<Back to Index>
- Engineer Jonas Hesselman, 1877
- Engineer Alan Arnold Griffith, 1893
- Physicist and Inventor Robert Hutchings Goddard, 1882
- Engineer and Physicist Aurel Boleslav Stodola, 1859
PAGE SPONSOR

Jonas Hesselman (1877 – 1957), was a Swedish engineer. He built the first spark ignition engine with direct injection of fuel into the cylinder.
Hesselman worked from 1899 to 1916 for AB Diesel Engines (later Atlas Diesel, now Atlas Copco) in Sickla in Nacka just outside Stockholm, from 1901 as Head of Construction. Here he also developed Rudolf Diesel's engine further and won international recognition as an authority on diesel engines. In 1916 he opened his own factory and in 1925 presented the Hesselman engine, a hybrid between an Otto engine and diesel engine.
Jonas Hesselman also designed electrical vehicle components, among others, the motor that became the basis for Hesselman Elhydraulik, now Haldex Hydraulics. In 1970, Hesselman Elhydraulik developed the hydraulic power unit that still serves as the prototype for the existing lifts for trucks.
He was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1934.

Alan Arnold Griffith (13 June 1893 – 13 Oct 1963) was an English engineer, who, among many other contributions, is best known for his work on stress and fracture in metals that is now known as metal fatigue, as well as being one of the first to develop a strong theoretical basis for the jet engine.
A.A. Griffith took a first in mechanical engineering, followed by a Master’s Degree and a Doctorate from Liverpool University. In 1915 he was accepted by the Royal Aircraft Factory as a trainee, before joining the Physics and Instrument Department the following year in what was now been renamed as the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE).
Some of Griffith's earlier works remain in widespread use today. In 1917 he and G.I. Taylor
suggested the use of soap films as a way of studying stress problems.
Using this method a soap bubble is stretched out between several strings
representing the edges of the object under study, and the coloration of
the film shows the patterns of stress. This method, and similar ones,
were used well into the 1990s when computer power became generally
available that could do the same experiment numerically.
Griffith is more famous for a theoretical study on the nature of stress and failure in metals. At the time it was generally taken that the strength of a material was E/10, where E was the Young's modulus for that material. However it was well known that those materials would often fail at 1000 times less than this predicted value. Griffith discovered that there were many microscopic cracks in every material, and hypothesized that these cracks lowered the overall strength of the material. This was because any void in a solid concentrates stress, a fact already well known to machinists at the time. This concentration would allow the stress to reach E/10 at the head of the crack long before it would seem to for the material as a whole.
From this work Griffith formulated his own theory of brittle fracture, using elastic strain energy concepts. His theory described the behavior of crack propagation of an elliptical nature by considering the energy involved. The equation, Griffith's criterion, basically states that when a crack is able to propagate enough to fracture a material, that the gain in the surface energy is equal to the loss of strain energy, and is considered to be the primary equation to describe brittle fracture. Because the strain energy released is directly proportional to the square of the crack length, it is only when the crack is relatively short that its energy requirement for propagation exceeds the strain energy available to it. Beyond the critical Griffith crack length, the crack becomes dangerous.
The work, published in 1920 ("The phenomenon of rupture and flow in
solids"), resulted in sweeping changes in many industries. Suddenly the
"hardening" of materials due to processes such as cold rolling
were no longer mysterious. Aircraft designers immediately understood
why their designs had failed even though they were built much stronger
than was thought necessary at the time, and soon turned to polishing
their metals in order to remove cracks. The result was a series of
particularly beautiful designs in the 1930s, such as the Boeing 247.
This work was later generalized by G.R. Irwin, in the 1950s, applying it to almost all materials, not just rigid ones.
In 1926 he published a seminal paper, An Aerodynamic Theory of Turbine Design. He demonstrated that the woeful performance of existing turbines was due to a flaw in their design which meant the blades were "flying stalled", and proposed a modern airfoil shape for the blades that would dramatically improve their performance. The paper went on to describe an engine using an axial compressor and two stage turbine, the first stage driving the compressor, the second a power - take - off shaft that would be used to power a propeller. This early design was a forerunner of the turboprop engine. As a result of the paper, the Aeronautical Research Committee supported a small scale experiment with a single stage axial compressor and single stage axial turbine. Work was completed in 1928 with a working testbed design, and from this a series of designs was built to test various concepts.
At about this time Frank Whittle wrote his thesis on turbine engines, using a centrifugal compressor and single stage turbine, the leftover power in the exhaust being used to power the aircraft directly. Whittle sent his paper to the Air Ministry in 1930, who passed it on to Griffith for comment. After pointing out an error in Whittle's calculations, he stated that the large frontal size of the compressor would make it impractical for aircraft use, and that the exhaust itself would provide little thrust. The Air Ministry replied to Whittle saying they were not interested in the design. Whittle was crestfallen, but was convinced by friends in the RAF to pursue the idea anyway. Luckily for all involved, Whittle patented his design in 1930 and was able to start Power Jets in 1935 to develop it.
Griffith went on to become the principal scientific officer in charge of the new Air Ministry Laboratory in South Kensington. There he invented the contraflow gas turbine, which used two sets of compressor disks rotating in opposite directions, one "inside" the other. This is as opposed to the more normal design in which the compressors blow the air against a stator, essentially a non - moving compressor disk. The effect on compression efficiency was noticeable, but so was the effect on complexity of the engine. In 1931 he returned to the RAE to take charge of engine research, but it was not until 1938, when he became head of the Engine Department, that work on developing an axial flow engine actually started. Joined by Hayne Constant, they started work on Griffith's original non - contraflow design, working with steam turbine manufacturer Metropolitan - Vickers (Metrovick).
After a short period Whittle's work at Power Jets started to make major progress and Griffith was forced to re-evaluate his stance on using the jet directly for propulsion. A quick redesign in early 1940 resulted in the Metrovick F.2, which ran for the first time later that year. The F.2 was ready for flight tests in 1943 with a thrust of 2,150 lbf, and flew as replacement engines on a Gloster Meteor, the F.2/40 in November. The smaller engine resulted in a design that looked considerably more like the Me 262, and had improved performance. Nevertheless the engine was considered too complex, and not put into production.
Griffith's original rejection of Whittle's concepts has long been commented on. It certainly set back development of the jet engine in England. His motivations have long been the topic of curiosity, with many people suggesting that his endless quest for perfectionism was the main reason he did not like Whittle's "ugly" little engine, or perhaps the belief that "his" design was innately superior.
Griffith joined Rolls - Royce in 1939, working there until 1960. He
designed the AJ.65 axial turbojet which led to the development of the
Avon engine, the company's first production axial turbojet. He then
turned to the turbofan (known as "bypass" in England) design and was
instrumental in introducing the Rolls - Royce Conway. Griffith carried
out pioneering research into vertical take off and landing (VTOL) technology, culminating in the development of the Rolls - Royce Thrust Measuring Rig.

Robert Hutchings Goddard (October 5, 1882 – August 10, 1945) was an American professor, physicist and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid fueled rocket, which he successfully launched on March 16, 1926. Goddard and his team launched 34 rockets between 1926 and 1941, achieving altitudes as high as 2.6 km (1.6 mi) and speeds as high as 885 km/h (550 mph).
As both theorist and engineer, Goddard's work anticipated many of the developments that made spaceflight possible. Two of Goddard's 214 patents — one for a multi - stage rocket design (1914), and another for a liquid fuel rocket design (1914) — are regarded as important milestones toward spaceflight. His 1919 monograph, A Method of Reaching Extreme Altitudes, is considered one of the classic texts of 20th century rocket science. Goddard successfully applied three - axis control, gyroscopes and steerable thrust to rockets, all of which allow rockets to be controlled effectively in flight.
Goddard received little public support for his research during his lifetime. Though his work in the field was revolutionary, he was sometimes ridiculed in the press for his theories concerning spaceflight. As a result, he became protective of his privacy and his work. Years after his death, at the dawn of the Space Age, he came to be recognized as one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry. He was the first not only to recognize the scientific potential of missiles and space travel but also to bring about the design and construction of the rockets needed to implement those ideas.
Goddard was born in 1882 in Worcester, Massachusetts,
to Nahum Danford Goddard (1859 – 1928) and Fannie Louise Hoyt (1864 –
1920). Robert was their only child to survive; a younger son,
Richard Henry, was born with a spinal deformity, and died before his
first birthday.
With the introduction of electric power in American cities in the 1880s, the young Goddard became interested in science. When his father showed him how to generate static electricity on the family's carpet, the five year old's imagination was inspired. Robert experimented, believing he could jump higher if the zinc in batteries could somehow be charged with static electricity. Goddard halted the experiments after a warning from his mother that if he succeeded, he could "go sailing away and might not be able to come back."
Goddard's father further encouraged Robert's scientific interest by
providing him with a telescope, a microscope, and a subscription to Scientific American.
Robert developed a fascination with flight, first with kites and then
with balloons. He became a thorough diarist and documenter of his work, a
skill that would greatly benefit his later career. These interests
merged at age 16, when Goddard attempted to construct a balloon out of
aluminum, shaping the raw metal in his home workshop. After nearly five
weeks of methodical, documented efforts, he finally abandoned the
project, remarking, "Failior [sic] crowns enterprise." However,
the lesson of this failure did not restrain Goddard's growing
determination and confidence in his work.
He became interested in space when he read H.G. Wells' science fiction classic The War of the Worlds when he was 16 years old. His dedication to pursuing rocketry became fixed on October 19, 1899. The 17 year old Goddard climbed a cherry tree to cut off dead limbs. He was transfixed by the sky, and his imagination grew. He later wrote:
On this day I climbed a tall cherry tree at the back of the barn… and as I looked toward the fields at the east, I imagined how wonderful it would be to make some device which had even the possibility of ascending to Mars, and how it would look on a small scale, if sent up from the meadow at my feet. I have several photographs of the tree, taken since, with the little ladder I made to climb it, leaning against it.
It seemed to me then that a weight whirling around a horizontal shaft, moving more rapidly above than below, could furnish lift by virtue of the greater centrifugal force at the top of the path.
I was a different boy when I descended the tree from when I ascended. Existence at last seemed very purposive.
For the rest of his life he observed October 19 as "Anniversary Day", a private commemoration of the day of his greatest inspiration.
The young Goddard was a thin and frail boy, almost always in fragile
health. He suffered from stomach problems, colds and bronchitis, and
fell two years behind his classmates. He became a voracious reader,
regularly visiting the local public library to borrow books on the
physical sciences.
Goddard's interest in aerodynamics led him to study some of Samuel Langley's scientific papers in the periodical Smithsonian. In these papers, Langley wrote that birds flap their wings with different force on each side to turn in the air. Inspired by these articles, the teenage Goddard watched swallows and chimney swifts from the porch of his home, noting how subtly the birds moved their wings to control their flight. He noted how remarkably the birds controlled their flight with their tail feathers — Goddard called these the birds' equivalent of 'ailerons.' He took exception to some of Langley's conclusions, and in 1901 wrote a letter to St. Nicholas magazine with his own ideas. The editor of St. Nicholas declined to publish Goddard's letter, remarking that birds fly with a certain amount of intelligence and that "machines will not act with such intelligence." Goddard disagreed, believing that a man could control a flying machine with his own intelligence.
Around this time, Goddard read Newton's Principia Mathematica, and found that Newton's Third Law of Motion applied to motion in space. He wrote later about his own tests of the Law:
I began to realize that there might be something after all to Newton's Laws. The Third Law was accordingly tested, both with devices suspended by rubber bands and by devices on floats, in the little brook back of the barn, and the said law was verified conclusively. It made me realize that if a way to navigate space were to be discovered, or invented, it would be the result of a knowledge of physics and mathematics."
As his health improved, Goddard continued his formal schooling as an 18 year old sophomore at South High School in Worcester in 1901. He excelled in his coursework, and his peers twice elected him class president. At his graduation ceremony in 1904, he gave his class oration as valedictorian. In his speech, titled On Taking Things for Granted, Goddard included a section that would become emblematic of his life:
[J]ust as in the sciences we have learned that we are too ignorant safely to pronounce anything impossible, so for the individual, since we cannot know just what are his limitations, we can hardly say with certainty that anything is necessarily within or beyond his grasp. Each must remember that no one can predict to what heights of wealth, fame, or usefulness he may rise until he has honestly endeavored, and he should derive courage from the fact that all sciences have been, at some time, in the same condition as he, and that it has often proved true that the dream of yesterday is the hope of today and the reality of tomorrow.
Goddard enrolled at Worcester Polytechnic Institute in 1904. He quickly impressed the head of the physics department, A. Wilmer Duff, with his thirst for knowledge, and Professor Duff took him on as a laboratory assistant and tutor. At WPI, Goddard joined the Sigma Alpha Epsilon fraternity, and began a long courtship with high school classmate Miriam Olmstead, an honor student who had graduated with Goddard as salutatorian. Eventually, she and Goddard were engaged, but they drifted apart and ended the engagement around 1909.
Goddard received his B.S. degree in physics from Worcester
Polytechnic in 1908, and after serving there for a year as an instructor
in physics, he began his graduate studies at Clark University in
Worcester in the fall of 1909. Goddard received his M.A. degree in physics from Clark University in 1910, and then stayed at Clark to complete his Ph.D. degree in physics in 1911.
He spent another year at Clark as an honorary fellow in physics, and in
1912, he accepted a research fellowship at Princeton University's
Palmer Physical Laboratory.
While still an undergraduate, Goddard wrote a paper proposing a method for "balancing aeroplanes." He submitted the idea to Scientific American, which published the paper in 1907. Goddard later wrote in his diaries that he believed his paper was the first proposal of a way to automatically stabilize aircraft in flight. His proposal came around the same time as other scientists were making breakthroughs in developing functional gyroscopes.
His first writing on the possibility of a liquid fueled rocket came on February 2, 1909.
Goddard had begun to study ways of increasing a rocket's efficiency
using methods differing from conventional, powder rockets. He wrote in
his journal about using liquid hydrogen as a fuel with liquid oxygen as
the oxidizer. He believed a 50 percent efficiency could be achieved with liquid fuel.
In the decades around 1910, radio was a new technology, a fertile field for innovation. In 1911, while working at Clark University, Goddard investigated the effects of radio waves on insulators. In order to generate radio frequency power, he invented a vacuum tube that operated like a cathode ray tube. U.S. Patent 1,159,209 was issued on November 2, 1915. This was the first use of a vacuum tube to amplify a signal, preceding even Lee de Forest's claim.
By 1913 he had in his spare time, using calculus, developed the mathematics which allowed him to calculate the position and velocity of a rocket in vertical flight, given the weight of the rocket and weight of the propellant and the velocity of the exhaust gases. His first goal was to build a sounding rocket with which to study the atmosphere. He was very reluctant to admit that his ultimate goal was in fact to develop a vehicle for flights into space since most scientists, in the United States especially, did not consider such a goal to be a realistic or practical scientific pursuit, and the public was not yet ready to seriously consider such ideas as well.
Unfortunately, in early 1913, Goddard became seriously ill with tuberculosis and had to leave his position at Princeton. He then returned to Worcester, where he began a prolonged process of recovery.
It was during this period of recuperation, however, that Goddard began to produce his most important work. As his symptoms subsided, he allowed himself to work an hour per day with his notes. He began to see the importance of his ideas as intellectual property, and thus began working to secure those ideas. In May 1913, he wrote concerning his first rocket applications. His father brought them to a patent firm in Worcester, who helped him to refine his ideas for patent consideration. Goddard's first patent application was submitted in October 1913.
In 1914, his first two landmark patents were accepted and registered. The first, U.S. Patent 1,102,653, described a multi - stage rocket. The second, U.S. Patent 1,103,503,
described a rocket fueled with gasoline and liquid nitrous oxide. The
two patents would eventually become important milestones in the history
of rocketry.
In the fall of 1914, Goddard's health had improved, and he accepted a part - time position as an instructor and research fellow at Clark University.
His position at Clark allowed him to further his rocketry research. He ordered numerous supplies that could be used to build rocket prototypes for launch, and spent much of 1915 in preparation for his first tests.
Goddard's first test launch of a powder rocket came on an early evening in 1915 following his daytime classes at Clark. The launch was loud and bright enough to arouse the alarm of the campus janitor, and Goddard had to reassure him that his experiments, while being serious study, were also quite harmless. After this incident, Goddard took his experiments inside the physics lab to limit any disturbance.
At the Clark physics lab, Goddard conducted static tests of powder rockets to measure their thrust efficiency. He found his earlier estimates to be verified; powder rockets were only converting about 2 percent of their fuel into thrust. At this point he applied de Laval nozzles, which were generally used with steam turbine engines, and the de Laval nozzles greatly improved thrust efficiency. By mid summer of 1915, Goddard had obtained an average thrust efficiency of 40 percent with nozzle velocities up to 2051 meter per second.
Later that year, Goddard designed an elaborate experiment at the Clark physics lab to prove that a rocket would perform in a vacuum such as that in space. He believed it would, but the other scientists were not convinced. His experiment in fact demonstrated that a rocket's performance was actually decreased under atmospheric pressure.
From 1916 to 1917, Goddard built and tested experimental ion thrusters,
which he thought might be used for propulsion in the near vacuum
conditions of outer space. The small glass engines he built were tested
at atmospheric pressure, where they generated a stream of ionized air.
By 1916, the cost of Goddard's rocket research had become too much for his modest teaching salary to bear. He began to solicit potential sponsors for financial assistance, beginning with the Smithsonian Institution, the National Geographic Society and the Aero Club of America.
In his letter to the Smithsonian in September 1916, Goddard claimed he had achieved a 63% thrust efficiency and a nozzle velocity of almost 2438 meter per second. With these performance standards, he believed a rocket could lift a weight of 0.45 kg to a height of 373 km with an initial launch weight of only 40.64 kg.
The Smithsonian was interested, and asked Goddard to elaborate upon his initial inquiry. Goddard responded with a detailed manuscript he had already prepared, titled A Method of Reaching Extreme Altitudes.
In January 1917, the Smithsonian agreed to provide Goddard with a five year grant totaling 5000 USD. Afterward, Clark was able to contribute 3500 USD and the use of their physics lab to the project. Worcester Polytechnic Institute also allowed him to use its abandoned Magnetics Laboratory on the edge of campus during this time as a safe place for testing.
It wasn't until two years later, at the insistence of Arthur G. Webster, head of Clark's physics department, that Goddard arranged for the Smithsonian to publish his work.
While at Clark University, Goddard did research into solar power
using a dish to concentrate the sun's rays on a machined piece of quartz that was sprayed with mercury
which then heated water and drove a generator at the dish. Goddard
believed his invention had overcome all the obstacles that had
previously defeated other scientists and inventors and had his findings
published in the November 1929 issue of Popular Science.
Not all of Goddard's early work was geared towards space travel. As the United States entered World War I in 1917, the country's universities began to lend their services to the war effort. Goddard believed his rocket research could be applied to many different military applications, including mobile artillery, field weapons and naval torpedoes. He made proposals to the Navy and Army. No record exists of any interest by the Navy to Goddard's inquiry. However, Army Ordnance was quite interested, and Goddard met several times with Army personnel.
During this time, Goddard was also contacted by a civilian industrialist in Worcester about the possibility of manufacturing rockets for the military. However, as the businessman's enthusiasm grew, so did Goddard's suspicion. Talks eventually broke down as Goddard began to fear his work might be appropriated by the business.
Goddard proposed to the Army an idea for a tube rocket launcher as a light infantry weapon. The launcher concept became the precursor to the bazooka. The Rocket - Powered Recoil - free Weapon was the brainchild of Dr. Goddard as a side project (under Army contract) of his work on rocket propulsion. Goddard, during his tenure at Clark University, and working at Mount Wilson Observatory for security reasons, designed a tube fired rocket for military use during World War I. He and his co-worker, Dr. Clarence Hickman, successfully demonstrated his rocket to the U.S. Army Signal Corps at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland, on November 6, 1918 using a music rack for a launch platform, but the Compičgne Armistice was signed only five days later, further development was discontinued as World War I ended.
The delay in the development of the bazooka was as a result of Goddard's serious bout with tuberculosis. Goddard continued to be a part time consultant to the U.S. Government at Indian Head, Maryland, until 1923, but soon turned his focus to other projects involving rocket propulsion.
Later, a former Clark University researcher, Dr. C.N. Hickman,
continued Goddard's work on the bazooka, leading to the weapon used in
World War II and to many other powerful rocket weapons.
In 1919, the Smithsonian Institution published Goddard's groundbreaking work, A Method of Reaching Extreme Altitudes. The report describes Goddard's mathematical theories of rocket flight, his experiments with solid fuel rockets, and the possibilities he saw of exploring the earth's atmosphere and beyond. Along with Konstantin Tsiolkovsky's earlier work, The Exploration of Cosmic Space by Means of Reaction Devices. 1903., Goddard's little book is regarded as one of the pioneering works of the science of rocketry. It was distributed worldwide.
Goddard described extensive experiments with solid fuel rocket engines burning high grade nitrocellulose smokeless powder. A critical breakthrough was the use of the steam turbine nozzle invented by the Swedish inventor Gustaf de Laval. The de Laval nozzle allows the most efficient ("isentropic") conversion of the energy of hot gases into forward motion. By means of this nozzle, Goddard increased the efficiency of his rocket engines from 2 percent to 64 percent and obtained supersonic exhaust speeds of over Mach 7.
Though most of this work dealt with the theoretical and experimental relations between propellant, rocket mass, thrust and velocity, a final section titled Calculation of minimum mass required to raise one pound to an "infinite" altitude discussed the possible uses of rockets, not only to reach the upper atmosphere, but to escape from Earth's gravitation altogether. Included as a thought experiment was the idea of launching a rocket to the moon and igniting a mass of flash powder on its surface, so as to be visible through a telescope. He discussed the matter seriously, down to an estimate of the amount of powder required; Goddard's conclusion was that a rocket with starting mass of 3.21 tons could produce a flash "just visible" from Earth.
Goddard eschewed publicity, because he did not have time to reply to
criticism of his work, and his imaginative ideas about space travel were
shared only with private groups he trusted. He did, though, publish and
talk about the rocket principle and sounding rockets, since these
subjects were not too "far out." In a letter to the Smithsonian dated
March 1920, he discussed: photographing the Moon and planets from
rocket powered flyby probes, sending messages to distant civilizations
on inscribed metal plates, the use of solar energy in space, and the
idea of high velocity ion propulsion. In that same letter, Goddard clearly describes the concept of the ablative heat shield,
suggesting the landing apparatus be covered with "layers of a very
infusible hard substance with layers of a poor heat conductor between"
designed to erode in the same way as the surface of a meteor.
The publication of Goddard's document gained him national attention from U.S. newspapers, most of it negative. Although Goddard's discussion of targeting the moon was only a small part of the work as a whole and was intended as an illustration of the possibilities rather than a declaration of Goddard's intent, the papers sensationalized his ideas to the point of misrepresentation and ridicule. Even the Smithsonian had to abstain from publicity because of the amount of ridiculous correspondence they received from the general public.
On January 12, 1920 a front page story in The New York Times,
"Believes Rocket Can Reach Moon", reported a Smithsonian press release
about a "multiple charge high efficiency rocket." The chief application
seen was "the possibility of sending recording apparatus to moderate and
extreme altitudes within the earth's atmosphere", the advantage over
balloon carried instruments being ease of recovery since "the new rocket
apparatus would go straight up and come straight down." But it also
mentioned a proposal "to [send] to the dark part of the new moon a
sufficiently large amount of the most brilliant flash powder which, in
being ignited on impact, would be plainly visible in a powerful
telescope. This would be the only way of proving that the rocket had
really left the attraction of the earth as the apparatus would never
come back."
On January 13, the day after its front page story about Goddard's rocket, an unsigned New York Times editorial scoffed at the proposal. The article initially expressed skepticism about the prospect of carrying meteorological instruments on a rocket:
It is not obvious, however, that the instruments would return to the point of departure. . . .for parachutes drift just as balloons do. And the rocket, or what was left of it after the last explosion, would need to be aimed with amazing skill, and in a dead calm, to fall on the spot whence it started. But that is a slight inconvenience. . . . though it might be serious enough from the [standpoint] of the always innocent bystander. . . . a few thousand yards from the firing line.
The article pressed further on Goddard's proposal to launch rockets beyond the atmosphere:
[A]fter the rocket quits our air and really starts on its longer journey it will neither be accelerated nor maintained by the explosion of the charges it then might have left. To claim that it would be is to deny a fundamental law of dynamics, and only Dr. Einstein and his chosen dozen, so few and fit, are licensed to do that.
Finally, the Times pounced. It assumed, wrongly, that Goddard's understanding of Newton's laws was flawed:
That Professor Goddard with his "chair" in Clark College and the countenancing of the Smithsonian Institution, does not know the relation of action and reaction, and of the need to have something better than a vacuum against which to react — to say that would be absurd. Of course he only seems to lack the knowledge ladled out daily in high schools.
Unbeknownst to the Times, thrust is possible in a vacuum.
A week after the New York Times editorial, Goddard released a signed statement to the Associated Press, attempting to restore reason to what had become a sensational story:
Too much attention has been concentrated on the proposed flash pow[d]er experiment, and too little on the exploration of the atmosphere. . . . Whatever interesting possibilities there may be of the method that has been proposed, other than the purpose for which it was intended, no one of them could be undertaken without first exploring the atmosphere.
In 1924, Goddard published an article "How my speed rocket can propel itself in vacuum" in Popular Science that explained the physics and gave details of the vacuum experiments he had performed to prove the theory. However, even so, after one of Goddard's experiments in 1929, a local Worcester newspaper carried the mocking headline "Moon rocket misses target by 238,7991⁄2 miles."
As a result of harsh criticism from the media and from other
scientists, and understanding better than most the military applications
for which foreign powers could use this technology, Goddard became
increasingly suspicious of others and often worked alone, which limited
the impact of his work. Another limiting factor was the lack of support
from the American government, military and academia as to the study of
the atmosphere, near space and military applications. As Germany became
ever more war like, he refused to communicate with German rocket
experimenters, though he received more and more correspondence from
them.
Forty - nine years after its editorial mocking Goddard, on July 17, 1969 — the day after the launch of Apollo 11 — The New York Times published a short item under the headline "A Correction." The three paragraph statement summarized its 1920 editorial, and concluded:
Further investigation and experimentation have confirmed the findings of Isaac Newton in the 17th Century and it is now definitely established that a rocket can function in a vacuum as well as in an atmosphere. The Times regrets the error.
Goddard began experimenting with liquid oxygen and liquid fueled rockets in September 1921, and tested the first liquid fueled engine in November 1923. It had a cylindrical combustion chamber, using impinging jets to mix and atomize liquid oxygen and gasoline.
In 1924 – 25, Goddard had problems developing a high pressure piston pump to send fuel to the combustion chamber. He wanted to scale up the experiments, but his funding would not allow such growth. He decided to forgo the pumps and use a system applying back pressure from an inert gas.
On December 6, 1925, he tested the simpler back - pressure system. Goddard conducted a static test on the firing stand at the Clark University physics laboratory. The engine successfully lifted its own weight in a 27 second test in the static rack. It was a major success for Goddard, proving that a liquid fuel rocket was possible. The test moved Goddard an important step closer to launching a rocket with liquid fuel.
Goddard conducted an additional test in December, and two more in
January 1926. After that, Goddard began preparing for a possible launch
of the rocket system.
Goddard launched the first liquid fueled (gasoline and liquid oxygen) rocket on March 16, 1926, in Auburn, Massachusetts. Present at the launch were Goddard's crew chief Henry Sachs, Esther Goddard, and Percy Roope, who was Clark's assistant professor in the physics department. Goddard's diary entry of the event was notable for its understatement:
March 16. Went to Auburn with S[achs] in am. E[sther] and Mr. Roope came out at 1 p.m. Tried rocket at 2.30. It rose 41 feet & went 184 feet, in 2.5 secs., after the lower half of the nozzle burned off. Brought materials to lab. . . .
His diary entry the next day elaborated:
March 17, 1926. The first flight with a rocket using liquid propellants was made yesterday at Aunt Effie's farm in Auburn. . . .
Even though the release was pulled, the rocket did not rise at first, but the flame came out, and there was a steady roar. After a number of seconds it rose, slowly until it cleared the frame, and then at express train speed, curving over to the left, and striking the ice and snow, still going at a rapid rate.
The rocket, which was dubbed "Nell", rose just 41 feet during a 2.5 second flight that ended 184 feet away in a cabbage field, but it was an important demonstration that liquid propellants were possible. The launch site is now a National Historic Landmark, the Goddard Rocket Launching Site.
Viewers familiar with more modern rocket designs may find it
difficult to distinguish the rocket from its launching apparatus in the
well known picture of "Nell". The complete rocket is significantly
taller than Goddard, but does not include the pyramidal support
structure which he is grasping. The rocket's combustion chamber is the
small cylinder at the top; the nozzle
is visible beneath it. The fuel tank, which is also part of the rocket,
is the larger cylinder opposite Goddard's torso. The fuel tank is
directly beneath the nozzle, and is protected from the motor's exhaust
by an asbestos cone. Asbestos - wrapped aluminum tubes connect the motor
to the tanks, providing both support and fuel transport. This layout is
no longer used, since the experiment showed that this was no more stable
than placing the rocket engine at the base. By May, after a series of
modifications to simplify the plumbing, the engine was placed in the now
classic position, at the lower end of the rocket. This was just ten
years after colonel Ivan Platonovich Grave's first launch in 1916
(patent in 1924).
After a launch of one of Goddard's rockets in July 1929 again gained the attention of the newspapers, Charles Lindbergh learned of his work. At the time, Lindbergh had begun to wonder what would become of aviation in the distant future, and had settled on rocket flight as a probable next step. He contacted Goddard in November 1929. The professor met the aviator soon after in Goddard's office at Clark University. Upon meeting Goddard, Lindbergh was immediately impressed by his research, and Goddard was similarly impressed by the flier's interest. He discussed his work openly with Lindbergh, forming an alliance that would last for the rest of his life. This is an example, when many wanted to take advantage of him or deemed him a "nut", of Goddard's complete openness with those who shared his dream and that he felt he could trust.
By late 1929, Goddard had been attracting additional notoriety with
each rocket launch. He was finding it increasingly difficult to conduct
his research without unwanted distractions. Lindbergh discussed finding
additional financing for Goddard's work, and put his famous name to work
for Goddard. Into 1930, Lindbergh made several proposals to industry
and private investors for funding, which proved all but impossible to
find following the recent U.S. stock market crash in October 1929.
In the spring of 1930, Lindbergh finally found an ally in the Guggenheim family. Financier Daniel Guggenheim agreed to fund Goddard's research over the next four years for a total of $100,000 (~$1.7 million today). The Guggenheim family, especially Harry Guggenheim, would continue to support Goddard's work in the years to come. The Goddards soon moved to Roswell, New Mexico.
Because of the military potential of the rocket, Goddard, Lindbergh,
Harry Guggenheim, the Smithsonian Institution and others tried before
World War II to convince the Army and Navy of its value. Goddard's
services were offered, but there was no interest, initially. Two young
imaginative officers eventually got the services to attempt to contract
with Goddard just prior to the war. The Navy beat the Army and secured
his services to build liquid fueled rockets for jet assisted take off of
aircraft. These rockets were the precursors to some of the large rocket
engines that launched the space age.
With new financial backing, Goddard eventually relocated to Roswell, New Mexico, in 1930, where he worked with his team of technicians in near isolation and secrecy for a dozen years. Here they would not endanger anyone, would not be bothered by the curious, and experienced a more moderate climate (which was also better for Goddard's health).
By September 1931, his rockets had the now familiar appearance of a smooth casing and tail fins. He began experimenting with gyroscopic guidance and made an unsuccessful flight test of such a system in April 1932. A gyroscope mounted on gimbals electrically controlled steering vanes in the exhaust, similar to the system used by the German V-2 over 10 years later.
A temporary loss of funding from the Guggenheims forced Goddard to return to Clark University until 1934, when funding resumed. Upon his return to Roswell, he began work on his A series of rockets 4 to 4.5 meters long, powered by gasoline and liquid oxygen pressurized with nitrogen. The gyroscopic control system was housed in the middle of the rocket, between the propellant tanks. On March 28, 1935, the A-5 successfully flew to an altitude of 1.46 kilometers (0.91 mi; 4,800 ft) using his guidance system. This rocket also achieved supersonic velocity.
In 1936 – 1939, Goddard began work on the K and L series rockets, which were much more massive and designed to reach very high altitude. This work was plagued by trouble with engine burn through. Goddard had built a regeneratively cooled engine, which circulated liquid oxygen around the outside of the combustion chamber, in 1923 but deemed the idea too complicated. He was therefore using fuel curtain cooling, spraying excess gasoline on the inside wall of the combustion chamber, but this was not working well, and the larger rockets failed. Returning to a smaller design again, the L-13 reached an altitude of 2.7 kilometers (1.7 mi; 8,900 ft), the highest of any of Goddard's rockets. Weight was reduced by using thin walled fuel tanks wound with high tensile strength wire.
From 1940 to 1941, work was done on the P series of rockets, which used propellant turbopumps (also powered by gasoline and liquid oxygen). Higher fuel pressure permitted a more powerful engine, but two launches both ended in crashes after reaching an altitude of only a few hundred feet. The turbopumps worked well, however.
Goddard was able to flight test many of his rockets; but many
resulted in what the uninitiated would call failures because of engine
malfunction or loss of control. Goddard did not consider them failures
because he felt that he always learned something from a test. Most of
his work involved static tests, which are a standard procedure today,
before a flight test. Between 1930 and 1945, the following 31 rockets
were launched:
As an instrument for "reaching extreme altitudes", Goddard's rockets were not very successful; they did not achieve an altitude greater than 2.7 km (in 1937), at a time when airplanes could reach up to 15 km and balloons 22 km. By contrast, German rocket scientists had already achieved an altitude of 3.5 km with the A-2 rocket (in 1934), reached 12 km by 1939 with the A-5 and 84 km in 1942 with the A-4 (V-2), reaching the outer limits of the atmosphere.
Goddard's pace was slower than the Germans' because he did not have the resources they did. But he was trying to perfect his rocket and the subsystems such as guidance and control so that it could achieve high altitudes without tumbling in the rare atmosphere and provide a stable vehicle for the experiments it would eventually carry. He was on the verge of building larger rockets to reach "extreme altitudes" when World War II intervened and changed the path of American history.
Though Goddard brought his work in rocketry to the attention of the United States Army, he was rebuffed, since the Army largely failed to grasp the military application of large rockets.
German military intelligence had once paid attention to Goddard's work. An accredited military attaché to the US, Friedrich von Boetticher, sent a four page report in 1936, and the spy Gustav Guellich sent a mixture of facts and made-up information, claiming to have visited Roswell and witnessed a launch. But thereafter the Germans received very little information about Goddard.
The Soviet NKVD
had a spy in the U.S. Navy Bureau of Aeronautics. In 1935 she gave them
a report Goddard had written for the Navy in 1933. It contained results
of tests and flights and suggestions for military uses of his rockets.
The NKVD considered this to be very valuable information. It provided
few design details, but gave the Soviets the direction and progress of
Goddard's work.
A frequently repeated story, launched by Goddard himself, declared that at the end of World War II Goddard saw the remnants of the German V-2 ballistic missile and was convinced that the Germans had stolen his work. Although Goddard did study a V-2, there is confusion as to how it was obtained and also just how influential Goddard had been on its design.
In the spring of 1945 Goddard saw a captured German V-2 ballistic missile which had been sent to the naval laboratory in Annapolis, Maryland, where Goddard had been working under contract. It is not out of the question that parts were dispatched to Goddard in Annapolis, but there would not have been much time: Goddard died of throat cancer in August 1945.
One opinion, described in the May 1959 issue of Popular Science would have it that the V-2 which he inspected was wreckage retrieved from a test flight that had crashed in Sweden (the so-called Bäckebo Bomb). This wreckage had been analyzed and reconstructed by British (not US) engineers at Farnborough from July 1944 as part of Project Big Ben.
Another view is that this was not the wreckage from Sweden, but an unlaunched rocket that had been captured by the US Army from the Mittelwerk factory in the Harz mountains. Samples captured here were first shipped back by Special Mission V-2 on 22 May 1945.
After a thorough inspection Goddard was convinced that the Germans had "stolen" his work. Though the design details were not the same, the basic design of the V-2 was similar to one of Goddard's rockets. The V-2, however, was technically far more advanced than the most successful of the rockets designed and tested by Goddard. The Peenemünde rocket group led by Wernher von Braun may have benefited from the pre 1939 contacts to a limited extent, but had also started from the work of their own space pioneer, Hermann Oberth; they also had the benefit of intensive state funding as a war project, large scale production facilities (using slave labor), and repeated flight testing that allowed them to refine their designs. Nonetheless, in 1963, von Braun, reflecting on the history of rocketry, said of Goddard: "His rockets... may have been rather crude by present day standards, but they blazed the trail and incorporated many features used in our most modern rockets and space vehicles".
The official U.S. history comments that three features developed by
Goddard earlier appeared in the V-2: (1) Pumps were used to inject fuel
into the combustion chamber. (2) Gyroscopically controlled vanes in the
nozzle stabilized the rocket until external vanes in air could do so. (3)
Excess alcohol was fed in so that a blanket of gas protected the motor
from the combustion heat.
Goddard avoided sharing details of his work with other scientists, and preferred to work alone with his technicians. Frank Malina, who was then studying rocketry at the California Institute of Technology, visited Goddard in August 1936. Goddard refused to discuss any of his research, other than that which had already been published in Liquid - Propellant Rocket Development. Theodore von Kármán, Malina's mentor at the time, was unhappy with Goddard's attitude and later wrote, "Naturally we at Caltech wanted as much information as we could get from Goddard for our mutual benefit. But Goddard believed in secrecy.... The trouble with secrecy is that one can easily go in the wrong direction and never know it." Goddard's concerns about secrecy led to criticism for failure to cooperate with other scientists and engineers.
By 1939, von Kármán's Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory at Caltech had received Army Air Corps funding to develop rockets to assist in aircraft take off. Goddard learned of this in 1940, and openly expressed his displeasure. Malina could not understand why the Army did not arrange for an exchange of information between Goddard and Caltech, since both were under government contract at the same time. Goddard did not think he could be of that much help to Caltech because they were designing rockets with solid fuel and Goddard was using liquid fuels.
Goddard was concerned with avoiding the public criticism and ridicule he had faced in the 1920s, which he believed had harmed his professional reputation. Goddard also lacked interest in discussions with people who had less understanding of rocketry than he did, feeling that his time was extremely constrained. Goddard's health was frequently poor, as a result of his earlier bout of tuberculosis, and he was uncertain about how long he had to live. He felt, therefore, that he hadn't the time to spare arguing with other scientists and the press about his new field of research or helping all the amateur rocketeers who wrote to him.
Goddard spoke to professional groups, published articles and papers and patented his ideas; but while he discussed basic principles, he was unwilling to reveal the details of his designs until he had flown rockets to high altitudes and thus proven his theory. Goddard tended to avoid any mention of space flight, and spoke only of high altitude research, since he believed that other scientists regarded the subject as unscientific.
During the First and Second World Wars, Goddard offered his services, patents and technology to the military and made some significant contributions. Several young Army officers and some higher ranking ones believed Goddard's research was important, but were unable to generate funds for his work.
Toward the end of his life, Goddard, realizing he was no longer going to be able to make significant progress alone in his field, joined the American Rocket Society, became a director, and made plans to work in the budding aerospace industry.
Goddard was diagnosed with throat cancer in 1945, and died in August of that year in Baltimore, Maryland. He was buried in Hope Cemetery in his home town of Worcester, Massachusetts.
The Guggenheim Foundation and Goddard's estate filed suit in 1951 against the U.S. government for prior infringement of Goddard's work. In 1960, the parties settled the suit, and the U.S. armed forces and NASA paid out an award of $1 million (half went to his wife), at that time the highest government settlement ever paid in a patent case.
The settlement amount was more than the total of all the grants disbursed for Goddard's work over his career.
Goddard was credited with 214 patents for his work; 131 of these were awarded after his death.
The Goddard Space Flight Center, a NASA facility in Maryland, was established in 1959. The crater Goddard on the Moon is also named in his honor.
On September 16, 1959, the U.S. Congress authorized the issuance of a
gold medal in the honor of Professor Robert H. Goddard. The Dr. Robert
H. Goddard Collection and the Robert Goddard
Exhibition Room are housed in the Archives and Special Collections area
of Clark University's Robert H. Goddard Library. Outside the library
lies a structure depicting the flight path of Goddard's first liquid
fuel rocket. The Chemical Engineering department at Worcester
Polytechnic Institute is housed in Goddard Hall. Goddard's home town of
Worcester established the Goddard School of Science and Technology, an
elementary school, in 1992. Robert H. Goddard High School was completed
in 1965 in Roswell, New Mexico, and dedicated by Esther Goddard; the
school's mascot is appropriately titled "Rockets". The Civil Air Patrol
Cadet Program Goddard Achievement, corresponding to promotion to Cadet
Chief Master Sergeant is named for him. A small memorial with a statue
of Goddard is located at the site
where Goddard launched the first liquid propelled rocket, now the
Pakachoag golf course in Auburn, Massachusetts. Goddard Auditorium is
located on the Earlham College campus in Richmond, Indiana. The problem
of optimizing the altitude of a rocket under atmospheric drag and
gravity is referred to as the Goddard problem. Release 13 of the Linux
distribution Fedora is named after Goddard.
Goddard is also mentioned in the last episode of the TV series Fullmetal Alchemist. The protagonist, Edward Elric, shows interest in rocketry after reading Goddard's "A Method of Reaching Extreme Altitudes" and decides to study rocketry with Hermann Oberth. Jimmy Neutron has a robotic dog made of circuits, sprockets and several different widgets, and is named after Goddard. The television series "Star Trek: The Next Generation" had a shuttlecraft named after Goddard.
On June 21, 1924, Goddard married Esther Christine Kisk (March 31, 1901 – June 4, 1982),
a secretary in Clark University's President's office, whom he met in
1919. She had photographed some of his work as well as aided him in his
experiments and paperwork, including accounting. After his death, she
sorted out Goddard's papers and secured 131 additional patents on his
work. The couple did not have children.
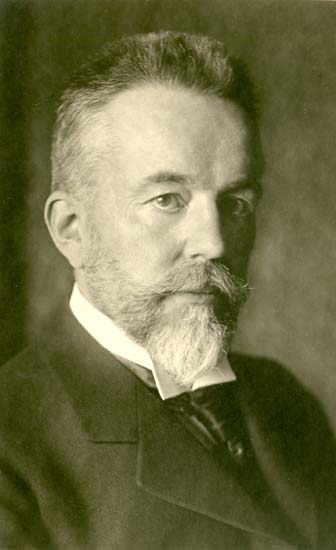
Aurel Boleslav Stodola (10 May 1859 Liptovský Mikuláš, Austro - Hungarian Empire - 25 December 1942 Zürich, Switzerland) was an engineer, physicist, and inventor. He was an ethnic Slovak. He was a pioneer in the area of technical thermodynamics and its applications and published his book Die Dampfturbine (the steam turbine) in 1903. In addition to the thermodynamic issues involved in turbine design the book discussed aspects of fluid flow, vibration, stress analysis of plates, shells and rotating discs and stress concentrations at holes and fillets. Stodola was a professor of mechanical engineering at the Swiss Polytechnical Institute (now ETH) in Zurich. One of his students was Albert Einstein. In 1892, Stodola founded the Laboratory for Energy Conversion.
Stodola's book Steam and Gas Turbines was cited by Soviet rocket scientist Fridrikh Tsander in the 1920s. Published in English in 1927 and reprinted many times up to 1945, it was a basic reference for engineers working on the first generation of jet propulsion engines in the United States. Stodola worked closely with industries on the development of the first practical gas turbines, in particular Brown, Boveri & Cie, who built the first gas turbine powered electric generator in 1939.
In 1915 - 1916 Stodola collaborated with Ferdinand Sauerbruch, a German surgeon, to develop an advanced mechanically driven prosthetic arm. This collaboration marked one of the first documented examples of a surgeon and engineer merging efforts. Sauerbruch said, “Henceforth, surgeon, physiologist and technician (prosthetist / engineer) will have to work together.”