, where X = Cl, OH, CH3, NH2, etc.) only one isomer was ever found, implying that all six carbons are equivalent, so that substitution on any carbon gives only a single possible product. For diderivatives such as the toluidines, C6H4(NH2)(CH3), three isomers were observed, for which Kekulé proposed structures with the two substituted carbon atoms separated by one, two and three carbon - carbon bonds, later named ortho, meta and para isomers respectively.
The counting of possible isomers for diderivatives was however criticized by Albert Ladenburg, a former student of Kekulé, who argued that Kekulé's 1865 structure implied two distinct "ortho" structures, depending on whether the substituted carbons are separated by a single or a double bond. Since ortho derivatives of benzene were never actually found in more than one isomeric form, Kekulé modified his proposal in 1872 and suggested that the benzene molecule oscillates between two equivalent structures, in such a way that the single and double bonds continually interchange positions. This implies that all six carbon - carbon bonds are equivalent, as each is single half the time and double half the time. A firmer theoretical basis for a similar idea was later proposed in 1928 by Linus Pauling, who replaced Kekulé's oscillation by the concept of resonance between quantum - mechanical structures.
The new understanding of benzene, and hence of all aromatic
compounds, proved to be so important for both pure and applied chemistry
after 1865 that in 1890 the German Chemical Society organized an
elaborate appreciation in Kekulé's honor, celebrating the twenty -
fifth
anniversary of his first benzene paper. Here Kekulé spoke of the
creation of the theory. He said that he had discovered the ring shape of
the benzene molecule after having a reverie or day dream of a snake
seizing its own tail (this is a common symbol in many ancient cultures
known as the Ouroboros).
This vision, he said, came to him after years of studying the nature of
carbon - carbon bonds. It is curious that a similar humorous depiction of
benzene had appeared in 1886 in the Berichte der Durstigen Chemischen Gesellschaft (Journal of the Thirsty Chemical Society), a parody of the Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, only the parody had monkeys seizing each other in a circle, rather than snakes as in Kekulé's anecdote.
Some historians have suggested that the parody was a lampoon of the
snake anecdote, possibly already well known through oral transmission
even if it had not yet appeared in print.
Others have speculated that Kekulé's story in 1890 was a re-parody of
the monkey spoof, and was a mere invention rather than a recollection of
an event in his life. Kekulé's 1890 speech in which these anecdotes appeared has been translated into English.
If one takes the anecdote as the memory of a real event, circumstances
mentioned in the story suggest that it must have happened early in 1862.
The other anecdote he told in 1890, of a vision of dancing atoms and
molecules that led to his theory of structure, happened (he said) while
he was riding on the upper deck of a horse drawn omnibus in London. If
true, this probably occurred in the late summer of 1855.
In 1895 Kekulé was ennobled by Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany, giving him the right to add "von Stradonitz" to his name, referring to a possession of his patrilineal ancestors in Stradonice, Bohemia. Of the first five Nobel Prizes in Chemistry, his students won three: van 't Hoff in 1901, Fischer in 1902 and Baeyer in 1905.
A larger - than - life size monument of Kekulé is situated in front of the former Chemical Institute at the University of Bonn. His monument is often decorated by students, e.g. for Valentine's Day.
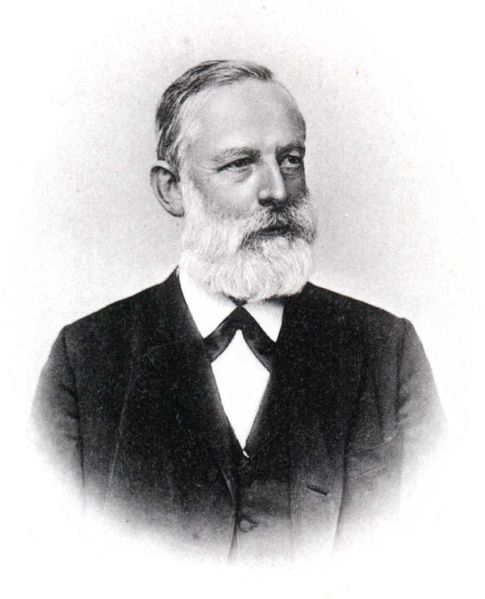


Julius Lothar von Meyer (August 19, 1830 - April 11, 1895) was a German chemist. He was contemporary and competitor of Dmitri Mendeleev to draw up the first periodic table of chemical elements. Some five years apart, both Mendeleev and Meyer worked with Robert Bunsen.
He was born in Varel, at that time belonging to the Duchy of Oldenburg, now part of Germany, the son of Friedrich August Meyer, a physician, and Anna Biermann. After high school (Altes Gymnasium Oldenburg AGO) he went to study medicine first at Zürich University in 1851, and then, two years later, at the University of Würzburg, where he had Rudolf Virchow as his teacher in pathology. The influence of C.F.W. Ludwig, under whom he studied at Zürich, decided him to devote his attention to physiological chemistry, and therefore he went, after his graduation (1854), to Heidelberg, where R. Bunsen held the chair of chemistry. There he was so influenced by G.R. Kirchhoff's mathematical teaching that he took up the study of mathematical physics at Königsberg under F.E. Neumann. In 1859 he became privat - docent in physics and chemistry at Breslau. In the preceding year, he had graduated as Ph.D. with a thesis on the action of carbon monoxide on the blood. In 1866 he accepted a post in the School of Forestry at Neustadt - Eberswalde, but soon moved to Carlsruhe Polytechnic. He married Johanna Volkmann on August 16, 1866.
Meyer is best known for the share he had in the periodic classification of the elements. He noted, as did J.A.R. Newlands in England, that if they are arranged in the order of their atomic weights they fall into groups in which similar chemical and physical properties are repeated at periodic intervals; and in particular he showed that if the atomic weights are plotted as ordinates and the atomic volumes as abscissae, the curve obtained presents a series of maxima and minima, the most electro - positive elements appearing at the peaks of the curve in the order of their atomic weights.
His book on Die modernen Theorien der Chemie, which was first published in Breslau in 1864, has an early version of the periodic table containing 28 elements classified into 6 families by their valence — the first time that elements had been grouped and ordered according to their valence. Work on organizing the elements by atomic weight had hitherto been stymied by inaccurate measurements of the atomic weights.
Mendeleev published his periodic table of all known elements (and predicted several new elements to complete the table, plus some corrected atomic weights) in 1869. Working completely independently, a few months later, Meyer published a revised and expanded version of his 1864 table, virtually identical to that published by Mendeleev (Meyer had been sent a copy of Mendeleev's table earlier, Mendeleev sent it to all well known chemists of those times) and a paper showing graphically the periodicity of the elements as a function of atomic weight. As well as other chemists, Meyer was doubtful about Mendeleev's periodic law, and he criticized Mendeleev for 'changing existing elements' atomic weights, only regarding possibility of periodical law in its structure', but Mendeleev's work provided significant support, particularly when the new elements were found as predicted and remeasured atomic weights accorded with those predicted.
In 1882, Meyer received from the Royal Society, at the same time as Mendeleev, the Davy Medal in recognition of his work on the Periodic Law.
Meyer's contributions also included the concept that the carbon atoms in benzene were arranged in a ring, although he did not propose the alternation of single and double bonds that later became included in the structure by August Kekulé.
During the Franco - German campaign, the Polytechnic was used as a hospital, and he took an active part in the care of the wounded. In 1876, Meyer became the first Professor of Chemistry at the University of Tübingen, where he served until his death there.