<Back to Index>
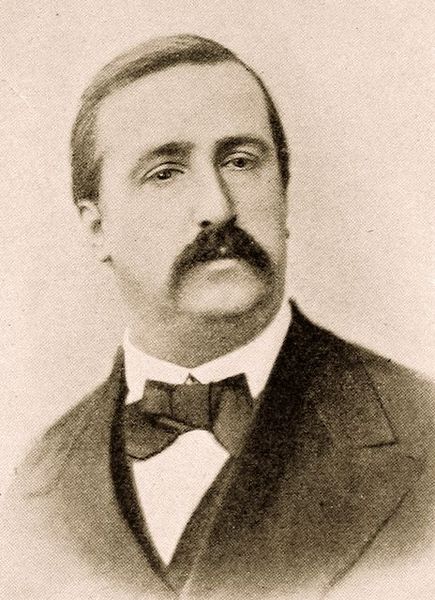
- Composer Alexander Porfiryevich Borodin, 1833
- Composer and Pianist Johannes Brahms, 1833
- Composer Amilcare Ponchielli, 1834
PAGE SPONSOR

Alexander Porfiryevich Borodin (12 November 1833 – 27 February 1887) was a Russian Romantic composer and chemist of Georgian – Russian parentage. He was a member of the group of composers called The Five (or "The Mighty Handful"), who were dedicated to producing a specifically Russian kind of art music. He is best known for his symphonies, his two string quartets, and his opera Prince Igor. Music from Prince Igor and his string quartets was later adapted for the US musical Kismet.
Borodin was born in Saint Petersburg, the illegitimate son of a Georgian noble, Luka Gedevanishvili (Georgian: ლუკა სიმონის ძე გედევანიშვილი) and a 24 year old Russian woman, Evdokia Konstantinovna Antonova (Евдокия Константиновна Антонова). The nobleman had him registered as the son of one of his serfs, Porfiry Borodin. As a boy he received a good education, including piano lessons. He entered the Medico – Surgical Academy in 1850, which was later home to Ivan Pavlov, and pursued a career in chemistry. On graduation he spent a year as surgeon in a military hospital, followed by three years of advanced scientific study in western Europe.
In 1862 Borodin became a professor of chemistry at the Academy of Medicine, and eventually was able to establish medical courses for women (1872). He spent the remainder of his life lecturing and overseeing the education of others.
He began taking lessons in composition from Mily Balakirev in 1862. He married Ekaterina Protopopova, a pianist, in 1863.
Music remained a secondary vocation for Borodin outside of his main
career as a chemist and physician. He suffered poor health, having
overcome cholera and several minor heart attacks. He died suddenly during a ball at the Academy, and was interred in Tikhvin Cemetery at the Alexander Nevsky Monastery, in Saint Petersburg.
In his profession Borodin gained great respect, being particularly noted for his work on aldehydes. Between 1859 and 1862 Borodin held a postdoctorate in Heidelberg. He worked in the laboratory of Emil Erlenmeyer working on benzene derivatives. He also spent time in Pisa, working on organic halogens. One experiment published in 1862 described the first nucleophilic displacement of chlorine by fluorine in benzoyl chloride. A related reaction known to the West as the Hunsdiecker reaction published in 1939 by the Hunsdieckers was promoted by the Soviet Union as the Borodin reaction. In 1862 he returned to the Medico – Surgical Academy, where he worked on self - condensation of small aldehydes. He published papers in 1864 and 1869, and in this field he found himself competing with August Kekulé.
Borodin is co-credited with the discovery of the Aldol reaction, with Charles - Adolphe Wurtz. In 1872 he announced to the Russian Chemical Society the discovery of a new byproduct in aldehyde reactions with alcohol like properties, and he noted similarities with compounds already discussed in publications by Wurtz from the same year.
He published his last full article in 1875 on reactions of amides and his last publication concerned a method for the identification of urea in animal urine.
His son - in - law and successor was fellow chemist A. P. Dianin.
Borodin met Mily Balakirev in 1862. While under Balakirev's tutelage in composition he began his Symphony No. 1 in E flat major; it was first performed in 1869, with Balakirev conducting. In that same year Borodin started on his Symphony No. 2 in B minor, which was not particularly successful at its premiere in 1877 under Eduard Nápravník, but with some minor re-orchestration received a successful performance in 1879 by the Free Music School under Rimsky - Korsakov's direction. In 1880 he composed the popular symphonic poem In the Steppes of Central Asia. Two years later he began composing a third symphony, but left it unfinished at his death; two movements of it were later completed and orchestrated by Glazunov.
In 1868 Borodin became distracted from initial work on the second symphony by preoccupation with the opera Prince Igor,
which is seen by some to be his most significant work and one of the
most important historical Russian operas. It contains the Polovtsian Dances,
often performed as a stand alone concert work forming what is probably
Borodin's best known composition. Borodin left the opera (and a few
other works) incomplete at his death. Prince Igor was completed
posthumously by Rimsky - Korsakov and Glazunov. It is set in the 12th
century, when the barbarous Polovtsians invaded southern Russia. The
story tells of the capture of Prince Igor and son Vladimir of Russia by
Polovtsian leader Khan Konchak, who entertains his prisoners lavishly
and calls on his slaves to perform the famous Polovtsian dances, which
provide a thrilling climax to the second act.
No other member of the Balakirev circle identified himself so openly with absolute music as did Borodin in his two string quartets. Himself a cellist, he was an enthusiastic chamber music player, an interest that deepened during his chemical studies in Heidelberg between 1859 and 1861. This early period yielded, among other chamber works, a string sextet and a piano quintet. In thematic structure and instrumental texture he based his pieces on those of Felix Mendelssohn.
In 1875 Borodin started his First String Quartet, much to the displeasure of Mussorgsky and Vladimir Stasov.
That Borodin did so in the company of The Five, who were hostile to
chamber music, speaks to his independence. From the First Quartet on, he
displayed mastery in the form. His Second Quartet, in which his strong lyricism is represented in the popular "Nocturne", followed in 1881. The First Quartet is richer in changes of mood. The
Second Quartet has a more uniform atmosphere and expression.
Borodin's fame outside the Russian Empire was made possible during his lifetime by Franz Liszt, who arranged a performance of the Symphony No. 1 in Germany in 1880, and by the Comtesse de Mercy - Argenteau in Belgium and France. His music is noted for its strong lyricism and rich harmonies. Along with some influences from Western composers, as a member of The Five his music exudes also an undeniably Russian flavor. His passionate music and unusual harmonies proved to have a lasting influence on the younger French composers Debussy and Ravel (in homage, the latter composed in 1913 a piano piece entitled "À la manière de Borodine").
The evocative characteristics of Borodin's music made possible the adaptation of his compositions in the 1953 musical Kismet, by Robert Wright and George Forrest, perhaps most notably in the song, "Stranger in Paradise". In 1954, Borodin was posthumously awarded a Tony Award for this show.
- Borodin's music is full of romantic charm and enticing melody, and much of it also rings with the pageantry and landscape of old Russia; of onion - domed churches, richly decorated icons, and the vastness of the land. (Betty Fry)
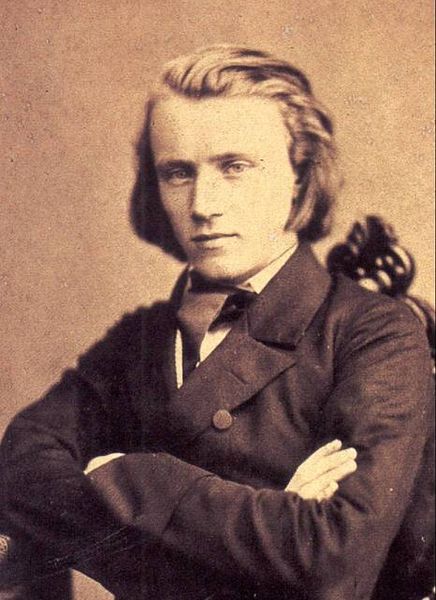

Johannes Brahms (7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer and pianist, and one of the leading musicians of the Romantic period. Born in Hamburg, Brahms spent much of his professional life in Vienna, Austria, where he was a leader of the musical scene. In his lifetime, Brahms's popularity and influence were considerable; following a comment by the nineteenth century conductor Hans von Bülow, he is sometimes grouped with Johann Sebastian Bach and Ludwig van Beethoven as one of the Three Bs.
Brahms composed for piano, chamber ensembles, symphony orchestra and for voice and chorus. A virtuoso pianist, he premiered many of his own works; he also worked with some of the leading performers of his time, including the pianist Clara Schumann and the violinist Joseph Joachim. Many of his works have become staples of the modern concert repertoire. Brahms, an uncompromising perfectionist, destroyed many of his works and left some of them unpublished.
Brahms is often considered both a traditionalist and an innovator. His music is firmly rooted in the structures and compositional techniques of the Baroque and Classical masters. He was a master of counterpoint, the complex and highly disciplined method of composition for which Johann Sebastian Bach is famous, and also of development, a compositional ethos pioneered by Joseph Haydn, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven. Brahms aimed to honor the "purity" of these venerable "German" structures and advance them into a Romantic idiom, in the process creating bold new approaches to harmony, melody and, especially, rhythm. While many contemporaries found his music too academic, his contribution and craftsmanship have been admired by subsequent figures as diverse as Arnold Schoenberg and Edward Elgar. The diligent, highly constructed nature of Brahms's works was a starting point and an inspiration for a generation of composers.
Brahms's father, Johann Jakob Brahms (1806 – 72), came to Hamburg from Dithmarschen, seeking a career as a town musician. He was proficient in several instruments, but found employment mostly playing the horn and double bass.
In 1830, he married Johanna Henrika Christiane Nissen (1789 – 1865), a
seamstress never previously married, who was seventeen years older than
he was. Johannes Brahms had an older sister and a younger brother.
Initially, they lived near the city docks, in the Gängeviertel quarter
of Hamburg, for six months, before moving to a small house on the
Dammtorwall, a small city in the Inner Alster.
Johann Jakob gave his son his first musical training. He studied piano from the age of seven with Otto Friedrich Willibald Cossel. Owing to the family's poverty, as a boy Brahms played in dance halls and brothels – some of the seediest places in Hamburg – surrounded by drunken sailors and prostitutes that often fondled the boy as he played. Early biographers found this shocking and played down this portion of his life. Modern writers have pointed to this as a reason for Brahms's later inability to have a successful relationship for marriage, etc., his view of women being warped by his experiences. Recently, Brahms scholars Styra Avins and Kurt Hoffman have suggested that this legend is false. Since Brahms himself clearly originated the story, however, some have questioned Hoffman's theory.
For a time, Brahms also learned the cello. After his early piano lessons with Otto Cossel, Brahms studied piano with Eduard Marxsen, who had studied in Vienna with Ignaz von Seyfried (a pupil of Mozart) and Carl Maria von Bocklet (a close friend of Schubert). The young Brahms gave a few public concerts in Hamburg, but did not become well known as a pianist until he made a concert tour at the age of nineteen. (In later life, he frequently took part in the performance of his own works, whether as soloist, accompanist, or participant in chamber music.) He conducted choirs from his early teens, and became a proficient choral and orchestral conductor.
He began to compose quite early in life, but later destroyed most copies of his first works; for instance, Louise Japha,
a fellow pupil of Marxsen, reported a piano sonata, that Brahms had
played or improvised at the age of 11, had been destroyed. His
compositions did not receive public acclaim until he went on a concert
tour as accompanist to the Hungarian violinist Eduard Reményi in April and May 1853. On this tour he met Joseph Joachim at Hanover, and went on to the Court of Weimar where he met Franz Liszt, Peter Cornelius, and Joachim Raff. According to several witnesses of Brahms's meeting with Liszt (at which Liszt performed Brahms's Scherzo, Op. 4, at sight), Reményi was offended by Brahms's failure to praise Liszt's Sonata in B minor
wholeheartedly (Brahms supposedly fell asleep during a performance of
the recently composed work), and they parted company shortly afterwards.
Brahms later excused himself, saying that he could not help it, having
been exhausted by his travels.
Joachim had given Brahms a letter of introduction to Robert Schumann, and after a walking tour in the Rhineland, Brahms took the train to Düsseldorf, and was welcomed into the Schumann family on arrival there. Schumann, amazed by the 20 year old's talent, published an article entitled "Neue Bahnen" (New Paths) in the 28 October 1853 issue of the journal Neue Zeitschrift für Musik alerting the public to the young man, who, he claimed, was "destined to give ideal expression to the times." This pronouncement was received with some skepticism outside of Schumann's immediate circle, and may have increased Brahms's naturally self critical need to perfect his works and technique. While he was in Düsseldorf, Brahms participated with Schumann and Albert Dietrich in writing a sonata for Joachim; this is known as the "F–A–E Sonata" (German: Frei aber einsam). He became very attached to Schumann's wife, the composer and pianist Clara, fourteen years his senior, with whom he would carry on a lifelong, emotionally passionate relationship. Brahms never married, despite strong feelings for several women and despite entering into an engagement, soon broken off, with Agathe von Siebold in Göttingen in 1859. After Schumann's attempted suicide and subsequent confinement in a mental sanatorium near Bonn in February 1854, Brahms was the main intercessor between Clara and her husband, and found himself virtually head of the household.
After Schumann's death, Brahms hurried to Düsseldorf and for the next
two years lived in an apartment above the Schumann's house, and
sacrificed his career and his art for Clara's sake. The question of
Brahms and Clara Schumann is perhaps the most mysterious in music
history, alongside that of Beethoven's "Immortal Beloved." Whether they
were actually lovers is unknown, but their destruction of their letters
to each other may point to something beyond mere privacy.
After Schumann's death at the sanatorium in 1856, Brahms divided his time between Hamburg, where he formed and conducted a ladies' choir, and Detmold in the Principality of Lippe, where he was court music teacher and conductor. He was the soloist at the premiere of his Piano Concerto No. 1 in 1859. He first visited Vienna in 1862, staying there over the winter, and, in 1863, was appointed conductor of the Vienna Singakademie. Though he resigned the position the following year, and entertained the idea of taking up conducting posts elsewhere, he based himself increasingly in Vienna and soon made his home there. From 1872 to 1875, he was director of the concerts of the Vienna Gesellschaft der Musikfreunde; afterwards, he accepted no formal position. He declined an honorary doctorate of music from University of Cambridge in 1877, but accepted one from the University of Breslau in 1879, and composed the Academic Festival Overture as a gesture of appreciation.
He had been composing steadily throughout the 1850s and 60s, but his
music had evoked divided critical responses, and the Piano Concerto No. 1
had been badly received in some of its early performances. His works
were labelled old fashioned by the 'New German School' whose principal
figures included Liszt and Richard Wagner.
Brahms admired some of Wagner's music and admired Liszt as a great
pianist, but the conflict between the two schools, known as the War of the Romantics, soon embroiled all of musical Europe. In the Brahms camp were his close friends: Clara Schumann, the influential music critic Eduard Hanslick, and the leading Viennese surgeon Theodor Billroth.
In 1860, Brahms attempted to organize a public protest against some of
the wilder excesses of the Wagnerians' music. This took the form of a
manifesto, written by Brahms and Joachim jointly. The manifesto, which
was published prematurely with only three supporting signatures, was a
failure, and he never engaged in public polemics again.
It was the premiere of A German Requiem, his largest choral work, in Bremen, in 1868, that confirmed Brahms's European reputation and led many to accept that he had conquered Beethoven and the symphony. This may have given him the confidence finally to complete a number of works that he had wrestled with over many years, such as the cantata Rinaldo, his first string quartet, third piano quartet, and most notably his first symphony. This appeared in 1876, though it had been begun (and a version of the first movement seen by some of his friends) in the early 1860s. The other three symphonies then followed in 1877, 1883, and 1885. From 1881, he was able to try out his new orchestral works with the court orchestra of the Duke of Meiningen, whose conductor was Hans von Bülow. He was the soloist at the premiere of his Piano Concerto No. 2 in 1881, in Pest.
Brahms frequently traveled, both for business (concert tours) and
pleasure. From 1878 onwards, he often visited Italy in the springtime,
and he usually sought out a pleasant rural location in which to compose
during the summer. He was a great walker and especially enjoyed spending
time in the open air, where he felt that he could think more clearly.
In 1889, one Theo Wangemann, a representative of American inventor Thomas Edison, visited the composer in Vienna and invited him to make an experimental recording. Brahms played an abbreviated version of his first Hungarian dance on the piano. The recording was later issued on an LP of early piano performances (compiled by Gregor Benko). Although the spoken introduction to the short piece of music is quite clear, the piano playing is largely inaudible due to heavy surface noise. Nevertheless, this remains the earliest recording made by a major composer. Analysts and scholars remain divided, however, as to whether the voice that introduces the piece is that of Wangemann or of Brahms. Several attempts have been made to improve the quality of this historic recording; a "denoised" version was produced at Stanford University which claims to solve the mystery.
In 1889, Brahms was named an honorary citizen of Hamburg, until 1948 the only one born in Hamburg.
In 1890, the 57 year old Brahms resolved to give up composing. However, as it turned out, he was unable to abide by his decision, and in the years before his death he produced a number of acknowledged masterpieces. His admiration for Richard Mühlfeld, clarinetist with the Meiningen orchestra, moved him to compose the Clarinet Trio, Op. 114, Clarinet Quintet, Op. 115 (1891), and the two Clarinet Sonatas, Op. 120 (1894). He also wrote several cycles of piano pieces, Opp. 116 – 119, the Four Serious Songs (Vier ernste Gesänge), Op. 121 (1896), and the Eleven Chorale Preludes for organ, Op. 122 (1896).
While completing the Op. 121 songs, Brahms developed cancer
(sources differ on whether this was of the liver or pancreas). His
condition gradually worsened and he died on April 3, 1897, aged 63.
Brahms is buried in the Zentralfriedhof in Vienna.
Later that year, the British composer Hubert Parry, who considered Brahms the greatest artist of the time, wrote an orchestral Elegy for Brahms. This was never played in Parry's lifetime, receiving its first performance at a memorial concert for Parry himself in 1918.
Brahms wrote a number of major works for orchestra, including two serenades, four symphonies, two piano concertos (No. 1 in D minor; No. 2 in B-flat major), a Violin Concerto, a Double Concerto for violin and cello, and two companion orchestral overtures, the Academic Festival Overture and the Tragic Overture.
His large choral work A German Requiem is not a setting of the liturgical Missa pro defunctis but a setting of texts which Brahms selected from the Lutheran Bible. The work was composed in three major periods of his life. An early version of the second movement was first composed in 1854, not long after Robert Schumann's attempted suicide, and this was later used in his first piano concerto. The majority of the Requiem was composed after his mother's death in 1865. The fifth movement was added after the official premiere in 1868, and the work was published in 1869.
Brahms's works in variation form include, among others, the Variations and Fugue on a Theme by Handel and the Paganini Variations, both for solo piano, and the Variations on a Theme by Haydn in versions for two pianos and for orchestra. The final movement of the Fourth Symphony, Op. 98, is formally a passacaglia.
His chamber works include three string quartets, two string quintets, two string sextets, a clarinet quintet, a clarinet trio, a horn trio, a piano quintet, three piano quartets, and four piano trios (the fourth being published posthumously). He composed several instrumental sonatas with piano, including three for violin, two for cello, and two for clarinet (which were subsequently arranged for viola by the composer). His solo piano works range from his early piano sonatas and ballades to his late sets of character pieces. Brahms was a significant lieder composer, who wrote over 200 songs. His chorale preludes for organ, Op. 122, which he wrote shortly before his death, have become an important part of the organist's repertoire.
Brahms strongly preferred writing absolute music that does not refer to an explicit scene or narrative, and he never wrote an opera or a symphonic poem.
Despite his reputation as a serious composer of large, complex
musical structures, some of Brahms's most widely known and most
commercially successful compositions during his life were small scale
works of popular intent aimed at the thriving contemporary market for
domestic music making; indeed, during the 20th century, the influential
American critic B.H. Haggin, rejecting more mainstream views, argued in his various guides to
recorded music that Brahms was at his best in such works and much less
successful in larger forms. Among the most cherished of these lighter
works by Brahms are his sets of popular dances — the Hungarian Dances, the Waltzes, Op. 39, for piano duet, and the Liebeslieder Waltzes for vocal quartet and piano — and some of his many songs, notably the Wiegenlied,
Op. 49, No. 4 (published in 1868). This last was written (to a folk
text) to celebrate the birth of a son to Brahms's friend Bertha Faber
and is universally known as Brahms's Lullaby.
Brahms maintained a Classical sense of form and order in his works – in contrast to the opulence of the music of many of his contemporaries. Thus many admirers (though not necessarily Brahms himself) saw him as the champion of traditional forms and "pure music", as opposed to the "New German" embrace of program music.
Brahms venerated Beethoven: in the composer's home, a marble bust of Beethoven looked down on the spot where he composed, and some passages in his works are reminiscent of Beethoven's style. Brahms's First Symphony bears strongly the influence of Beethoven's Fifth Symphony, as the two works are both in a formidable C Minor, and end in the struggle towards a C Major triumph. The main theme of the finale of the First Symphony is also reminiscent of the main theme of the finale of Beethoven's Ninth, and when this resemblance was pointed out to Brahms, he replied that any ass – jeder Esel – could see that. In 1876, when the work was premiered in Vienna, it was immediately hailed as "Beethoven's Tenth".
A German Requiem was partially inspired by his mother's death in 1865 (at which time he composed a funeral march that was to become the basis of Part Two, Denn alles Fleisch), but it also incorporates material from a Symphony which he started in 1854 but abandoned following Schumann's suicide attempt. He once wrote that the Requiem "belonged to Schumann". The first movement of this abandoned Symphony was re-worked as the first movement of the First Piano Concerto.
Brahms also loved the Classical composers Mozart and Haydn. He collected first editions and autographs of their works, and edited performing editions. He studied the music of pre - classical composers, including Giovanni Gabrieli, Johann Adolph Hasse, Heinrich Schütz, Domenico Scarlatti, George Frideric Handel, and, especially, Johann Sebastian Bach. His friends included leading musicologists, and, with Friedrich Chrysander, he edited an edition of the works of François Couperin. Brahms also edited works by C.P.E. and W.F. Bach. He looked to older music for inspiration in the art of counterpoint; the themes of some of his works are modelld on Baroque sources such as Bach's The Art of Fugue in the fugal finale of Cello Sonata No. 1 or the same composer's Cantata No. 150 in the passacaglia theme of the Fourth Symphony's finale.
The early Romantic composers also had a major influence on Brahms, particularly Schumann, who encouraged Brahms as a young composer. During his stay in Vienna in 1862 – 63, Brahms became particularly interested in the music of Franz Schubert. The latter's influence may be identified in works by Brahms dating from the period, such as the two piano quartets Op. 25 and Op. 26, and the Piano Quintet which alludes to Schubert's String Quintet and Grand Duo for piano four hands. The influence of Chopin and Mendelssohn on Brahms is less obvious, although occasionally one can find in his works what seems to be an allusion to one of theirs (for example, Brahms's Scherzo, Op. 4, alludes to Chopin's Scherzo in B-flat minor; the scherzo movement in Brahms's Piano Sonata in F minor, Op. 5, alludes to the finale of Mendelssohn's Piano Trio in C minor).
Brahms considered giving up composition when it seemed that other composers' innovations in extended tonality would result in the rule of tonality being broken altogether. Although Wagner became fiercely critical of Brahms as the latter grew in stature and popularity, he was enthusiastically receptive of the early Variations and Fugue on a Theme by Handel; Brahms himself, according to many sources, deeply admired Wagner's music, confining his ambivalence only to the dramaturgical precepts of Wagner's theory.
Brahms wrote settings for piano and voice of 144 German folk songs, and many of his lieder reflect folk themes or depict scenes of rural life. His Hungarian Dances were among his most profitable compositions.
Despite Brahms's humanist and skeptical tendencies, it is certain one of his musical influences was the Bible. He was reared to appreciate Luther's translation. His "Requiem" employs biblical texts to convey a humanist message, omitting words about salvation or immortality, and focuses on the living rather than the dead. Author Walter Niemann declared, "The fact that Brahms began his creative activity with the German folk song and closed with the Bible reveals... the true religious creed of this great man of the people." Some biographers and critics, however, see Brahms as more of a cultural Lutheran who embraced the cultural aspects of his upbringing but may or may not have adopted the religious beliefs. When asked by conductor Karl Reinthaler to add additional sectarian text to his "requiem", Brahms responded, "As far as the text is concerned, I confess that I would gladly omit even the word German and instead use Human; also with my best knowledge and will I would dispense with passages like John 3:16. On the other hand, I have chosen one thing or another because I am a musician, because I needed it, and because with my venerable authors I can't delete or dispute anything. But I had better stop before I say too much."
There is reason to believe that Brahms was a religious freethinker. Being a star of his age, he would frequently say deceptive things to the public. This means that the most reliable accounts on Brahms's innermost feelings may come from the people in the close circle around him. Among these was the pious Antonín Dvořák, the closest Brahms ever would come to having a protégé. In a letter, Dvořák disclosed his concerns regarding Brahms's religious views: "Such a man, such a fine soul — and he believes in nothing! He believes in nothing!"
The question of Brahms and religiosity has been controversial and elicited accusations of fraud. One example is the book Talks With Great Composers, released in the 1950s by Arthur Abell, which contains an unconfirmed interview with Brahms and Joseph Joachim, replete with biblical references. The interview has been declared fraudulent by Brahms biographer Jan Swafford.
Brahms's point of view looked both backward and forward; his output was often bold in its exploration of harmony and rhythm. As a result, he was an influence on composers of both conservative and modernist tendencies. Within his lifetime, his idiom left an imprint on several composers within his personal circle, who strongly admired his music, such as Heinrich von Herzogenberg, Robert Fuchs, and Julius Röntgen, as well as on Gustav Jenner, who was Brahms's only formal composition pupil. Antonín Dvořák, who received substantial assistance from Brahms, deeply admired his music and was influenced by it in several works such as the Symphony No 7 in D minor and the F minor Piano Trio. Features of the 'Brahms style' were absorbed in a more complex synthesis with other contemporary (chiefly Wagnerian) trends by Hans Rott, Wilhelm Berger, Max Reger and Franz Schmidt, whereas the British composers Hubert Parry and Edward Elgar and the Swede Wilhelm Stenhammar all testified to learning much from Brahms's example. As Elgar said, "I look at the Third Symphony of Brahms, and I feel like a pygmy."
Ferruccio Busoni's early music shows much Brahmsian influence, and Brahms took an interest in him, though Busoni later tended to disparage Brahms. Towards the end of his life, Brahms offered substantial encouragement to Ernő Dohnányi and also to Alexander von Zemlinsky. Their early chamber works (and those of Béla Bartók, who was friendly with Dohnányi) show a thoroughgoing absorption of the Brahmsian idiom. Zemlinsky, moreover, was in turn the teacher of Arnold Schoenberg, and Brahms was apparently impressed by two movements of Schoenberg's early Quartet in D major which Zemlinsky showed him. In 1933, Schoenberg wrote an essay "Brahms the Progressive" (re-written 1947), which drew attention to Brahms's fondness for motivic saturation and irregularities of rhythm and phrase; in his last book (Structural Functions of Harmony, 1948), he analyzed Brahms's "enriched harmony" and exploration of remote tonal regions. These efforts paved the way for a re-evaluation of Brahms's reputation in the 20th century. Schoenberg went so far as to orchestrate one of Brahms's piano quartets. Schoenberg's pupil Anton Webern, in his 1933 lectures, posthumously published under the title The Path to the New Music, claimed Brahms as one who had anticipated the developments of the Second Viennese School, and Webern's own Op. 1, an orchestral passacaglia, is clearly in part a homage to, and development of, the variation techniques of the passacaglia - finale of Brahms's Fourth Symphony.
Brahms was honored by the German Hall of Fame, the Walhalla temple. On 14 September 2000, he was introduced there as the 126th "rühmlich ausgezeichneter Teutscher" and 13th composer among them, with a bust by sculptor Milan Knobloch.
Like Beethoven, Brahms was fond of nature and often went walking in the woods around Vienna. He often brought penny candy with him to hand out to children. To adults, Brahms was often brusque and sarcastic, and he sometimes alienated other people. His pupil Gustav Jenner wrote, "Brahms has acquired, not without reason, the reputation for being a grump, even though few could also be as lovable as he." He also had predictable habits, which were noted by the Viennese press, such as his daily visit to his favorite "Red Hedgehog" tavern in Vienna, and the press also particularly took into account his style of walking with his hands firmly behind his back complete with a caricature of him in this pose walking alongside a red hedgehog. Those who remained his friends were very loyal to him, however, and he reciprocated with equal loyalty and generosity.
Brahms had amassed a small fortune in the second half of his career,
around 1860, when his works sold widely. But despite his wealth, he
lived very simply, with a modest apartment – a mess of music papers and
books – and a single housekeeper who cleaned and cooked for him. He was
often the butt of jokes for his long beard, his cheap clothes and often
not wearing socks, etc. Brahms gave away large sums of money to friends
and to aid various musical students, often with the term of strict
secrecy. Brahms' domicile was hit during World War II, destroying his
piano and other possessions that were still kept there for posterity by
the Viennese.
Brahms was a lifelong friend of Johann Strauss II, though they were very different as composers. Brahms even struggled to get to the Theater an der Wien in Vienna for the premiere of Strauss's operetta Die Göttin der Vernunft in 1897 before his death. Perhaps the greatest tribute that Brahms could pay to Strauss was his remark that he would have given anything to have written The Blue Danube waltz. An anecdote dating around the time Brahms became acquainted with Strauss is that when Strauss's wife Adele asked Brahms to autograph her fan, he wrote a few notes from the "Blue Danube" waltz, and then cheekily inscribed the words "Alas, not by Brahms!"
Brahms was an extreme perfectionist. He destroyed many early works –
including a Violin Sonata he had performed with Reményi and violinist Ferdinand David
– and once claimed to have destroyed 20 string quartets before he
issued his official First in 1873. Over the course of several years, he
changed an original project for a symphony in D minor into his first piano concerto. In another instance of devotion to detail, he labored over the
official First Symphony for almost fifteen years, from about 1861 to
1876. Even after its first few performances, Brahms destroyed the
original slow movement and substituted another before the score was
published. Another factor that contributed to
Brahms's perfectionism was that Schumann
had announced early on that Brahms was to become the next great
composer like Beethoven, a prediction that Brahms was determined to live
up to. This prediction hardly added to the composer's self confidence,
and may have contributed to the delay in producing the First Symphony.
However, Clara Schumann
noted before that Brahms's First Symphony was a product that was not
reflective of Brahms's real nature. She felt that the final exuberant
movement was "too brilliant", as she was encouraged by the dark and
tempestuous opening movement she had seen in an early draft. However,
she recanted in accepting the Second Symphony,
which has often been seen in modern times as one of his sunniest works.
Other contemporaries, however, found the first movement especially
dark, and Reinhold Brinkmann, in a study of Symphony No. 2 in relation to 19th century ideas of melancholy, has published a revealing letter from Brahms to the composer and conductor Vinzenz Lachner
in which Brahms confesses to the melancholic side of his nature and
comments on specific features of the movement that reflect this.

Amilcare Ponchielli (August 31, 1834 – January 16, 1886) was an Italian composer, mainly of operas.
Born in Paderno Fasolaro, now Paderno Ponchielli, near Cremona, Ponchielli won a scholarship at the age of nine to study music at the Milan Conservatory, writing his first symphony by the time he was ten years old.
Two years after leaving the conservatory he wrote his first opera -- it was based on Alessandro Manzoni's great novel The Betrothed (I promessi sposi) -- and it was as an opera composer that he eventually found fame.
His early career was disappointing. He was bypassed out of a good professorship at the Milan Conservatory that he had won in a competition. He was forced to take small-time jobs in smaller cities, and composed many commercially unsuccessful operas. In spite of his disappointment, he gained much experience as the bandmaster (capobanda) in Piacenza and Cremona, arranging and composing over 200 works for a wind band. Notable among his "original" compositions for band are the first ever concerto for euphonium (Concerto per Flicornobasso, 1872), fifteen variations on the Neapolitan song "Carnevale di Venezia" and a series of festive and funeral marches that resound with the pride of the newly unified Italy and the private grief of his fellow Cremonese. The turning point was the big success of the revised version of I promessi sposi in 1872, which brought him a contract with the music publisher G. Ricordi & Co. and the musical establishment at the Conservatory and at La Scala. The ballet Le due gemelle (1873) confirmed his success.
The following opera, I Lituani (The Lithuanians) (1874), was also well received, being performed later at Saint Petersburg (as Aldona - November 20, 1884). His best known opera is La Gioconda, which his librettist Arrigo Boito adapted from the same play by Victor Hugo that had been previously set by Mercadante (Il giuramento, 1837) and Carlos Gomes (Fosca, 1873). It was first produced in 1876 and revised several times. The version that has become so popular today was first given in 1880.
In 1876 he started working on I mori di Valenza (the project dates back to 1873), an opera he never finished, although it was completed later by Arturo Cadore and performed posthumously in 1914.
After La Gioconda, Ponchielli wrote the monumental biblical melodrama in four acts Il figliuol prodigo (Milan, Teatro alla Scala, December 26, 1880) and Marion Delorme, from another play by Victor Hugo (Milan, Teatro alla Scala, March 17, 1885). In spite of their rich musical invention, neither of these operas met with the same success but both exerted great influence on the composers of the rising generation, like Giacomo Puccini, Pietro Mascagni and Umberto Giordano.
In 1881, Ponchielli was appointed maestro di cappella of the Bergamo Cathedral, and from the same year he was a professor of composition at the Milan Conservatory, where among his students were Puccini, Mascagni and Emilio Pizzi.
He died in Milan and was interred there in the Cimitero Monumentale.
Although in his lifetime Ponchielli was very popular and influential, in introducing an enlarged orchestra and more complex orchestration, the only one of his operas regularly performed today is La Gioconda. It contains the great tenor romanza "Cielo e mar", a superb duet for tenor and baritone "Enzo Grimaldo", the soprano set - piece "Suicidio!" and the ballet music "The Dance of the Hours", known even to the non - musical from its use in Walt Disney's Fantasia (1940), Alan Sherman's novelty song, "Hello Muddah, Hello Fadduh", and other popular works.