<Back to Index>
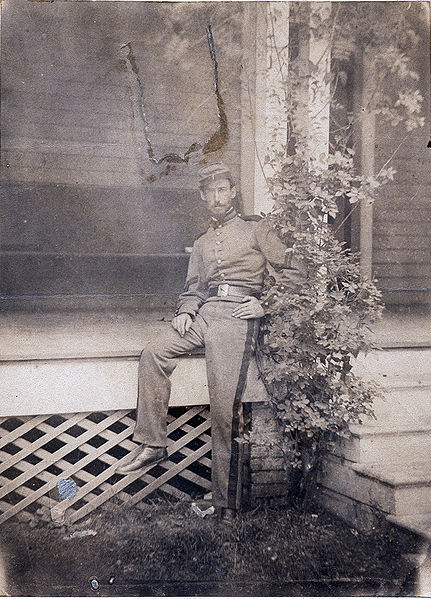
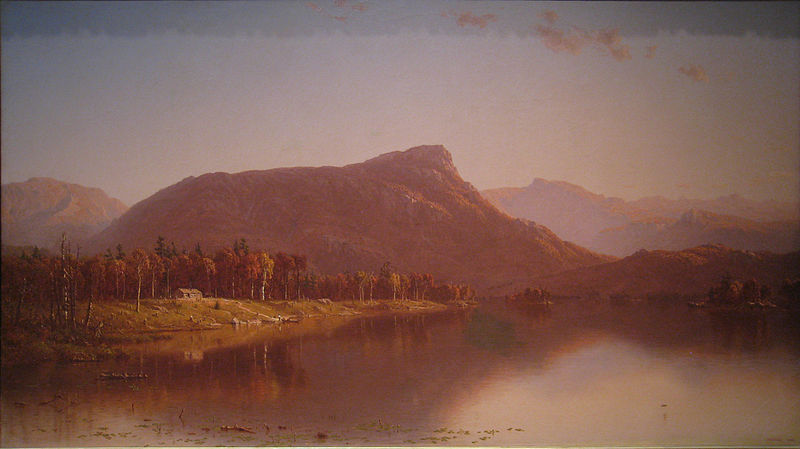
- Painter Sanford Robinson Gifford, 1823
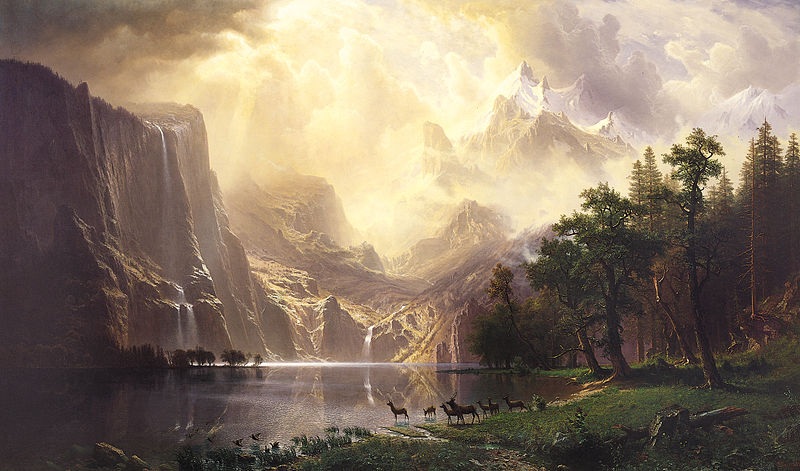
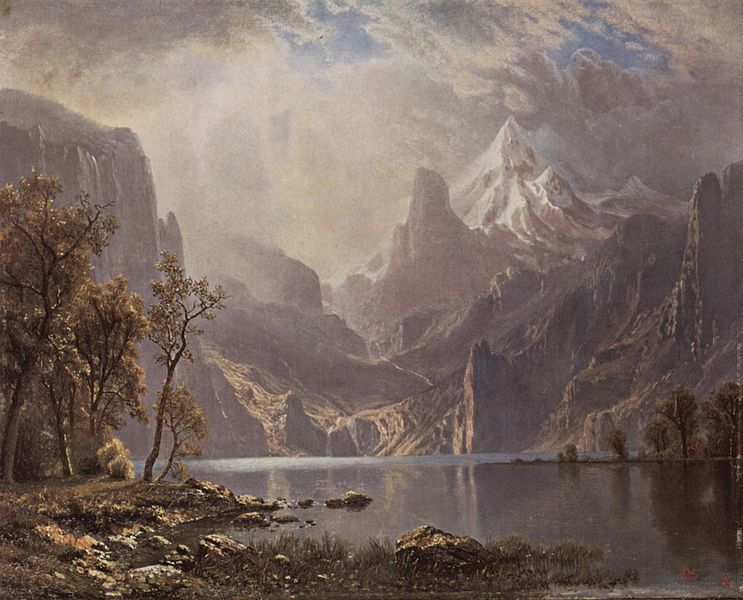
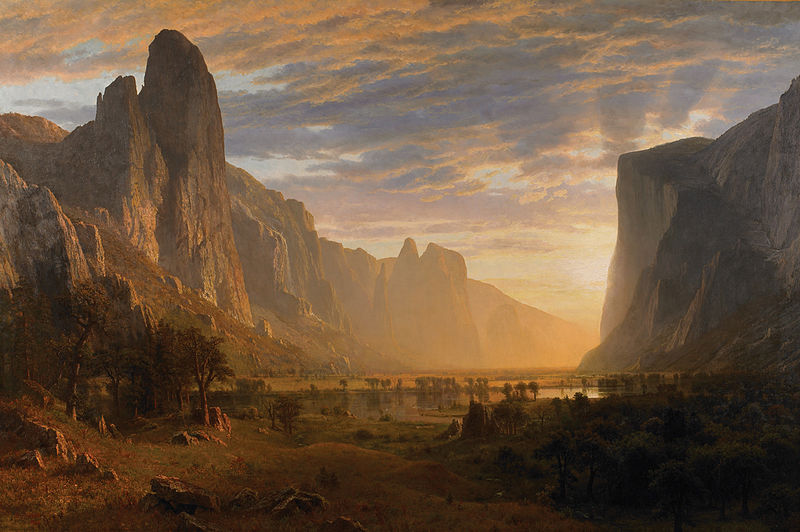
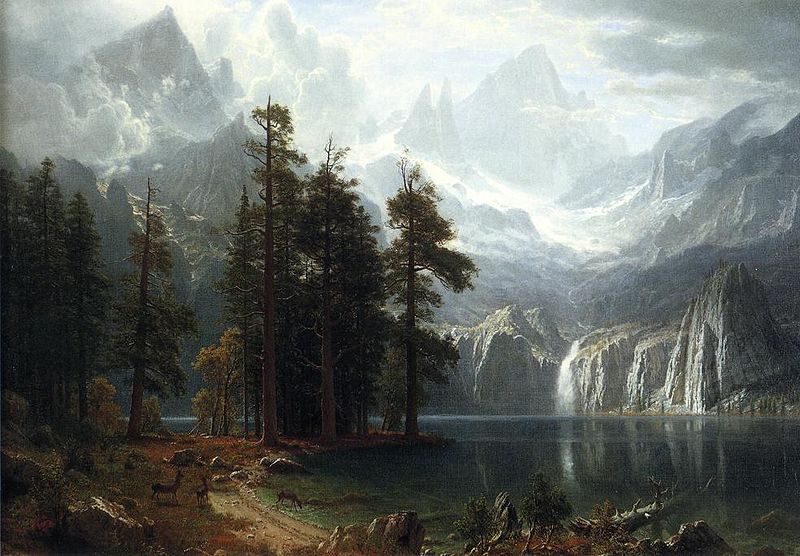
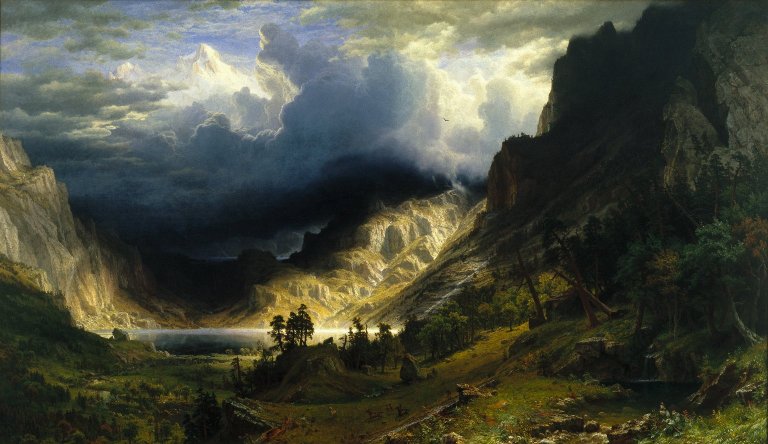
- Painter Albert Bierstadt, 1830
PAGE SPONSOR

Sanford Robinson Gifford (July 10, 1823 – August 29, 1880) was an American landscape painter and one of the leading members of the Hudson River School. Gifford's landscapes are known for their emphasis on light and soft atmospheric effects, and he is regarded as a practitioner of Luminism, an offshoot style of the Hudson River School.
Not to be confused with artist Robert Swain Gifford (1840 – 1905), no apparent relation.
Gifford was born in Greenfield, New York, and spent his childhood in Hudson, New York, the son of an iron foundry owner. He attended Brown University 1842 - 44, where he joined Delta Phi, before leaving to study art in New York City in 1845. He studied drawing, perspective and anatomy under the direction of the British watercolorist and drawing master, John R. Smith. He also studied the human figure in anatomy classes at the Crosby Street Medical college and took drawing classes at the National Academy of Design. By 1847 he was sufficiently skilled at painting to exhibit his first landscape at the National Academy and was elected an associate in 1851, an academician in 1854. Thereafter Gifford devoted himself to landscape painting, becoming one of the finest artists of the early Hudson River School.
Like most Hudson River School artists, Gifford traveled extensively to find scenic landscapes to sketch and paint. In addition to exploring New England, upstate New York and New Jersey, Gifford made extensive trips abroad. He first traveled to Europe from 1855 to 1857, to study European art and sketch subjects for future paintings. During this trip Gifford also met and traveled extensively with Albert Bierstadt and Worthington Whittredge.
In 1858, he traveled to Vermont, "apparently" with his friend and fellow painter Jerome Thompson. Details of their visit were carried in the contemporary Home Journal. Both artists submitted paintings of Mount Mansfield, Vermont's tallest peak, to the National Academy of Design's annual show in 1859 ("Mt. Mansfield paintings controversy"). 'Thompson's work, "Belated Party on Mansfield Mountain," is now owned by the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York,' according to the report.
Thereafter, he served in the Union Army as a corporal in the 7th Regiment of the New York Militia upon the outbreak of the Civil War. A few of his canvases belonging to New York City's Seventh Regiment and the Union League Club of New York are testament to that troubled time.
During the summer of 1867, Gifford spent most of his time painting on the New Jersey coast, specifically at Sandy Hook and Long Branch. "The Mouth of the Shrewsbury River," one noted canvas from the period, is a dramatic scene depicting a series of telegraph poles extending into an atmospheric distance underneath ominous storm clouds.
Another journey, this time with Jervis McEntee and his wife, took him across Europe in 1868. Leaving the McEntees behind, Gifford traveled to the Middle East, including Egypt in 1869. Then in the summer of 1870 Gifford ventured to the Rocky Mountains in the western United States, this time with Worthington Whittredge and John Frederick Kensett. At least part of the 1870 travels were as part of a Hayden Expedition, led by Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden.
Returning to his studio in New York City, Gifford painted numerous major landscapes from scenes he recorded on his travels. Gifford's method of creating a work of art was similar to other Hudson River School artists. He would first sketch rough, small works in oil paint from his sketchbook pencil drawings. Those scenes he most favored he then developed into small, finished paintings, then into larger, finished paintings.
Gifford referred to the best of his landscapes as his "chief pictures". Many of his chief pictures are characterized by a hazy atmosphere with soft, suffuse sunlight. Gifford often painted a large body of water in the foreground or middle distance, in which the distant landscape would be gently reflected. Examples of Gifford's "chief pictures" in museum collections today include:
- Lake Nemi (1856 – 57), Toledo Museum of Art, Toledo, Ohio;
- The Wilderness (1861), Toledo Museum of Art, Toledo, Ohio;
- A Passing Storm (1866), Wadsworth Atheneum, Hartford, Connecticut;
- Ruins of the Parthenon (1880), Corcoran Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.
On August 29, 1880, Gifford died in New York City, having been diagnosed with malarial fever. The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City celebrated his life that autumn with a memorial exhibition of 160 paintings. A catalog of his work published shortly after his death recorded in excess of 700 paintings during his career.
Between 1955 and 1973, Gifford's heirs donated the artist's collection of letters and personal papers to the Archives of American Art, a research center which is part of the Smithsonian Institution. In 2007, these papers were digitally scanned in their entirety and made available to researchers as the Sanford Robinson Gifford Papers Online.
Gifford painted some 20 paintings from the sketches he did while in Vermont in 1858. Of these, "Mount Mansfield, 1858" was the National Academy submission in 1859, and another painted in 1859, "Mount Mansfield, Vermont," came in 2008 to be in the center of a controversy over its deaccession by the National Academy in New York. The controversy had been reported in December, saying that the sale of paintings to cover operating expenses was against the policy of the Association of Art Museum Directors, which organization in turn was asking its members to "cease lending artworks to the academy and collaborating with it on exhibitions." The report also said the 1859 painting in question was "donated to the academy in 1865 by another painter, James Augustus Suydam." Among much more detail about on the deaccession, a later Times report said that the National Academy had sold works by Thomas Eakins and Richard Caton Woodville in the 1970s and 1990s, respectively, according to David Dearinger, a former curator. "When the academy later applied to the museum association for accreditation, Mr. Dearinger recalled, it was asked about the Woodville sale and promised not to repeat such a move," the Times reported. News of the sale was originally broken, as reported in the Times, by arts blogger Lee Rosenbaum. As cited by Rosenbaum, her original story, with additional details on other contemplated sales by the Academy, ran December 5. The Times did subsequently report on the other contemplated sales, without credit to Rosenbaum.
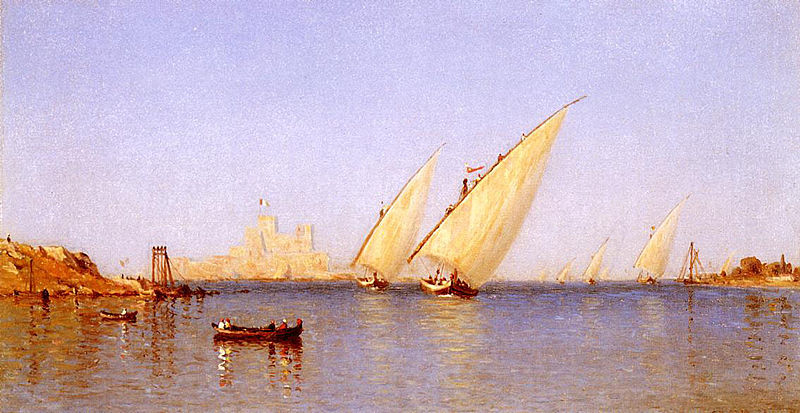










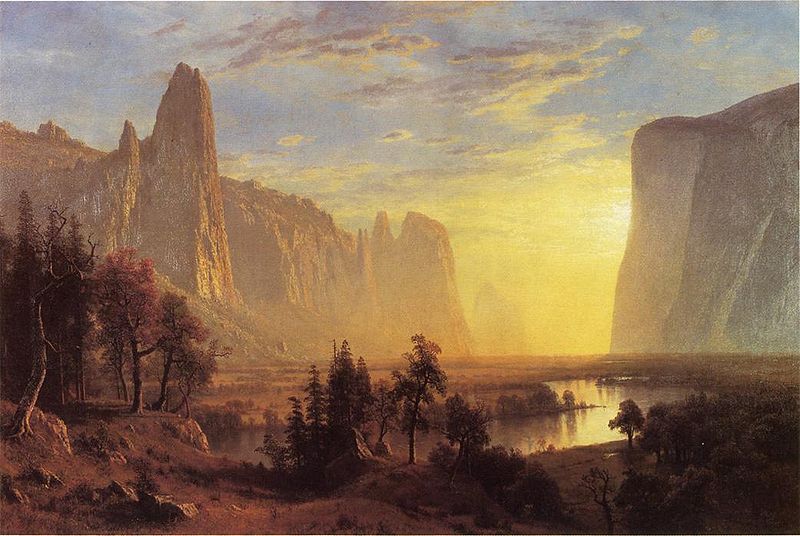
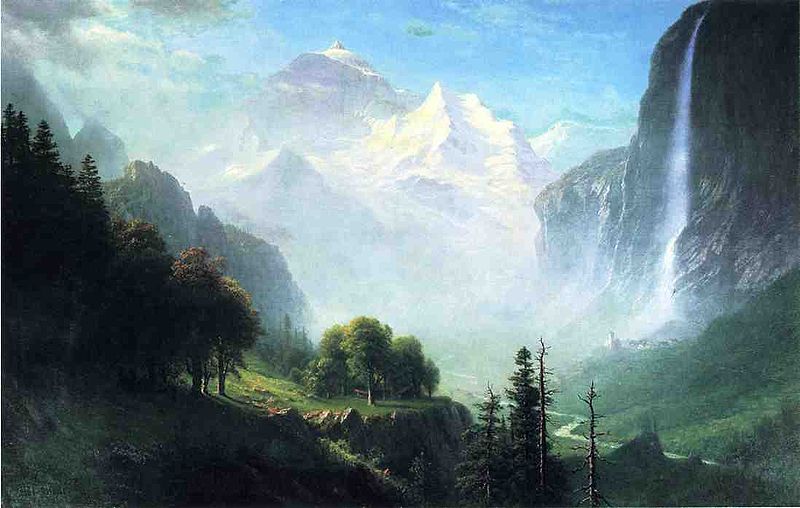
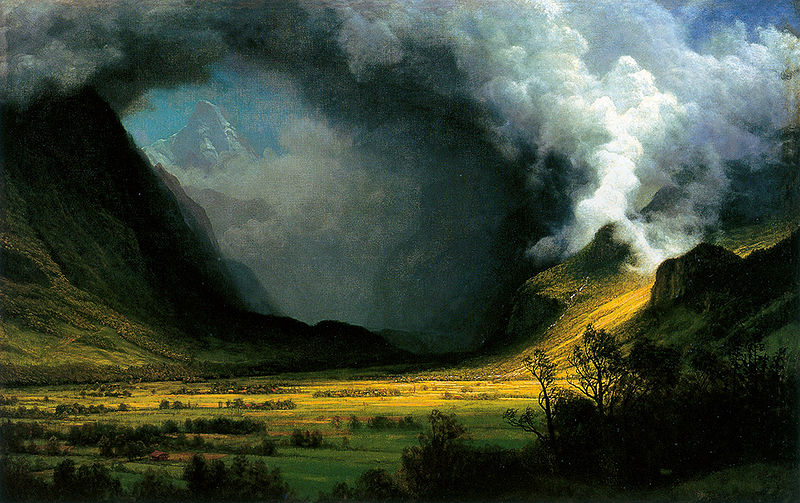
Albert Bierstadt (January 7, 1830 – February 18, 1902) was a German - American painter best known for his lavish, sweeping landscapes of the American West. In obtaining the subject matter for these works, Bierstadt joined several journeys of the Westward Expansion. Though not the first artist to record these sites, Bierstadt was the foremost painter of these scenes for the remainder of the 19th century.
Bierstadt was part of the Hudson River School, not an institution but rather an informal group of like minded painters. The Hudson River School style involved carefully detailed paintings with romantic, almost glowing lighting, sometimes called luminism. An important interpreter of the western landscape, Bierstadt, along with Thomas Moran, is also grouped with the Rocky Mountain School.
Bierstadt was born in Solingen, Germany. His family moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts, in 1831. He developed a taste for art early and made clever crayon sketches in his youth. In 1851, he began to paint in oils. He studied painting with the members of the Düsseldorf school of painting in Düsseldorf from 1853 to 1857. He taught drawing and painting briefly before devoting himself to painting.
Bierstadt began making paintings in New England and upstate New York. In 1859, he traveled westward in the company of Frederick W. Lander, a land surveyor for the U.S. government, returning with sketches that would result in numerous finished paintings. In 1863 he returned west again, in the company of the author Fitz Hugh Ludlow, whose wife he would later marry. He continued to visit the American West throughout his career.
Though his paintings sold for princely sums, Bierstadt was not held in particularly high esteem by critics of his day. His use of uncommonly large canvases was thought to be an egotistical indulgence, as his paintings would invariably dwarf those of his contemporaries when they were displayed together. The romanticism evident in his choices of subject and in his use of light was felt to be excessive by contemporary critics. His paintings emphasized atmospheric elements like fog, clouds and mist to accentuate and complement the feel of his work. Bierstadt sometimes changed details of the landscape to inspire awe. The colors he used are also not always true. He painted what he believed was the way things should be: water is ultramarine, vegetation is lush and green, etc.
Nonetheless, in 1860 he was elected a member of the National Academy; he received medals in Austria, Bavaria, Belgium and Germany; and his paintings remain popular. He was a prolific artist, having completed over 500 (possibly as many as 4000) paintings during his lifetime, most of which have survived. Many are scattered through museums around the United States. Prints are available commercially for many. Original paintings themselves do occasionally come up for sale, at ever increasing prices.
In 1882 his studio at Irvington, New York, was destroyed by fire, with many of his pictures.
- Because of Bierstadt's interest in mountain landscapes, Mount Bierstadt and Bierstadt Lake in Colorado are named in his honor. Bierstadt was probably the first European to visit the summit of Mount Evans in 1863, 1.5 miles from Mount Bierstadt. Bierstadt named it Mount Rosa, a reference to both Monte Rosa above Zermatt and, Rosalie Ludlow, his future wife, but the name was changed from Rosalie to Evans in 1895 in honor of Colorado governor John Evans.
- In 1998, the United States Postal Service issued a set of 20 commemorative stamps entitled "Four Centuries of American Art", one of which featured Albert Bierstadt's The Last of the Buffalo. In 2008, the USPS issued a commemorative stamp in its "American Treasures" series featuring Bierstadt's 1864 painting "Valley of the Yosemite."
- "Valley of the Yosemite" also appears in a scene in Terry Gilliam's 1995 film "Twelve Monkeys", accompanied by several doctors singing Blueberry Hill (song).
- William Bliss Baker, another landscape artist, studied under Bierstadt.









