<Back to Index>
- Painter Rufino Tamayo, 1899
- Painter and Sculptor Jorge González Camarena, 1908
PAGE SPONSOR



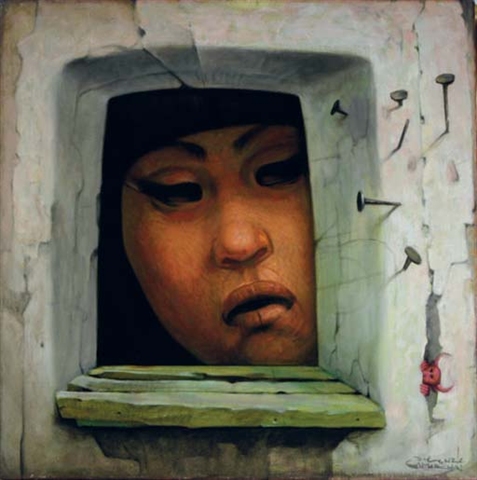
Rufino Tamayo (August 26, 1899 – June 24, 1991) was a Mexican painter of Zapotec heritage, born in Oaxaca de Juárez, Mexico. Tamayo was active in the mid 20th century in Mexico and New York, painting figurative abstraction with surrealist influences.
Tamayo's Zapotec heritage is often cited as an early influence. In 1911, he was orphaned and moved to Mexico City to live with his aunt.
He enrolled at Escuela Nacional de Artes Plasticas in 1917 to study art. While studying, Tamayo experimented with and was influenced by Cubism, Impressionism and Fauvism, among other popular art movements of the time, but with a distinctly Mexican feel.
After the Mexican Revolution, Tamayo devoted himself to creating an identity in his work. Tamayo expressed what he believed was the traditional Mexico and refused to follow the more political trend that many of his contemporaries did, such as José Clemente Orozco, Diego Rivera, Oswaldo Guayasamin, and David Alfaro Siqueiros. Due to this choice, he was seen by some as a "traitor" to the political cause, and he felt he could not freely express his art, so in 1926, he decided to leave Mexico and move to New York. Prior to leaving, he organized a one-man show of his work in Mexico City, where he was noticed for his individuality. Tamayo returned to Mexico in 1929 to have another solo show, this time being met with high praise and media coverage.
Rufino Tamayo’s legacy to the history of art is truly found in Tamayo’s oeuvre of original graphic prints, in which Tamayo cultivated every technique. Rufino Tamayo’s graphic work was produced between 1925 and 1991 and includes the mediums of woodcuts, lithographs, etchings and mixografia prints. With the help of Mexican painter and engineer Luis Remba, Rufino Tamayo expanded the technical and aesthetic possibilities of the graphic arts by developing a new genre of multiples, which they named "Mixografia". The Mixografia technique is a unique fine art printing process that allows for the production of prints with three - dimensional texture. The technique not only registered the texture and volume of Rufino Tamayo's design, but it also granted Tamayo the freedom to use any combination of solid materials in its creation. Rufino Tamayo was delighted with the Mixografia process, and Tamayo created some 80 Original Mixographs.
One of their most famous mixografía was titled Dos Personajes Atacados por Perros ("Two Characters Attacked by Dogs").
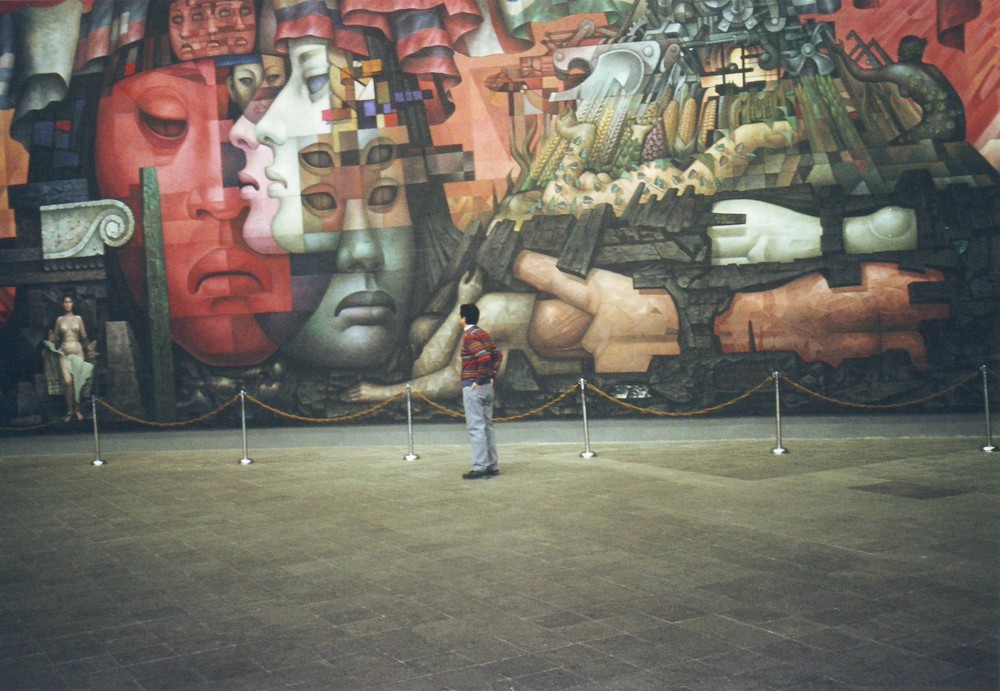
Tamayo also painted murals, some of which are displayed inside Palacio Nacional de Bellas Artes opera house in Mexico City, such as Nacimiento de la nacionalidad ("Birth of the Nationality") (1952).
From
1937 to 1949, Tamayo and his wife Olga lived in New York, becoming
widely recognized, and he painted some of his most valuable works during
that time. He had his first show in New York City at Valentine Gallery.
He gained credibility and went on to show at Knoedler Gallery and
Marlborough Gallery. While in New York, he helped train Helen
Frankenthaler at the Dalton School in New York. In
1948 his first major retrospective was done at the Palacio de Bellas
Artes in Mexico City, and while he was still controversial, his
popularity was high. Still uncomfortable with the political differences
and controversy, Tamayo and Olga moved to Paris in 1949, where he was
welcomed by the artists of Europe. He remained in Paris for 10 years.
In 1959, Tamayo and his wife returned to Mexico permanently, where Tamayo built an art museum in his home town of Oaxaca, the Museo Rufino Tamayo. In 1972, Tamayo was the subject of the documentary film, Rufino Tamayo: The Sources of his Art by Gary Conklin.
The Tamayo Contemporary Art Museum (Museo Tamayo de Arte Contemporáneo), located on Mexico City's Paseo de la Reforma boulevard, where it crosses Chapultepec Park, was opened in 1981 as a repository for the collections that Rufino Tamayo and his wife acquired during their lifetimes, and ultimately donated to the nation.
In 1988, Tamayo received the Belisario Domínguez Medal of Honor.
Tamayo painted his last painting in 1989, at the age of 90, Hombre con flor (Man with flower), a self portrait.
Tamayo's work has been displayed in museums throughout the world, including the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum in New York City, The Phillips Collection in Washington, the Naples Museum of Art in Naples, Florida, and The Museo Nacional Centro de Arte Reina Sofia in Madrid, Spain.
| “ | "If I could express with a single word what it is that distinguishes Tamayo from other painters, I would say without a moment's hesitation: Sun. For the sun is in all his pictures, whether we see it or not." - Nobel Prize - winning poet Octavio Paz | ” |
On June 12, 1991, Tamayo was admitted to Mexico City's National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition for respiratory and heart failure. He suffered a heart attack and died on June 24, 1991.
Tamayo's 1970 painting Tres Personajes was bought by a Houston man as a gift for his wife in 1977, then stolen from their storage locker in 1987 during a move. In 2003, Elizabeth Gibson found the painting in the trash on a New York City curb. Although she knew little about modern art, Gibson felt the painting "had power" and took it without knowing its
origin or market value. She spent four years trying to learn about the
work, eventually learning from the PBS website that it had been featured on an episode of Antiques Roadshow. After seeing the Missing Masterpieces segment about Tres Personajes, Gibson and the former owner arranged to sell the painting at a Sotheby's auction. In November, 2007 Gibson received a $15,000 reward plus a portion of the $1,049,000 auction sales price.
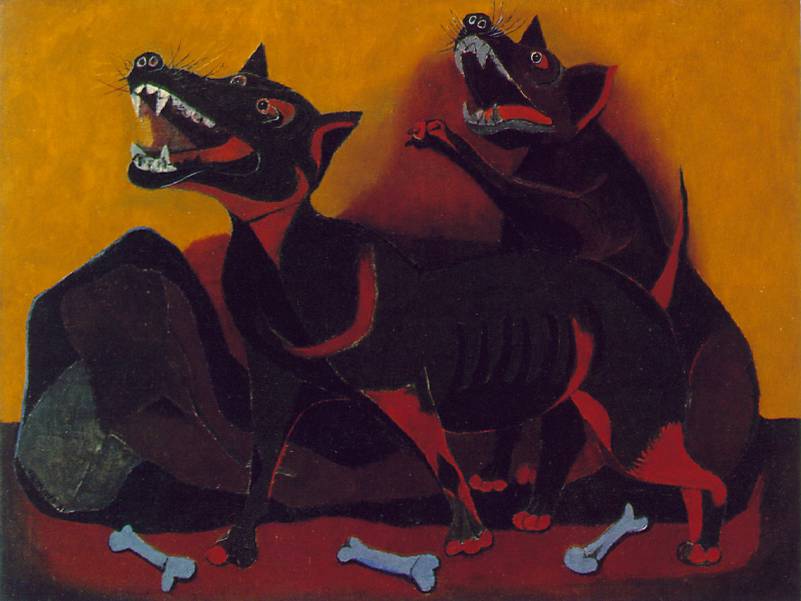
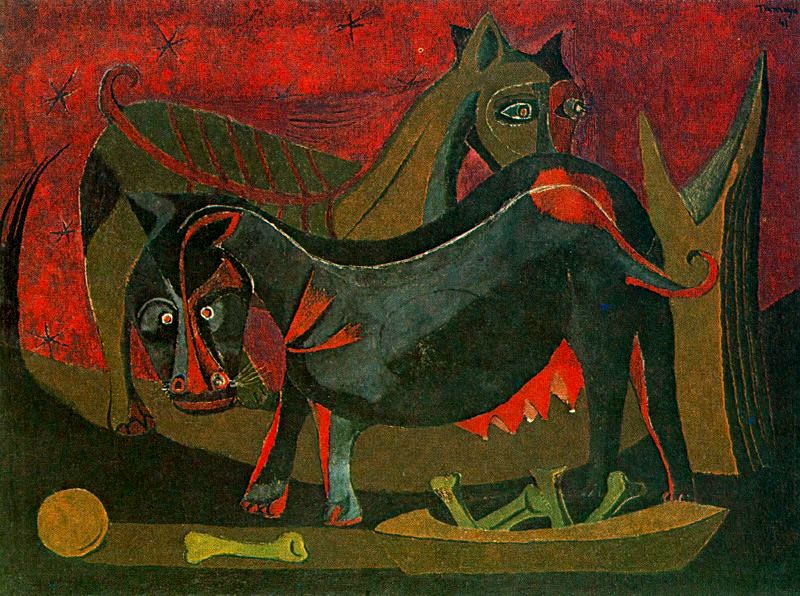







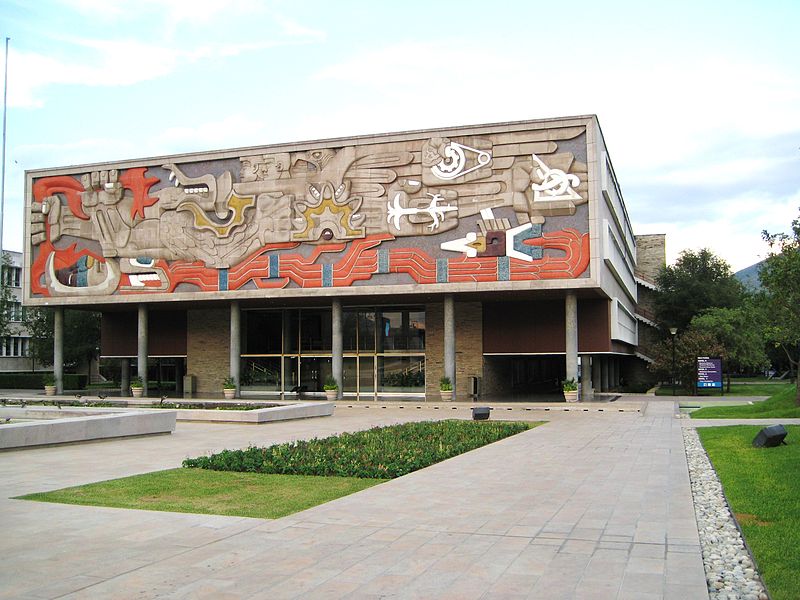
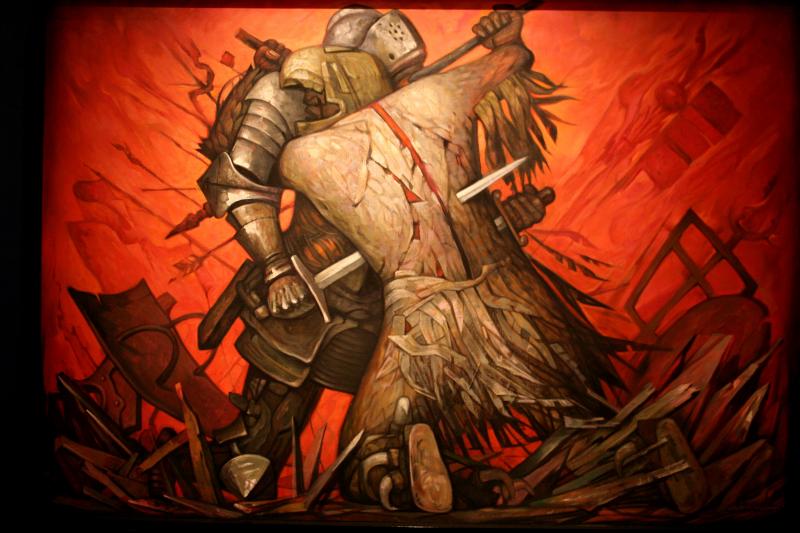
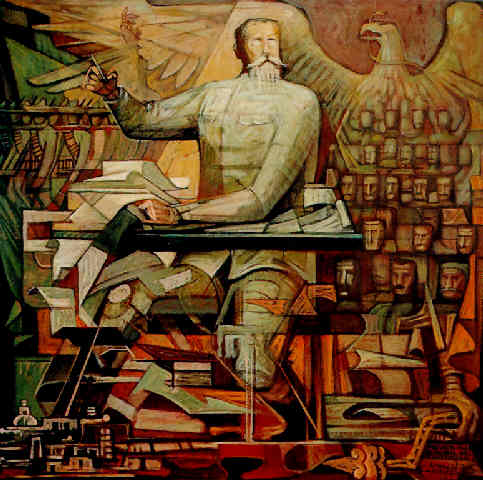
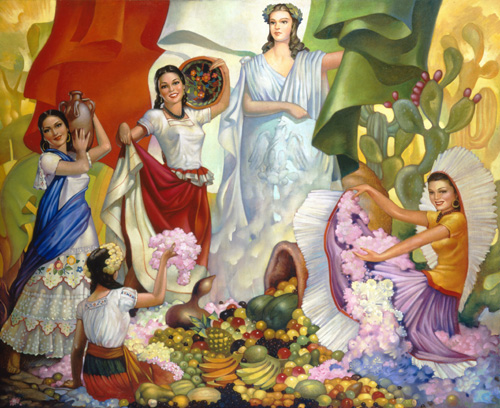
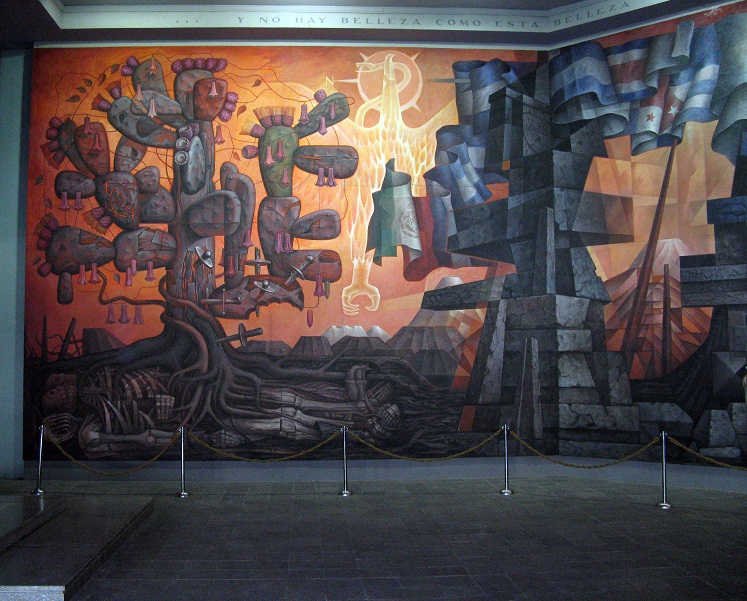
Jorge González Camarena (24 March 1908 – 24 May 1980) was a prominent Mexican painter, muralist and sculptor who received the Mexican National Prize for Arts and Sciences (Fine Arts, 1970). For his portrait of Michelangelo Buonarotti, which hangs at his birthplace at Caprese, he was awarded the Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana in 1967.
González Camarena was born in Guadalajara, into a family composed by Arturo González and Sara Camarena, originally from Arandas, Jalisco. His younger brother, Guillermo, would later be known for inventing a chromoscopic adapter for television equipment and becoming one of the best known television pioneers in the country.
After being encouraged by a local instructor, he enrolled the National School of Plastic Arts at San Carlos Academy and became an apprentice of Dr. Atl. In 1929 he started to contribute and illustrate for Revista de Revistas and Nuestro México. Three years later he was commissioned to restore the 16th century Franciscan frescos at the Convent of Huejotzingo, Puebla, where he allegedly discovered contributions by Marcos Cipactli, one of the last Aztec painters and, controversially, attributed him the authorship of Our Lady of Guadalupe.
He died of a brain hemorrhage on 24 May 1980. After being mourned at the Palace of Fine Arts, he was buried at the Dolores Cemetery in Mexico City. In 2008, on the 100th anniversary of his birth, he was honored by the Mexican Academy of Arts, the Mexican Institute of Social Security and the Soumaya Museum, among others.