<Back to Index>
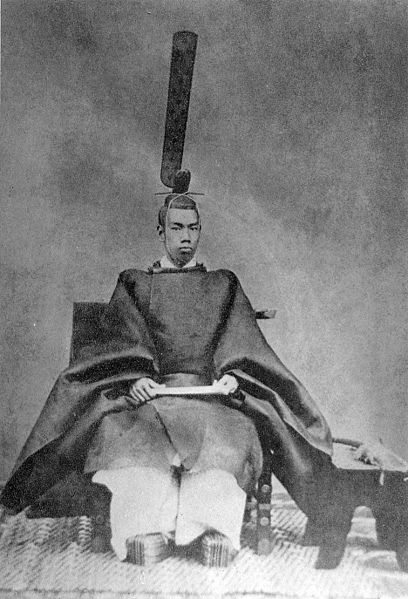
- Emperor of Japan Meiji, 1852
PAGE SPONSOR
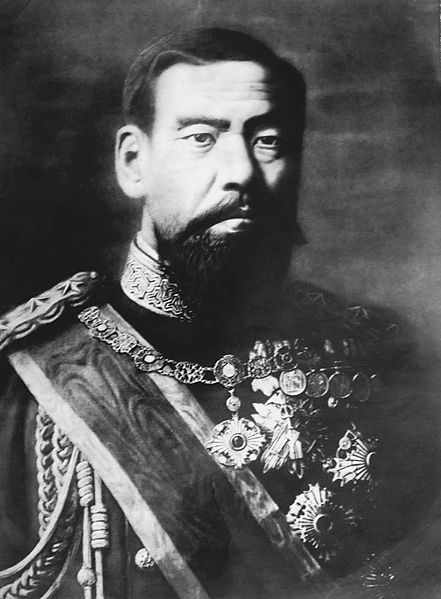
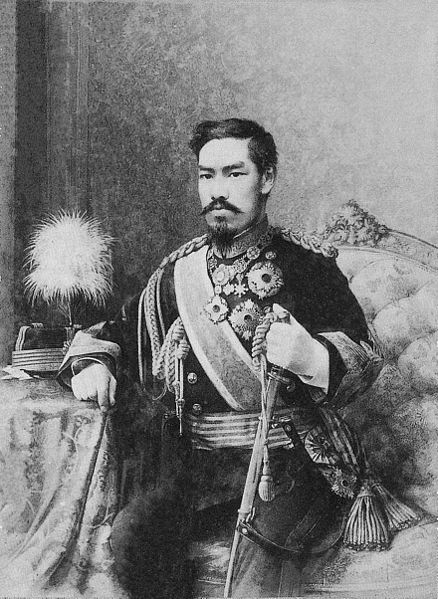
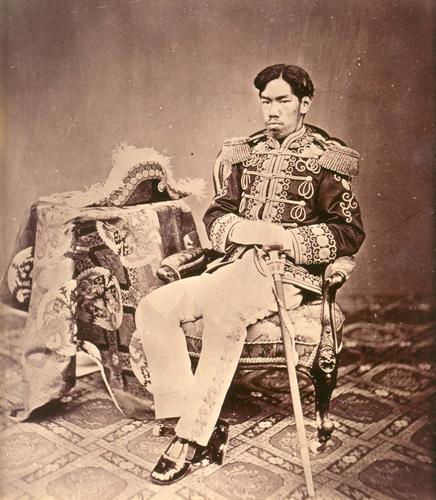



Emperor Meiji (明治天皇 Meiji - tennō) (3 November 1852 30 July 1912), or Meiji the Great (明治大帝 Meiji - taitei), was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession, reigning from 3 February 1867 until his death. He presided over a time of rapid change in Japan, as the nation rose from a feudal shogunate to become a world power.
His personal name was Mutsuhito (睦仁), and although outside of Japan he is sometimes called by this name or Emperor Mutsuhito, in Japan deceased emperors are referred to only by their posthumous names.
At the time of his birth in 1852, Japan was an isolated, pre-industrial, feudal country, dominated by the Tokugawa Shogunate and the daimyo, who ruled over the country's more than 250 decentralized domains. By the time of his death in 1912, Japan had undergone a political, social and industrial revolution at home (Meiji Restoration) and emerged as one of the great powers on the world stage.
A detailed account of the state funeral in the New York Times concluded with an observation: "The contrast between that which preceded the funeral car and that which followed it was striking indeed. Before it went old Japan; after it came new Japan."
The Tokugawa Shogunate had established itself in the early 17th century. Under its rule, the shogun governed Japan. About 180 lords, known as daimyo, ruled autonomous realms under the shogun, who occasionally called upon the daimyo for gifts, but did not tax them. The shogun controlled the daimyo in other ways; only the shogun could approve their marriages, and the shogun could divest a daimyo of his lands.
In 1615, the first Tokugawa shogun, Tokugawa Ieyasu, who had officially retired from his position, and his son Tokugawa Hidetada, the titular shogun, issued a code of behavior for the nobility. Under it, the emperor was required to devote his time to scholarship and the arts. The emperors under the shogunate appear to have closely adhered to this code, studying Confucian classics and devoting time to poetry and calligraphy. They were only taught the rudiments of Japanese and Chinese history and geography. The shogun did not seek the consent or advice of the emperor for his actions.
Emperors almost never left their palace compound, or Gosho in Kyoto, except after an emperor retired or to take shelter in a temple if the palace caught on fire. Few emperors lived long enough to retire; of the Emperor Meiji's five predecessors, only his grandfather lived into his forties, and died aged forty - six. The imperial family suffered very high rates of infant mortality; all five of the emperor's brothers and sisters died as infants, and only five of fifteen of his own children would reach adulthood.
Soon after taking control in the early seventeenth century, shogunate officials (known generically as bakufu) ended much Western trade with Japan, and barred missionaries from the islands. Only the Dutch continued trade with Japan, maintaining a post on the island of Dejima by Nagasaki. However, by the early 19th century, European and American vessels appeared in the waters around Japan with increasing frequency.
Mutsuhito was born on 3 November 1852 in a small house on his maternal grandfather's property at the north end of the Gosho. At the time, a birth was believed to be polluting, and so imperial princes were not born in the Palace, but usually in a structure, often temporary, near the pregnant woman's father's house. The boy's mother, Nakayama Yoshiko was a concubine (gon no tenji) to the Emperor Kōmei and the daughter of the acting major counselor, Nakayama Tadayasu. The young prince was given the name Sachinomiya, or Prince Sachi.
The young prince was born at a time of change for Japan. This change was symbolized dramatically when Commodore Matthew Perry and his squadron of what the Japanese dubbed "the Black Ships", sailed into the harbor at Edo (known since 1868 as Tokyo) in July 1853. Perry sought to open Japan to trade, and warned the Japanese of military consequences if they did not agree. During the crisis brought on by Perry's arrival, the bakufu took the highly unusual step of consulting with the Imperial Court, and the Emperor Kōmei's officials advised that they felt the Americans should be allowed to trade and asked that they be informed in advance of any steps to be taken upon Perry's return. This request was initially honored by the bakufu, and for the first time in at least 250 years, they consulted with the Imperial Court before making a decision. Feeling that it could not win a war, the Japanese government allowed trade and submitted to what it dubbed the "Unequal Treaties", giving up tariff authority and the right to try foreigners in its own courts. The bakufu willingness to consult with the Court was short lived: in 1858, word of a treaty arrived with a letter stating that due to shortness of time, it had not been possible to consult. The Emperor Kōmei was so incensed that he threatened to abdicate though even this action would have required the consent of the Shogun.
Much of the Emperor's boyhood is known only through later accounts, which his biographer, Donald Keene, points out are often contradictory. One contemporary described the young prince as healthy and strong, somewhat of a bully and exceptionally talented at sumo. Another states that the prince was delicate and often ill. Some biographers state that he fainted when he first heard gunfire, while others deny this account. On 16 August 1860, Sachinomiya was proclaimed as prince of the blood and heir to the throne, and was formally adopted by his father's consort. Later that year on 11 November, he was proclaimed as the crown prince and given an adult name, Mutsuhito. The prince began his education at the age of seven. He proved an indifferent student, and later in life wrote poems regretting that he had not applied himself more in writing practice.
By the early 1860s, the shogunate was under several threats. Representatives of foreign powers sought to increase their influence in Japan. Many daimyo were increasingly dissatisfied with bakufu handling foreign affairs. Large numbers of young samurai, known as shishi or "men of high purpose" began to meet and speak against the shogunate. The shishi revered the Emperor Kōmei and favored direct violent action to cure societal ills. While they initially desired the death or expulsion of all foreigners, the shishi would later prove more pragmatic, and begin to advocate the modernization of the country. The bakufu enacted several measures to appease the various groups, and hoped to drive a wedge between the shishi and daimyo.
Kyoto was a major center for the shishi, who had influence over the Emperor Kōmei. In 1863, they persuaded him to issue an "Order to expel barbarians". The Order placed the shogunate in a difficult position, since it knew it lacked the power to carry it out. Several attacks were made on foreigners or their ships, and foreign forces retaliated. Bakufu forces were able to drive most of the shishi out of Kyoto, and an attempt by them to return in 1864 was driven back. Nevertheless, unrest continued throughout Japan.
The prince's awareness of the political turmoil is uncertain. During this time, he studied tanka poetry, first with his father, then with the court poets. As the prince continued his classical education in 1866, a new shogun, Tokugawa Yoshinobu took office, a reformer who desired to transform Japan into a Western style state. Yoshinobu, who would prove to be the final shogun, met with resistance from among the bakufu, even as unrest and military actions continued. In mid 1866, a bakufu army set forth to punish rebels in southern Japan. The army was defeated.
The Emperor Kōmei had always enjoyed excellent health, and was only 36 years old in January 1867. In that month, however, he fell seriously ill. Though he appeared to make some recovery, he suddenly worsened and died on 30 January. Many historians believe the Emperor Kōmei was poisoned, a view not unknown at the time: British diplomat Sir Ernest Satow wrote, "it is impossible to deny that [the Emperor Kōmei's] disappearance from the political scene, leaving as his successor a boy of fifteen or sixteen [actually fourteen], was most opportune".
The crown prince formally ascended to the throne on 3 February 1867, in a brief ceremony in Kyoto. The new Emperor continued his classical education, which did not include matters of politics. In the meantime, the shogun, Yoshinobu, struggled to maintain power. He repeatedly asked for the Emperor's confirmation of his actions, which he eventually received, but there is no indication that the young Emperor was himself involved in the decisions. The shishi and other rebels continued to shape their vision of the new Japan, and while they revered the Emperor, they had no thought of having him play an active part in the political process.
The political struggle reached its climax in late 1867. In November, an agreement was reached by which Yoshinobu would maintain his title and some of his power, but the lawmaking power would be vested in a bicameral legislature on the British model. The following month, the agreement fell apart as the rebels marched on Kyoto, taking control of the Imperial Palace. On 4 January 1868, the Emperor ceremoniously read out a document before the court proclaiming the "restoration" of Imperial rule, and the following month, documents were sent to foreign powers:
The Emperor of Japan announces to the sovereigns of all foreign countries and to their subjects that permission has been granted to the Shogun Tokugawa Yoshinobu to return the governing power in accordance with his own request. We shall henceforward exercise supreme authority in all the internal and external affairs of the country. Consequently the title of Emperor must be substituted for that of Tycoon, in which the treaties have been made. Officers are being appointed by us to the conduct of foreign affairs. It is desirable that the representatives of the treaty powers recognize this announcement.
Mutsuhito
Yoshinobu resisted only briefly, but it was not until late 1869 that the final bakufu holdouts were finally defeated. In the ninth month of the following year, the era was changed to Meiji, or enlightened rule, which was later used for the emperor's posthumous name. This marked the beginning of the custom of an era coinciding with an emperor's reign, and posthumously naming the emperor after the era during which he ruled.
Soon after his accession, the Emperor's officials presented Ichijō Haruko to him as a possible bride. The future Empress was the daughter of an Imperial official, and was three years older than the groom, who would have to wait to wed until after his gembuku (manhood ceremony). The two married on 11 January 1869. Known posthumously as Empress Shōken, she was the first Imperial Consort to receive the title of kōgō (literally, the Emperor's wife, translated as Empress Consort), in several hundred years. Although she was the first Japanese Empress Consort to play a public role, she bore no children. However, the Meiji emperor had fifteen children by five official ladies - in - waiting. Only five of his children, a prince born to Lady Naruko (1855 1943), the daughter of Yanagiwara Mitsunaru, and four princesses born to Lady Sachiko (1867 1947), the eldest daughter of Count Sono Motosachi, lived to adulthood. They were:
- Crown Prince Yoshihito (Haru no miya Yoshihito Shinnō), 3rd son, (31 August 1879 25 December 1926) (Emperor Taishō).
- Princess Masako (Tsune - no - miya Masako Naishinnō), 6th daughter, (30 September 1888 8 March 1940), titled Tsune - no - miya (Princess Tsune) until marriage; m. at Imperial Palace, Tokyo, 30 April 1908 to Prince Takeda Tsunehisa (Takeda - no - miya Tsunehisa ō, 22 September 1882 23 April 1919), and had issue (offspring).
- Princess Fusako (Kane - no - miya Fusako Naishinnō), 7th daughter, (28 January 1890 11 August 1974), titled Kane - no - miya (Princess Kane) until marriage; m. at Imperial Palace, Tokyo 29 April 1909 to Prince Kitashirakawa Naruhisa (Kitashirakawa - no - miya Naruhisa ō, 1 April 1887 2 April 1923), and had issue.
- Princess Nobuko (Fumi - no - miya Nobuko Naishinnō), 8th daughter, (7 August 1891 3 November 1933); titled Fumi - no - miya (Princess Fumi) until marriage; m. at Imperial Palace, Tokyo 6 May 1909 to Prince Asaka Yasuhiko (Asaka - no - miya Yasuhiko ō, 2 October 1887 13 April 1981), and had issue.
- Princess Toshiko (Yasu - no - miya Toshiko Naishinnō), 9th daughter, (11 May 1896 5 March 1978); titled Yasu - no - miya (Princess Yasu) until marriage; m. at Imperial Palace, Tokyo 18 May 1915 to Prince Higashikuni Naruhiko (Higashikuni - no - miya Naruhiko τ, 3 December 1887 20 January 1990), and had issue.
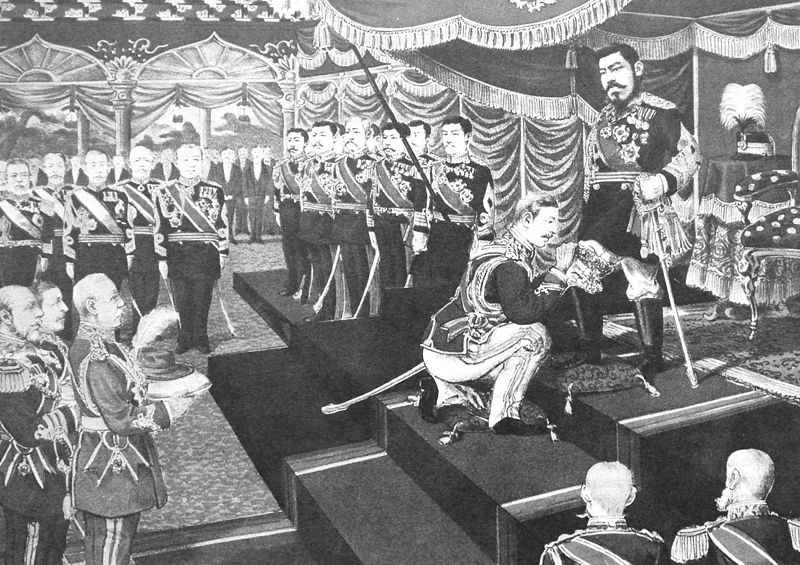
On 19 September 1868, the Emperor announced that the name of the city of Edo was being changed to Tokyo, or "eastern capital". He was formally crowned in Kyoto on 15 October (a ceremony which had been postponed from the previous year due to the unrest). Shortly before the coronation, he announced that the new era, or nengō, would be called Meiji or "enlightened rule". Heretofore the nengō had often been changed multiple times in an emperor's reign; from now on, it was announced, there would only be one nengō per reign.
Soon after his coronation, the Emperor journeyed to Tokyo by road, visiting it for the first time. He arrived in late November, and began an extended stay by distributing sake among the population. The population of Tokyo was eager for an Imperial visit; it had been the site of the Shogun's court and the population feared that with the abolition of the shogunate, the city might fall into decline. It would not be until 1889 that a final decision was made to move the capital to Tokyo. While in Tokyo, the Emperor boarded a Japanese naval vessel for the first time, and the following day gave instructions for studies to see how Japan's navy could be strengthened. Soon after his return to Kyoto, a rescript was issued in the Emperor's name (but most likely written by court officials). It indicated his intent to be involved in government affairs, and indeed he attended cabinet meetings and innumerable other government functions, though rarely speaking, almost until the day of his death.
The successful revolutionaries organized themselves into a Council of State, and subsequently into a system where three main ministers led the government. This structure would last until the establishment of a prime minister, who would lead a cabinet in the western fashion, in 1885. Initially, not even the retention of the emperor was certain; revolutionary leader Gotō Shōjirō later stated that some officials "were afraid the extremists might go further and abolish the Mikado".
Japan's new leaders sought to reform the patchwork system of domains governed by the daimyo. In 1869, several of the daimyo who had supported the revolution gave their lands to the Emperor and were reappointed as governors, with considerable salaries. By the following year, all other daimyo had followed suit.
In 1871, the Emperor announced that domains were entirely abolished, as Japan was organized into 72 prefectures. The daimyo were compensated with annual salaries equal to ten percent of their former revenues (from which they did not now have to deduct the cost of governing), but were required to move to the new capital, Tokyo. Most retired from politics.
The new administration gradually abolished most privileges of the samurai, including their right to a stipend from the government. However, unlike the daimyo, many samurai suffered financially from this change. Most other class based distinctions were abolished. Legalized discrimination against the burakumin ended. However, these classes continue to suffer discrimination in Japan to the present time.
Although a parliament was formed, it had no real power, and neither did the emperor. Power had passed from the Tokugawa into the hands of those Daimyo and other samurai who had led the Restoration. Japan was thus controlled by the Genro, an oligarchy, which comprised the most powerful men of the military, political and economic spheres. The emperor, if nothing else, showed greater political longevity than his recent predecessors, as he was the first Japanese monarch to remain on the throne past the age of 50 since the abdication of Emperor Ōgimachi in 1586.
The Japanese take pride in the Meiji Restoration, as it and the accompanying industrialization allowed Japan to become the preeminent power in the Pacific and a major player in the world within a generation. Yet, the Meiji emperor's role in the Restoration remains debatable. He certainly did not control Japan, but how much influence he wielded is unknown. It is unlikely it will ever be clear whether he supported the Sino - Japanese War (1894 1895) or the Russo - Japanese War (1904 1905). One of the few windows we have into the Emperor's own feelings is his poetry, which seems to indicate a pacifist streak, or at least a man who wished war could be avoided. He composed the following pacifist poem or tanka:
- よもの海
- みなはらからと思ふ世に
- など波風のたちさわぐらむ
- Yomo no umi
- mina harakara to omofu yo ni
- nado namikaze no tachi sawaguramu
- The seas of the four directions
- all are born of one womb:
- why, then, do the wind and waves rise in discord?
Near the end of his life several anarchists, including Kotoku Shusui, were executed (1911) on charges of having conspired to murder the sovereign. This conspiracy was known as the High Treason Incident (1910).
Emperor Meiji, suffering from diabetes, nephritis and gastroenteritis, died of uremia. Although the official announcement said he died at 00:42 on 30 July 1912, the actual death was at 22:40 on 29 July.
The Meiji era ushered in many far reaching changes to the ancient feudal society of Japan. A timeline of major events might include:
- 3 November 1852: the Meiji emperor (then known as Sachinomiya) is born to the imperial concubine Nakayama Yoshiko and Emperor Komei.
- 1853: A fleet of ships headed by Commodore Matthew Perry arrives in Japan on 8 July; considered by German Japanologist Johannes Justus Rein and described by Francis L. Hawks and Commodore Matthew Perry in their 1856 work, Narrative of the Expedition of an American Squadron to the China Seas and Japan Performed in the Years 1852, 1853 and 1854 under the Command of Commodore M.C. Perry, United States Navy., as the "Opening" of Japan. Death of the Shogun.
- 1854 55: Treaties are signed with the United States by the Bakufu.
- late 1850s 1860s: The "Sonnō jōi" movement is in full force.
- 1858: The Bakufu sign treaties with the Netherlands, Imperial Russia and Great Britain.
- March 1860: The Tairo, Ii Naosuke, is assassinated.
- 11 November: Sachinomiya is formally proclaimed Crown Prince and given the personal name Mutsuhito.
- 1862: Namamugi Incident.
- 1864 65: Bombardment of Shimonoseki by British, American, French and Dutch ships; fighting ensues between the shogunate and Chōshū.
- 1866: Death of the Shogun Tokugawa Iemochi on 29 August; appointment of Tokugawa Yoshinobu as Shogun.
- 31 January 1867: Death of Emperor Komei from hemorrhagic smallpox, unofficial accession of Mutsuhito to the throne.
- 4 January 1868: Formal restoration of imperial rule; end of 265 years of rule by the Tokugawa Shogunate.
- 12 September: Formal coronation of the emperor Meiji.
- 23 October: The nengo is changed to the first year of Meiji.
- 6 November: The capital is moved from Kyoto to Edo, renamed Tokyo.
- 5 November 1872: Emperor Meiji Receives The Grand Duke Alexei Alexandrovich of Russia.
- late 1860s 1881: Period of rebellion and assassination in Japan.
- 11 January 1869: Marriage of Meiji to Ichijo Haruko, thenceforth the Empress Shoken.
- 4 September: Meiji receives The Duke of Edinburgh.
- 1871: The abolition of the han domains is proclaimed.
- 1873: Edo castle is destroyed in a conflagration; the emperor moves to the Akasaka Palace. Meiji's first children are born, but die at birth.
- 1877: The Satsuma Rebellion.
- 1878: Assassination of Okubo Toshimichi.
- 31 August 1879: Prince Yoshihito, the future Taisho Tenno and Meiji's only surviving son, is born.
- 1881: Receives the first state visit of a foreign monarch, King Kalakaua of Hawaii.
- 1889: Meiji Constitution promulgated; Ito Hirobumi becomes first Prime Minister of Japan.
- 1894: Sino - Japanese War; Japanese victory establishes Japan as a regional power.
- 1904 1905: Russo - Japanese War; Japanese victory earns Japan the status of a great power.
- 1910: The Annexation of Korea by the Empire of Japan.
- 1912: The emperor dies.