<Back to Index>
- Cartographer and Geographer Abraham Ortelius (Ortels), 1527
- Philosopher and Statesman Francis Bacon, 1561
PAGE SPONSOR

Abraham Ortelius (Abraham Ortels) (April 14, 1527 – June 28, 1598) was a Flemish cartographer and geographer, generally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Theater of the World). He is also believed to be the first person to imagine that the continents were joined together before drifting to their present positions.
Ortelius was born in the city of Antwerp, which was then in the Habsburg ruled Seventeen Provinces. The Orthellius family were originally from Augsburg, a Free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1535, the family, had fallen under suspicion of Protestantism. Following the death of Ortelius' father, his uncle Jacobus van Meteren returned from religious exile in England to take care of Ortelius. Abraham remained close to his cousin Emanuel van Meteren who would later move to London. In 1575 he was appointed geographer to the king of Spain, Philip II, on the recommendation of Arias Montanus, who vouched for his orthodoxy.
He traveled extensively in Europe. He is specifically known to have traveled throughout the Seventeen Provinces; in southern, western, northern and eastern Germany (e.g., 1560, 1575 – 1576); France (1559 – 1560); England and Ireland (1576), and Italy (1578, and perhaps twice or thrice between 1550 and 1558).
Beginning as a map engraver, in 1547 he entered the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as an illuminator of maps. He supplemented his income trading in books, prints and maps, and his journeys included yearly visits to the Frankfurt book and print fair where he met Gerardus Mercator in 1554. In 1560, however, when traveling with Mercator to Trier, Lorraine and Poitiers, he seems to have been attracted, largely by Mercator’s influence, towards the career of a scientific geographer.
In 1564 he published his first map, Typus Orbis Terrarum, an eight - leaved wall map of the world, which subsequently appeared in reduced form in the Terrarum (the only extant copy is in now at Basel University Library). He also published a two - sheet map of Egypt in 1565, a plan of the Brittenburg castle on the coast of the Netherlands in 1568, an eight - sheet map of Asia in 1567, and a six - sheet map of Spain before the appearance of his atlas.
In England Ortelius' contacts included William Camden, Richard Hakluyt, Thomas Penny, puritan controversialist William Charke, and Humphrey Llwyd, who would contribute the map of England and Wales to Ortelius's 1573 edition of the Theatrum.
In 1578 he laid the basis of a critical treatment of ancient geography by his Synonymia geographica, issued by the Plantin press at Antwerp and republished in expanded form as Thesaurus geographicus in 1587 and again expanded in 1596. In this last edition, Ortelius considers the possibility of continental drift, a hypothesis proved correct only centuries later.
In 1596 he received a presentation from Antwerp city, similar to that afterwards bestowed on Rubens. His death on June 28, 1598, and burial, in St Michael’s Præmonstratensian Abbey church in Antwerp, were marked by public mourning. Quietis cultor sine lite, uxore, prole, reads the inscription on his tombstone.
On May 20, 1570, Gilles Coppens de Diest at Antwerp issued Ortelius’ Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, the "first modern atlas" (of 53 maps). Three Latin editions of this (besides a Dutch, a French and a German edition) appeared before the end of 1572; twenty - five editions came out before Ortelius' death in 1598; and several others were published subsequently, for the atlas continued to be in demand until about 1612. Most of the maps were admittedly reproductions (a list of 87 authors is given in the first Theatrum by Ortelius himself, growing to 183 names in the 1601 Latin edition), and many discrepancies of delineation or nomenclature occur. Errors, of course, abound, both in general conceptions and in detail; thus South America is initially very faulty in outline, but corrected in the 1587 French edition, and in Scotland the Grampians lie between the Forth and the Clyde; but, taken as a whole, this atlas with its accompanying text was a monument of rare erudition and industry. Its immediate precursor and prototype was a collection of thirty - eight maps of European lands, and of Asia, Africa, Tartary and Egypt, gathered together by the wealth and enterprise, and through the agents, of Ortelius’ friend and patron, Gilles Hooftman, lord of Cleydael and Aertselaer: most of these were printed in Rome, eight or nine only in the Southern Netherlands.
In 1573 Ortelius published seventeen supplementary maps under the title Additamentum Theatri Orbis Terrarum. Four more Additamenta were to follow, the last one appearing in 1597. He also had a keen interest and formed a fine collection of coins, medals and antiques, and this resulted in the book (also in 1573, published by Philippe Galle of Antwerp) Deorum dearumque capita ... ex Museo Ortelii (reprinted in 1582, 1602, 1612, 1680, 1683 and finally in 1699 by Gronovius, Thesaurus Graecarum Antiquitatum. vol. vii).
The Theatrum Orbis Terrarum inspired a six volume work entitled Civitates orbis terrarum edited by Georg Braun and illustrated by Frans Hogenberg with the assistance of Ortelius himself.
In 1579 Ortelius brought out his Nomenclator Ptolemaicus and started his Parergon (a series of maps illustrating ancient history, sacred and secular). He also published Itinerarium per nonnuilas Galliae Belgicae partes (at the Plantin press in 1584, and reprinted in 1630, 1661 in Hegenitius, Itin. Frisio - Hoil., in 1667 by Verbiest, and finally in 1757 in Leuven), a record of a journey in Belgium and the Rhineland made in 1575. In 1589 he published Maris Pacifici, the first dedicated map of the Pacific to be printed. Among his last works were an edition of Caesar (C. I. Caesaris omnia quae extant, Leiden, Raphelingen, 1593), and the Aurei saeculi imago, sive Germanorum veterum vita, mores, ritus et religio. (Philippe Galle, Antwerp, 1596). He also aided Welser in his edition of the Peutinger Table in 1598.
Originals of Ortelius' maps are popular collector's items and often sell for tens of thousands of dollars. Facsimiles of his maps are also available from many retailers. A map he made of North and South America is also included in the world's largest commercially available jigsaw puzzle which is of four world maps. This puzzle is made by Ravensburger, measures 6 feet (1.8 m) × 9 feet (2.7 m), and has over 18,000 pieces.
Ortelius was the first to underline the geometrical coincidence between the coasts of America and Europe - Africa, and to propose continental drift as an explanation. Kious described Ortelius' thoughts in this way:
Abraham Ortelius in his work Thesaurus Geographicus ... suggested that the Americas were "torn away from Europe and Africa ... by earthquakes and floods" and went on to say: "The vestiges of the rupture reveal themselves, if someone brings forward a map of the world and considers carefully the coasts of the three [continents]."
The continental drift theory was generally accepted in geosciences only during the second half of the 20th century, after the hypotheses of Alfred Wegener had been supported through the discovery of a mechanism for continental drift, and an adequate energy source, in the convection currents of the plastic, very weak upper mantle, or asthenosphere.


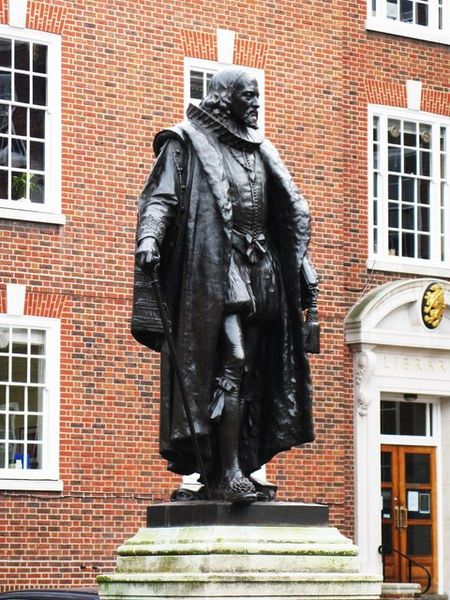
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St. Alban, Kt., KC (22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626) was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, jurist and author. He served both as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Although his political career ended in disgrace, he remained extremely influential through his works, especially as philosophical advocate and practitioner of the scientific method during the scientific revolution.
Bacon has been called the creator of empiricism. His works established and popularized inductive methodologies for scientific inquiry, often called the Baconian method, or simply the scientific method. His demand for a planned procedure of investigating all things natural marked a new turn in the rhetorical and theoretical framework for science, much of which still surrounds conceptions of proper methodology today.
Bacon was knighted in 1603, and created both the Baron Verulam in 1618 and the Viscount St. Alban in 1621; as he died without heirs, both peerages became extinct upon his death. He famously died by contracting pneumonia while studying the effects of freezing on the preservation of meat.
Bacon was born on 22 January 1561 at York House near the Strand in London, the son of Sir Nicholas Bacon by his second wife Anne (Cooke) Bacon, the daughter of noted humanist Anthony Cooke. His mother's sister was married to William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, making Burghley Francis Bacon's uncle. Biographers believe that Bacon was educated at home in his early years owing to poor health (which plagued him throughout his life), receiving tuition from John Walsall, a graduate of Oxford with a strong leaning towards Puritanism. He entered Trinity College, Cambridge, on 5 April 1573 at the age of twelve, living for three years there together with his older brother Anthony Bacon under the personal tutelage of Dr John Whitgift, future Archbishop of Canterbury. Bacon's education was conducted largely in Latin and followed the medieval curriculum. He was also educated at the University of Poitiers. It was at Cambridge that he first met Queen Elizabeth, who was impressed by his precocious intellect, and was accustomed to calling him "the young Lord Keeper".
His studies brought him to the belief that the methods and results of science as then practiced were erroneous. His reverence for Aristotle conflicted with his loathing of Aristotelian philosophy, which seemed to him barren, disputatious, and wrong in its objectives.
On 27 June 1576, he and Anthony entered de societate magistrorum at Gray's Inn. A few months later, Francis went abroad with Sir Amias Paulet, the English ambassador at Paris, while Anthony continued his studies at home. The state of government and society in France under Henry III afforded him valuable political instruction. For the next three years he visited Blois, Poitiers, Tours, Italy and Spain. During his travels, Bacon studied language, statecraft and civil law while performing routine diplomatic tasks. On at least one occasion he delivered diplomatic letters to England for Walsingham, Burghley and Leicester, as well as for the queen.
The sudden death of his father in February 1579 prompted Bacon to return to England. Sir Nicholas had laid up a considerable sum of money to purchase an estate for his youngest son, but he died before doing so, and Francis was left with only a fifth of that money. Having borrowed money, Bacon got into debt. To support himself, he took up his residence in law at Gray's Inn in 1579.
Bacon had three goals: to uncover truth, to serve his country and to serve his church. He sought to further these ends by seeking a prestigious post. In 1580, through his uncle, Lord Burghley, he applied for a post at court which might enable him to pursue a life of learning. His application failed. For two years he worked quietly at Gray's Inn, until he was admitted as an outer barrister in 1582.
His parliamentary career began when he was elected MP for Bossiney, Devon, in a 1581 by-election. In 1584, he took his seat in parliament for Melcombe in Dorset, and subsequently for Taunton (1586). At this time, he began to write on the condition of parties in the church, as well as on the topic of philosophical reform in the lost tract, Temporis Partus Maximus. Yet he failed to gain a position he thought would lead him to success. He showed signs of sympathy to Puritanism, attending the sermons of the Puritan chaplain of Gray's Inn and accompanying his mother to the Temple Church to hear Walter Travers. This led to the publication of his earliest surviving tract, which criticized the English church's suppression of the Puritan clergy. In the Parliament of 1586, he openly urged execution for Mary, Queen of Scots.
About this time, he again approached his powerful uncle for help; this move was followed by his rapid progress at the bar. He became Bencher in 1586, and he was elected a reader in 1587, delivering his first set of lectures in Lent the following year. In 1589, he received the valuable appointment of reversion to the Clerkship of the Star Chamber, although he did not formally take office until 1608 – a post which was worth £16,000 a year.
In 1588 he became MP for Liverpool and then for Middlesex in 1593. He later sat three times for Ipswich (1597, 1601, 1604) and once for Cambridge University (1614).
He became known as a liberal - minded reformer, eager to amend and simplify the law. He opposed feudal privileges and dictatorial powers, though a friend of the crown. He was against religious persecution. He struck at the House of Lords in their usurpation of the Money Bills. He advocated for the union of England and Scotland, thus being one of the influences behind the consolidation of the United Kingdom; and also advocated, later on, for the integration of Ireland into the Union. Closer constitutional ties, he believed, would bring greater peace and strength to these countries.
Bacon soon became acquainted with Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, Queen Elizabeth's favorite. By 1591, he acted as the earl's confidential adviser.
In 1592, he was commissioned to write a tract in response to the Jesuit Robert Parson's anti - government polemic, which he titled Certain observations made upon a libel, identifying England with the ideals of democratic Athens against the belligerence of Spain.
Bacon took his third parliamentary seat for Middlesex when in February 1593 Elizabeth summoned Parliament to investigate a Roman Catholic plot against her. Bacon's opposition to a bill that would levy triple subsidies in half the usual time offended many people. Opponents accused him of seeking popularity. For a time, the royal court excluded him.
When the Attorney Generalship fell vacant in 1594, Lord Essex's influence was not enough to secure Bacon that office. Likewise, Bacon failed to secure the lesser office of Solicitor General in 1595. To console him for these disappointments, Essex presented him with a property at Twickenham, which he sold subsequently for £1,800.
In 1596, Bacon became Queen's Counsel, but missed the appointment of Master of the Rolls. During the next few years, his financial situation remained bad. His friends could find no public office for him, and a scheme for retrieving his position by a marriage with the wealthy and young widow Lady Elizabeth Hatton failed after she broke off their relationship upon accepting marriage to a wealthier man. In 1598 Bacon was arrested for debt. Afterwards however, his standing in the Queen's eyes improved. Gradually, Bacon earned the standing of one of the learned counsels, though he had no commission or warrant and received no salary. His relationship with the Queen further improved when he severed ties with Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, a shrewd move because Essex was executed for treason in 1601.
With others, Bacon was appointed to investigate the charges against Essex, his former friend and benefactor. A number of Essex's followers confessed that Essex had planned a rebellion against the Queen. Bacon was subsequently a part of the legal team headed by Attorney General Sir Edward Coke at Essex's treason trial. After the execution, the Queen ordered Bacon to write the official government account of the trial, which was later published as A DECLARATION of the Practices and Treasons attempted and committed by Robert late Earle of Essex and his Complices, against her Majestie and her Kingdoms ... after Bacon's first draft was heavily edited by the Queen and her ministers.
According to his personal secretary and chaplain, William Rawley, as a judge Bacon was always tender hearted, "looking upon the examples with the eye of severity, but upon the person with the eye of pity and compassion". And also that "he was free from malice", "no revenger of injuries", and "no defamer of any man".
The succession of James I brought Bacon into greater favor. He was knighted in 1603. In another shrewd move, Bacon wrote his Apologie in defense of his proceedings in the case of Essex, as Essex had favored James to succeed to the throne.
The following year, during the course of the uneventful first parliament session, Bacon married Alice Barnham. In June 1607 he was at last rewarded with the office of Solicitor General. The following year, he began working as the Clerkship of the Star Chamber. In spite of a generous income, old debts still could not be paid. He sought further promotion and wealth by supporting King James and his arbitrary policies.
In 1610 the fourth session of James' first parliament met. Despite Bacon's advice to him, James and the Commons found themselves at odds over royal prerogatives and the king's embarrassing extravagance. The House was finally dissolved in February 1611. Throughout this period Bacon managed to stay in the favor of the king while retaining the confidence of the Commons.
In 1613, Bacon was finally appointed attorney general, after advising the king to shuffle judicial appointments. As attorney general, Bacon successfully prosecuted Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset and his wife, Frances Howard, Countess of Somerset, for murder in 1616. The so-called "Prince's Parliament" of April 1614 objected to Bacon's presence in the seat for Cambridge and to the various royal plans which Bacon had supported. Although he was allowed to stay, parliament passed a law that forbade the attorney general to sit in parliament. His influence over the king had evidently inspired resentment or apprehension in many of his peers. Bacon, however, continued to receive the King's favor, which led to his appointment in March 1617 as the temporary Regent of England (for a period of a month), and in 1618 as Lord Chancellor. On 12 July 1618 the king created Bacon Baron Verulam, of Verulam, in the Peerage of England. As a new peer he then styled himself as "Francis, Lord Verulam".
Bacon continued to use his influence with the king to mediate between the throne and Parliament and in this capacity he was further elevated in the same peerage, as Viscount St Alban, on 27 January 1621.
Bacon's public career ended in disgrace in 1621. After he fell into debt, a Parliamentary Committee on the administration of the law charged him with twenty - three separate counts of corruption. To the lords, who sent a committee to inquire whether a confession was really his, he replied, "My lords, it is my act, my hand and my heart; I beseech your lordships to be merciful to a broken reed." He was sentenced to a fine of £40,000 and committed to the Tower of London during the king's pleasure; the imprisonment lasted only a few days and the fine was remitted by the king. More seriously, parliament declared Bacon incapable of holding future office or sitting in parliament. He narrowly escaped undergoing degradation, which would have stripped him of his titles of nobility. Subsequently the disgraced viscount devoted himself to study and writing.
There seems little doubt that Bacon had accepted gifts from litigants, but this was an accepted custom of the time and not necessarily evidence of deeply corrupt behavior. While acknowledging that his conduct had been lax, he countered that he had never allowed gifts to influence his judgement and, indeed, he had on occasion given a verdict against those who had paid him. The true reason for his acknowledgement of guilt is the subject of debate, but it may have been prompted by his poor state of health, or by a view that through his fame and the greatness of his office he would be spared harsh punishment. He may even have been blackmailed, with a threat to charge him with sodomy, into confession.
The British jurist Basil Montagu wrote in Bacon's defense, concerning the episode of his public disgrace:
Bacon has been accused of servility, of dissimulation, of various base motives, and their filthy brood of base actions, all unworthy of his high birth, and incompatible with his great wisdom, and the estimation in which he was held by the noblest spirits of the age. It is true that there were men in his own time, and will be men in all times, who are better pleased to count spots in the sun than to rejoice in its glorious brightness. Such men have openly libeled him, like Dewes and Weldon, whose falsehoods were detected as soon as uttered, or have fastened upon certain ceremonious compliments and dedications, the fashion of his day, as a sample of his servility, passing over his noble letters to the Queen, his lofty contempt for the Lord Keeper Puckering, his open dealing with Sir Robert Cecil, and with others, who, powerful when he was nothing, might have blighted his opening fortunes for ever, forgetting his advocacy of the rights of the people in the face of the court, and the true and honest counsels, always given by him, in times of great difficulty, both to Elizabeth and her successor. When was a "base sycophant" loved and honored by piety such as that of Herbert, Tennison and Rawley, by noble spirits like Hobbes, Ben Jonson and Selden, or followed to the grave, and beyond it, with devoted affection such as that of Sir Thomas Meautys.When he was 36, Bacon engaged in the courtship of Elizabeth Hatton, a young widow of 20. Reportedly, she broke off their relationship upon accepting marriage to a wealthier man — Edward Coke. Years later, Bacon still wrote of his regret that the marriage to Hatton had not taken place.
At the age of forty - five, Bacon married Alice Barnham, the fourteen year old daughter of a well connected London alderman and MP. Bacon wrote two sonnets proclaiming his love for Alice. The first was written during his courtship and the second on his wedding day, 10 May 1606. When Bacon was appointed Lord Chancellor, "by special Warrant of the King", Lady Bacon was given precedence over all other Court ladies.
Reports of increasing friction in his marriage to Alice appeared, with speculation that some of this may have been due to financial resources not being as readily available to her as she was accustomed to having in the past. Alice was reportedly interested in fame and fortune, and when reserves of money were no longer available, there were complaints about where all the money was going. Alice Chambers Bunten wrote in her Life of Alice Barnham that, upon their descent into debt, she actually went on trips to ask for financial favors and assistance from their circle of friends. Bacon disinherited her upon discovering her secret romantic relationship with Sir John Underhill. He rewrote his will, which had previously been very generous to her (leaving her lands, goods and income), revoking it all.
Bacon's personal secretary and chaplain, William Rawley, however, wrote in his biography of Bacon that his inter - marriage with Alice Barnham was one of "much conjugal love and respect", mentioning a robe of honor that he gave to her, and which "she wore unto her dying day, being twenty years and more after his death".
The well connected antiquary John Aubrey noted in his Brief Lives concerning Bacon, "He was a Pederast. His Ganimeds and Favourites tooke Bribes", biographers continue to debate about Bacon's sexual inclinations and the precise nature of his personal relationships. Several authors believe that despite his marriage Bacon was primarily attracted to the same sex. Professor Forker, for example, has explored the "historically documentable sexual preferences" of both King James and Bacon – and concluded they were all oriented to "masculine love", a contemporary term that "seems to have been used exclusively to refer to the sexual preference of men for members of their own gender." The Jacobean antiquarian, Sir Simonds D'Ewes implied there had been a question of bringing him to trial for buggery.
This conclusion has been disputed by others, who point to lack of consistent evidence, and consider the sources to be more open to interpretation. In his "New Atlantis", Bacon describes his utopian island as being "the chastest nation under heaven", in which there was no prostitution or adultery, and further saying that "as for masculine love, they have no touch of it".
On 9 April 1626 Bacon died of pneumonia while at Arundel mansion at Highgate outside London. An influential account of the circumstances of his death was given by John Aubrey's Brief Lives. Aubrey has been criticized for his evident credulousness in this and other works; on the other hand, he knew Thomas Hobbes, Bacon's fellow philosopher and friend. Aubrey's vivid account, which portrays Bacon as a martyr to experimental scientific method, had him journeying to Highgate through the snow with the King's physician when he is suddenly inspired by the possibility of using the snow to preserve meat: "They were resolved they would try the experiment presently. They alighted out of the coach and went into a poor woman's house at the bottom of Highgate hill, and bought a fowl, and made the woman exenterate it".
After stuffing the fowl with snow, Bacon contracted a fatal case of pneumonia. Some people, including Aubrey, consider these two contiguous, possibly coincidental events as related and causative of his death: "The Snow so chilled him that he immediately fell so extremely ill, that he could not return to his Lodging ... but went to the Earle of Arundel's house at Highgate, where they put him into ... a damp bed that had not been layn-in ... which gave him such a cold that in 2 or 3 days as I remember Mr Hobbes told me, he died of Suffocation."
Being unwittingly on his deathbed, the philosopher wrote his last letter to his absent host and friend Lord Arundel:
My very good Lord, — I was likely to have had the fortune of Caius Plinius the elder, who lost his life by trying an experiment about the burning of Mount Vesuvius; for I was also desirous to try an experiment or two touching the conservation and induration of bodies. As for the experiment itself, it succeeded excellently well; but in the journey between London and Highgate, I was taken with such a fit of casting as I know not whether it were the Stone, or some surfeit or cold, or indeed a touch of them all three. But when I came to your Lordship's House, I was not able to go back, and therefore was forced to take up my lodging here, where your housekeeper is very careful and diligent about me, which I assure myself your Lordship will not only pardon towards him, but think the better of him for it. For indeed your Lordship's House was happy to me, and I kiss your noble hands for the welcome which I am sure you give me to it. I know how unfit it is for me to write with any other hand than mine own, but by my troth my fingers are so disjointed with sickness that I cannot steadily hold a pen."
Another account appears in a biography by William Rawley, Bacon's personal secretary and chaplain:
He died on the ninth day of April in the year 1626, in the early morning of the day then celebrated for our Saviour's resurrection, in the sixty - sixth year of his age, at the Earl of Arundel's house in Highgate, near London, to which place he casually repaired about a week before; God so ordaining that he should die there of a gentle fever, accidentally accompanied with a great cold, whereby the defluxion of rheum fell so plentifully upon his breast, that he died by suffocation.
At the news of his death, over thirty great minds collected together their eulogies of him, which was then later published in Latin.
He left personal assets of about £7,000 and lands that realized £6,000 when sold. His debts amounted to more than £23,000, equivalent to more than £3m at current value.
Francis Bacon's Philosophy is displayed in the vast and varied writings he left, which might be divided in three great branches:
- Scientifical works - in which his ideas for an universal reform of knowledge, scientific method and the improvement of mankind's state are presented.
- Religious / literary works - in which he presents his moral philosophy and theological meditations.
- Juridical works - in which his reforms in Law are proposed.
Bacon's ideas were influential in the 1630s and 1650s among scholars, in particular Sir Thomas Browne, who in his encyclopaedia Pseudodoxia Epidemica (1646 – 1672) frequently adheres to a Baconian approach to his scientific inquiries. During the Restoration, Bacon was commonly invoked as a guiding spirit of the Royal Society founded under Charles II in 1660. In the nineteenth century his emphasis on induction was revived and developed by William Whewell, among others. He has been reputed as the "Father of Experimental Science".
Bacon is also considered to be the philosophical influence behind the dawning of the Industrial age. In his works, Bacon called for a "spring of a progeny of inventions, which shall overcome, to some extent, and subdue our needs and miseries", always proposing that all scientific work should be done for charitable purposes, as matter of alleviating mankind's misery, and that therefore science should be practical and have as purpose the inventing of useful things for the improvement of mankind's estate. This changed the course of science in history, from a merely contemplative state, as it was found in ancient and medieval ages, to a practical, inventive state - that would have eventually led to the inventions that made possible the Industrial Revolutions of the following centuries.
The Industrial Revolution marks a major turning point in history. In the two centuries following 1800, the world's average per capita income increased over tenfold, while the world's population increased over sixfold. In the words of Nobel Prize winner Robert E. Lucas, Jr., "For the first time in history, the living standards of the masses of ordinary people have begun to undergo sustained growth ... Nothing remotely like this economic behavior has happened before".
He also wrote a long treatise on Medicine, History of Life and Death, with natural and experimental observations for the prolongation of life.
For one of his biographers, Hepworth Dixon, Bacon's influence in modern world is so great that every man who rides in a train, sends a telegram, follows a steam plough, sits in an easy chair, crosses the channel or the Atlantic, eats a good dinner, enjoys a beautiful garden, or undergoes a painless surgical operation, owes him something.
Some authors believe that Bacon's vision for a Utopian New World in North America was laid out in his novel New Atlantis, which depicts a mythical island, Bensalem, located somewhere between Peru and Japan. In this work he depicted a land where there would be freedom of religion - showing a Jew treated fairly and equally in an island of Christians, but it has been debated whether this work had influenced others reforms, such as greater rights for women, the abolition of slavery, elimination of debtors' prisons, separation of church and state, and freedom of political expression, although there is no hint of these reforms in The New Atlantis itself. His propositions of legal reform (which were not established in his life time), though, are considered to have been one of the influences behind the Napoleonic Code, and therefore could show some resemblance with or influence in the drafting of other liberal constitutions that came in the centuries after Bacon's lifetime, such as the American.
Francis Bacon played a leading role in creating the British colonies, especially in Virginia, the Carolinas and Newfoundland in northeastern Canada. His government report on "The Virginia Colony" was submitted in 1609. In 1610 Bacon and his associates received a charter from the king to form the Tresurer and the Companye of Adventurers and planter of the Cittye of London and Bristoll for the Collonye or plantacon in Newfoundland and sent John Guy to found a colony there. In 1910 Newfoundland issued a postage stamp to commemorate Bacon's role in establishing the province. The stamp describes Bacon as, "the guiding spirit in Colonization Schemes in 1610." Moreover, some scholars believe he was largely responsible for the drafting, in 1609 and 1612, of two charters of government for the Virginia Colony. Thomas Jefferson, the third President of the United States and author of the Declaration of Independence, wrote: "Bacon, Locke and Newton. I consider them as the three greatest men that have ever lived, without any exception, and as having laid the foundation of those superstructures which have been raised in the Physical and Moral sciences". Historian and biographer William Hepworth Dixon considered that Bacon's name could be included in the list of Founders of the United States of America.
It is also believed by the Rosicrucian organization AMORC, that Bacon would have influenced a settlement of mystics in North America, stating that his work "The New Atlantis" inspired a colony of Rosicrucians led by Johannes Kelpius, to journey across the Atlantic Ocean in a chartered vessel called Sarah Mariah, and move on to Pennsylvania in late XVII Century. According to their claims, these rosicrucian communities "made valuable contributions to the newly emerging American culture in the fields of printing, philosophy, the sciences and arts".
Johannes Kelpius and his fellows moved to Wissahickon Creek, in Pennsylvania, and became known as "Hermits of Mystics of the Wissahickon" or simply "Monks of the Wissahickon".
Although much of his legal reform proposals were not established in his life time, his legal legacy was considered by the magazine New Scientist, in a publication of 1961, as having influenced the drafting of the Code Napoleon, and the law reforms introduced by Sir Robert Peel.
The historian William Hepworth Dixon referred to the Code Napoleon as "the sole embodiment of Bacon's thought", saying that Bacon's legal work "has had more success abroad than it has found at home", and that in France "it has blossomed and come into fruit".
The scholar Harvey Wheeler attributed to Bacon, in his work "Francis Bacon's Verulamium - the Common Law Template of The Modern in English Science and Culture", the creation of these distinguishing features of the modern common law system:
- Using cases as repositories of evidence about the "unwritten law";
- Determining the relevance of precedents by exclusionary principles of evidence and logic;
- Treating opposing legal briefs as adversarial hypotheses about the application of the "unwritten law" to a new set of facts.
As late as the eighteenth century some juries still declared the law rather than the fact, but already before the end of the seventeenth century Sir Matthew Hale explained modern common law adjudication procedure and acknowledged Bacon as the inventor of the process of discovering unwritten laws from the evidences of their applications. The method combined empiricism and inductivism in a new way that was to imprint its signature on many of the distinctive features of modern English society.
In brief, Bacon is considered by some jurists to be the father of modern Jurisprudence.
Political scientist James McClellan, from the University of Virginia, considered Bacon to have had "a great following" in the American colonies.
The Baconian theory of Shakespearean authorship, first proposed in the mid 19th century, contends that Sir Francis Bacon wrote some or all the plays conventionally attributed to William Shakespeare, in opposition to the scholarly consensus that William Shakespeare of Stratford was the author.
Francis Bacon often gathered with the men at Gray's Inn to discuss politics and philosophy, and to try out various theatrical scenes that he admitted writing. Bacon's alleged connection to the Rosicrucians and the Freemasons has been widely discussed by authors and scholars in many books. However others, including Daphne du Maurier (in her biography of Bacon), have argued there is no substantive evidence to support claims of involvement with the Rosicrucians. Frances Yates does not make the claim that Bacon was a Rosicrucian, but presents evidence that he was nevertheless involved in some of the more closed intellectual movements of his day. She argues that Bacon's movement for the advancement of learning was closely connected with the German Rosicrucian movement, while Bacon's New Atlantis portrays a land ruled by Rosicrucians. He apparently saw his own movement for the advancement of learning to be in conformity with Rosicrucian ideals.
The link between Bacon's work and the Rosicrucians ideals which Yates allegedly found, was the conformity of the purposes expressed by the Rosicrucian Manifestos and Bacon's plan of a "Great Instauration", for the two were calling for a reformation of both "divine and human understanding", as well as both had in view the purpose of mankind's return to the "state before the Fall".
Another major link is said to be the resemblance between Bacon's "New Atlantis" and the German Rosicrucian Johann Valentin Andreae's "Description of the Republic of Christianopolis (1619)". In his book, Andreae shows a utopic island in which Christian theosophy and applied science ruled, and in which the spiritual fulfillment and intellectual activity constituted the primary goals of each individual, the scientific pursuits being the highest intellectual calling – linked to the achievement of spiritual perfection. Andreae's island also depicts a great advancement in technology, with many industries separated in different zones which supplied the population's needs – which shows great resemblance to Bacon's scientific methods and purposes.
The Rosicrucian organization AMORC claims that Francis Bacon was the "Imperator" (leader) of the Rosicrucian Order in both England and the European continent, and would have directed it at that time of the Renaissance.
Francis Bacon's influence can also be seen on a variety of religious and spiritual authors, and on groups that have utilized his writings in their own belief systems.


